Mitosis - Staff Web Pages
advertisement

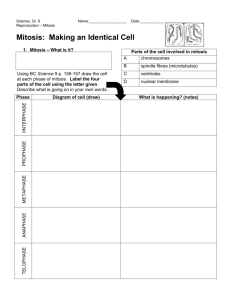
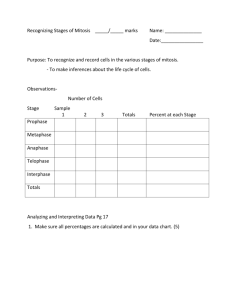
MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS Cell Reproduction • Cell division – - process by which new cells are produced from one cell – - Mitosis - produces 2 cells identical to parent cell The Cell Cycle • - the sequence of growth and division of a cell • - a cell’s life cycle from origin to division 2 major periods • Interphase • Cell division G1 S G2 Interphase G1 phase-• Cell grows, produces many proteins, functions • Chromatin present, not coiled, chromosomes not visible, nucleus looks grainy, nucleolus visible Interphase Rapid growth and metabolic activity S Phase--DNA replication – copies chromosomes Interphase DNA synthesis and replication G2 phase --• - mitochondria and centrioles double S Interphase G1 G2 Centrioles replicate; cell prepares for division • Cell Division Phase –Mitosis –Cytokinesis S Interphase G1 G2 Mitosis – 4 phases Cytokinesis Mitosis---•Prophase •Metaphase •Anaphase •Telophase Intro to Mitosis 1:51 Eukaryotic chomosomes Prophase: The first phase of mitosis • - Chromatin coils and condenses • - Chromosomes become visible • Centrioles in centrosomes Spindle fibers form – from centrioles Nuclear membrane and nucleolus dissappears Chromosomes are replicated Centrioles begin to move to poles Prophase 3:47 SPINDLE FIBERS Prophase: The first phase of mitosis 1 chromosome – made up of 2 sister chromatids Centromere Sister chromatidsReplicated DNA strands Metaphase: The second stage of mitosis • Chromosomes move to the equator of the spindle – centromeres align Centromere Sister chromatids Metaphase :30 Anaphase: The third phase of mitosis • Spindle fibers pull centromeres apart • Separates sister chromatids • Begin to move to poles Anaphase :35 Telophase: The fourth phase of mitosis • Chromosomes at the poles/centrioles • 2 distinct daughter cells are forming • Nuclei reforming; chromatin relaxing • Cytokinesis beginning • DIVIDES THE NUCLEAR CONTENTS! DNA! Nuclear envelope reappears Two daughter cells are formed Telophase 1:15 Cytokinesis • Divides cytoplasm and membrane of cells • Differs between plants and animals– Animal cells “pinched” into 2 cells – “cleavage furrow” – Plant cells divided by new cell wall = “cell plate” • Cytokinesis- divides cytoplasm • In animals, first sign of cytokinesis (cleavage) is appearance of cleavage furrow in cell surface Figure 12.5x Mitosis Figure 12-09x Mitosis in an onion root End Mitosis & Cytokinesis Question 1 The stringy structures in the cell nucleus that contain DNA are __________. A. centromeres B. chromosomes C. genes D. chlorophylls Question 2 Look at the diagram and identify the stage of mitosis that is depicted. Centromere Sister chromatids A. prophase C. anaphase B. metaphase D. telophase Question 3 What is the process by which a cell's cytoplasm divides? A. cytokinesis B. telekinesis C. meiosis D. mitosis Question 4 In multicellular organisms, groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function are called __________. A. organ systems B. organs C. tissues D. cell cycles END • Cytokinesis- divides cytoplasm, typically follows mitosis • In animals, first sign of cytokinesis (cleavage) is appearance of cleavage furrow in cell surface near old metaphase plate Figure 12.5x Mitosis • Contraction of protein fiber ring pinches cell in two Cytokinesis in plants • During telophase, vesicles from Golgi fuse at metaphase plate forming cell plate. –plate enlarges until membranes fuse with plasma membrane at perimeter, with contents of vesicles forming new wall between cells Figure 12.8 Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells Figure 12-09x Mitosis in an onion root Results of Mitosis • When mitosis is complete, unicellular organisms remain as single cells. • In multicellular organisms, cell growth and reproduction result in groups of cells that work together as tissue to perform a specific function. Results of Mitosis • Tissues organize in various combinations to form organs that perform more complex roles within the organism. • Multiple organs that work together form an organ system. Results of Mitosis Click image to view movie. Mitosis