Irene's Myomassology Institute Anatomy Lecture Review Guide
advertisement
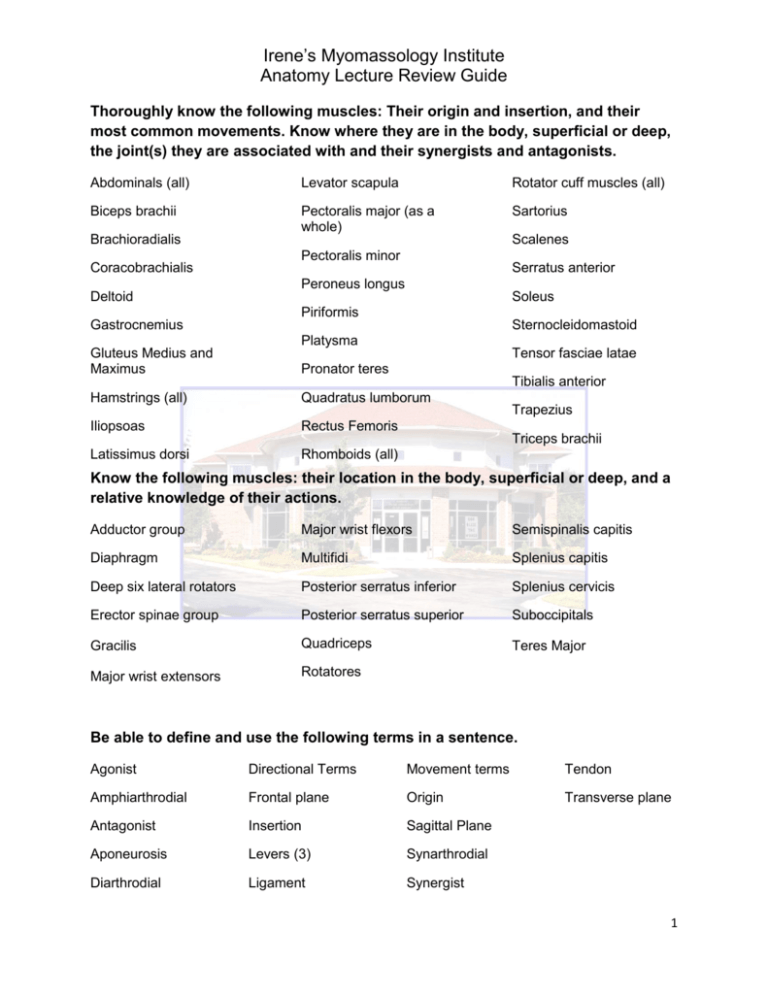
Irene’s Myomassology Institute Anatomy Lecture Review Guide Thoroughly know the following muscles: Their origin and insertion, and their most common movements. Know where they are in the body, superficial or deep, the joint(s) they are associated with and their synergists and antagonists. Abdominals (all) Levator scapula Rotator cuff muscles (all) Biceps brachii Pectoralis major (as a whole) Sartorius Brachioradialis Coracobrachialis Deltoid Gastrocnemius Gluteus Medius and Maximus Pectoralis minor Scalenes Serratus anterior Peroneus longus Soleus Piriformis Sternocleidomastoid Platysma Tensor fasciae latae Pronator teres Tibialis anterior Hamstrings (all) Quadratus lumborum Iliopsoas Rectus Femoris Latissimus dorsi Rhomboids (all) Trapezius Triceps brachii Know the following muscles: their location in the body, superficial or deep, and a relative knowledge of their actions. Adductor group Major wrist flexors Semispinalis capitis Diaphragm Multifidi Splenius capitis Deep six lateral rotators Posterior serratus inferior Splenius cervicis Erector spinae group Posterior serratus superior Suboccipitals Gracilis Quadriceps Teres Major Major wrist extensors Rotatores Be able to define and use the following terms in a sentence. Agonist Directional Terms Movement terms Tendon Amphiarthrodial Frontal plane Origin Transverse plane Antagonist Insertion Sagittal Plane Aponeurosis Levers (3) Synarthrodial Diarthrodial Ligament Synergist 1 Irene’s Myomassology Institute Anatomy Lecture Review Guide As a reference guide and as general knowledge, know the following information about the skeleton. The major bones of the skeleton Bony landmarks (be able to locate them and know what they are for; i.e. are they projections for attachments, or are they places for bones to articulate.) Shapes of bones (be able to list examples) Divisions of the skeleton (axial/appendicular) and what bones belong to each division Classification of joints (defined by what initially holds them together and how much they move) Ligament names and locations Types of Diarthrodial joints (names, examples and how they move) Know your movements Abduction and adduction Plantar flexion and dorsiflexion Flexion and extension Inversion and eversion Rotation Pronation and supination Medial and lateral rotation Protraction and retraction Lateral Flexion Elevation and depression 2