Mitosis
advertisement

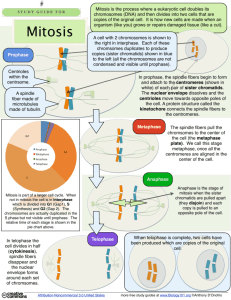
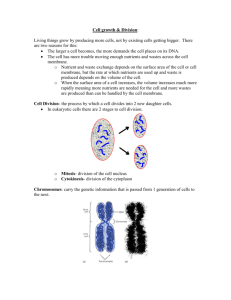
Mitosis • Deals exclusively with the division of the cell nucleus. • Creates identical daughter cells. Interphase • Period of time between splits. • Most of cells growth takes place during this time. • Chromosomes are replicated (copied). – There are now 2 copies of every chromosome. – Important: humans are diploid ( we have two copies of each chromosome arranged in 23 pairs) • Organelles are made. 4 phases of Mitosis • • • • Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Prophase • First and longest phase of mitosis. – Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes – Chromosomes become visible – Centrioles separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. – Spindle fibers form – Nuclear envelope and nucleolus begin to break down. • Near the end of prophase the nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear. Nuclear membrane begins to dissolve Centrioles move to opposite ends Gary E. Kaiser By end of prophase • Nucleolus has disappeared • Spindle fibers span the cell • Sister chromatids are attached to spindle by centromere. Metaphase • Chromatids align down the center of the cell. Each chromosome remains attached to a spindle fiber at its centromere. Anaphase • Sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and begin to be pulled to opposite ends of the cell. Telophase • Chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell and loose their distinctive shape. • Nucleolus and nuclear membranes reform • Spindle fibers dissolve. • Essentially the reverse of prophase. • Telophase overlaps with Cytokinesis Cytokinesis • Divides the cytoplasm of the cell. • In animal cell, the cell membrane pinches the cell in half creating two daughter cells at the cleavage furrow. • In plant cells, a cell plate forms between the two nuclei, gradually develops into separate membrane and then cell wall. • Each cell has an identical set of duplicate chromosomes. Cleavage Furrow Formation of 2 daughter cells