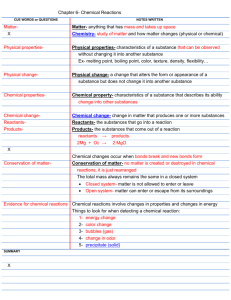
Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up
advertisement

Chapter 2 Section 1 1. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. 2. Substance- is a single kind of matter that is pure, maning it always has a specific makeup- or composition- and a specific set of prosperities. 3. Physical property- is a characteristic of a pure substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance. 4. Chemical property- is a characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into different substance. 5. Element- is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into any other substance by chemical or physical means. 6. Atom- is the basic particle from which all elements are made. 7. Chemical bond- is a force of attraction between two atoms. 8. Molecules- groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. 9. Compound- is a pure substance made of two or more elements chemically combined in a set ratio. 10. Chemical formula- which shows he elements in the compound and the ratio of atoms. 11. Mixture- is made of two or more substances- elements, compounds, or both – that are together in the same place but are not chemically combined. 12. Heterogeneous mixture- you can see the different parts. 13. Homogeneous mixture- are so evenly mixed that you can’t see the different parts. 14. Solution- is an example of homogeneous mixture. Section 2 1. Physical change- is any change that alters the form or appearance of matter but does not make any substance in the matter into a different substance. 2. Chemical change- is a change in matter that produces one or more new substances. 3. Law of conversation or matter- the fact that matter is not created or destroyed in any chemical or physical change. Section 3 1. Energy- is the ability to do work or cause change. 2. Temperature- is a measure of the average energy of random motion of particles of matter. 3. Thermal energy- is the total energy of all of the particles in an object. 4. Endothermic change- a change in which energy is taken in. 5. Exothermic change- releases energy. 6. Chemical energy- the energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms is a form of energy. 7. Electromagnetic energy- a form of energy that travels through space as a wave. 8. Electrical energy- is the energy of electrically charged particles moving from one place atom to another in many chemical changes. 9. Electrodes- two metal strips that are placed in a solution, but they don’t touch.