Answers
advertisement

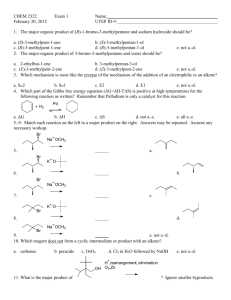
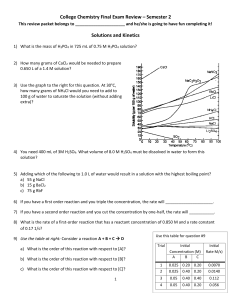
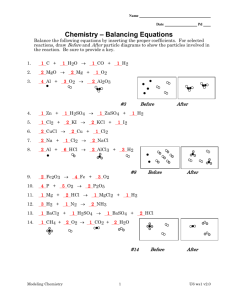
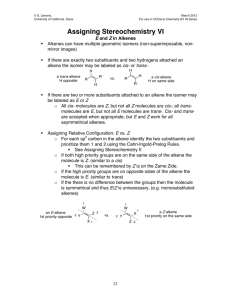
CHM 221 Organic Chemistry II Winter Term 2001 Addition Reactions Answers 1. Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions. OH (a) O H2SO4 H -H H O OH H + H2O (b) OH H2SO4 H2O 2. What product is obtained from the reaction of HCl with 1-butene? With 2-butene? Draw the mechanisms. Cl H Cl H Cl Cl Cl Cl 3. Which of the two reactions in question 2 has the greater free energy of activation? The reaction of 2-butene with HCl has a greater free energy of activation. This is because the more substituted alkene is lower in energy and more stable (less reactive). Since both 1- and 2butene pass through the same secondary carbocation intermediate, we can assume that 2butene will have a higher activation energy for reaction. 4. Which of the two alkenes in question 2 reacts more rapidly with HCl? 1-Butene, for the reasons outlined in the answer to question 3. 5. Which of the following compounds will react more rapidly with HCl, (Z)-2-butene or (E)-2-butene? (Z)-2-butene will react faster because ir is less stable (higher in energy). Having the two alkyl groups on the same side of the double bond causes steric interactions which raise the relative energy of cis compounds compared to trans compounds. 6. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction. H OCH3 + CH3OH CH3OH H -H OCH3 7. Which step is the rate determining step for the above reaction? The first step. Protonation of the alkene. 8. What is the electrophile in the first step? The hydrogen ion 9. What is the nucleophile in the first step? The π-bond of the alkene 10. What is the electrophile in the second step? The secondary carbocation. 11. What is the nucleophile in the second step? The lone pair of electrons on the oxygen of methanol. 12. There are two alkenes that react with HBr to give 1-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane. Identify these alkenes. and 13. When 3-methyl-1-butene reacts with HBr, two alkylhalides are formed, 2-bromo-3-methylbutane and 2-bromo2-methylbutane. Provide a mechanism that explains the formation of these products. H Br Br 1,2-hydride shift Br Br H Br 14. Give the reagents that would be required to carry out the following syntheses. Br2 Br Br HCl Cl 1. BH3 OH 2. H2O2 Br2 Br OH H2O/NaOH H2SO4 CH3OH OCH3 15. How could you prepare the following compounds, starting from any alkene and using any other needed reagents. H2SO4/H2O OH Br2/H2O2 Br 1. Hg(OAc)2 H2O OH 2. NaBH4 OH 1. BH3 2. H2O2 aq. NaOH MCPBA O 16. Briefly explain why oxymercuration and hydroboration can be considered complimentary methods of alkene hydration. Oxymercuration and hydroboration are complimentary because they give opposite types of products. Oxymercuration will always give the Markovnikov addition product and hydroboration will always give the anti-Markovnikov product. In addition, neither method allows for rearrangement products, since free carbocations are not involved. 17. Draw a mechanism for epoxide formation using m-chloroperbenzoic acid (MCPBA). H O O Cl O H O O Cl O O