Migration_and_Industrialization_files/People and
advertisement
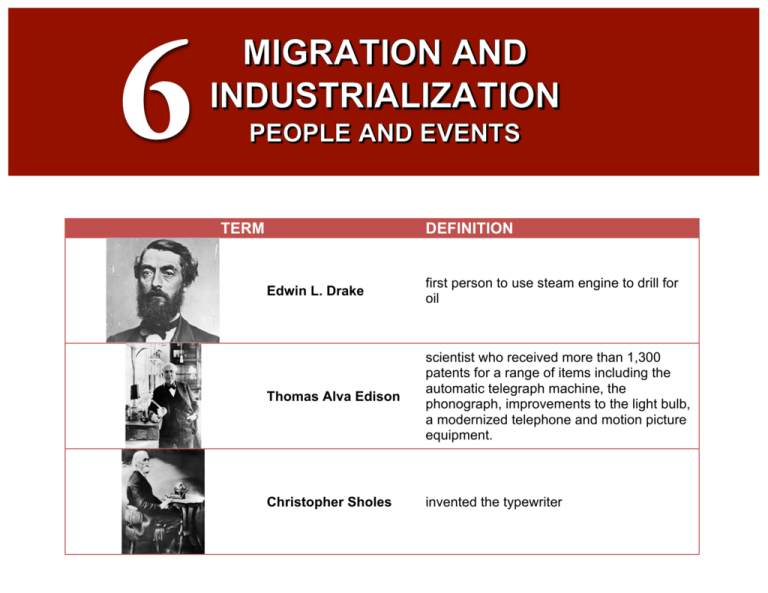
6 MIGRATION AND INDUSTRIALIZATION TERM DEFINITION Edwin L. Drake first person to use steam engine to drill for oil Thomas Alva Edison scientist who received more than 1,300 patents for a range of items including the automatic telegraph machine, the phonograph, improvements to the light bulb, a modernized telephone and motion picture equipment. Christopher Sholes invented the typewriter Alexander Graham Bell inventor of the telephone George M. Pullman invented sleeping cars for trains and built a town to house his workers Munn v. Illinois an 1877 case in which the Supreme Court upheld stats’ regulation of railroads for the benefit of farmers and consumers, thus establishing the right of government to regulate private industry to serve the public interest Interstate Commerce Act a law, enacted in 1887, that reestablished the federal government’s right to supervise railroad activities and created a five-member Interstate Commerce Commission to do so Andrew Carnegie a Scottish-American industrialist who led the enormous expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century John D. Rockefeller industrialist who founded the Standard Oil Company, a monopoly that controlled more than 90% of the oil business in the US Sherman Antitrust Act a law, enacted in 1890, that was intended to prevent the creation of monopolies by making it illegal to establish trusts that interfered with free trade Samuel Gompers founder and president of the American Federation of Labor Eugene V. Debs leader of the American Railway Union; he was the Socialist Party candidate for president five times Mary Harris “Mother” Jones organized coal miners, their wives, and their children to fight for better working conditions a law, enacted in 1882, that prohibited all Chinese except students, teachers, Chinese Exclusion Act merchants, tourists, and government officials from entering the United States Gentlemen’s Agreement 1907-1908 agreement by the government of Japan to limit Japanese emigration to the United States Americanization movement education program designed to help immigrants assimilate to American culture Social Gospel movement a 19th-century reform movement based on the belief that Christians have a responsibility to help improve working conditions and alleviate poverty. Jane Addams the founder of Hull House, which provided English lessons for immigrants, daycare, and child care classes Tweed Ring a group of corrupt New York politicians, led by William Marcy “Boss” Tweed, who took as much as $2 million from the city between 1869 and 1871 Thomas Nast American political cartoonist who helped turn public attention to the corruption of Tammany Hall and Boss Tweed Rutherford B. Hayes 19th President of the United States who attempted civil service reform Stalwart a Republican who supported the new York political boss Roscoe Conkling and opposed civil service reform James A. Garfield 20th President of the United States who was assassinated four months into his presidency by Charles Guiteau Chester A. Arthur 21st President of the United States who supported the Pendleton Act Pendleton Act a law, enacted in 1883, that established a bipartisan civil service commission to make appointments to government jobs by means of the merit system Grover Cleveland 22nd and 24th President of the United States who lowered tariffs and handled the Panic of 1893 poorly Benjamin Harrison 23rd President of the United States who won passage of the McKinley Tariff, which raised tariffs to their highest level ever