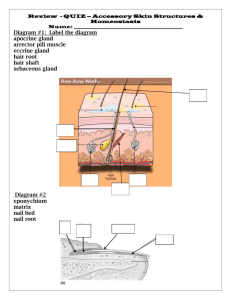
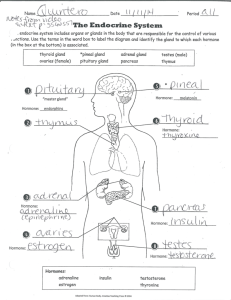
A. EXOCRINE GLANDS
advertisement

Department of Histology and Embryology Faculty of Medicine, PU, Olomouc, CZ Histology practical No. Topics: 4 1- STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF GLANDULAR EPITHELIA AND THEIR CLASSIFICATION (pre-lab rev.ppt). 2- RECOGNITION OF SEROUS AND MUCOUS GLADS IN STAINED HISTOLOGY AND PC-MONITORED SLIDES OR PRINTED IMAGES. 3- REVISION OF THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF SPECIALIZED PROTEINSYNTHESIZIG AND MUCUS-SECRETING EPITHELIAL CELLS. (Recommended textbook and Atlas with CD-ROM and websites) 4- COMPARE THE STRUCTURE OF EXOCRINE AND ENDOCRINE GLANDS. Contents: A. EXOCRINE GLANDS 1. Parotid gland (glandula parotis, sl. no. 19) sect., H&E stain. This is a large purely serous-sec reting gland that contains many serous cells arranged in multiple compound acini (alveoli). Study the serous cells at high magnification and note the shape and location of their nuclei. Draw a simple alveolus containing a few serous cells. They are practically everywhere in this section. What kind of ultrastructures are located under the nucleus of these cells? Among the alveoli, there are many excretory ducts lined with different epithelial cells. Connective tissue is stained pale pink, and adipose cells are large and empty-looking. 2. Duodenum (duodenum, sl. no. 26) sect., H&E stain. This slide shows part of a transverse section of the initial portion of small intestine (duodenum) that is composed of several layers of different tissues. The surface epithelium is lined with a simple 1 columnar epithelium (locate it first). Then go to the glandular tissue under the epithelium (arrow) and locate the multiple, compound mucous tubuli of the purely mucus-secreting gland there (Brunner’s gland). Draw a simple tubulus containing a few mucous cells. Note the shape and position of the nuclei. The next layers in this slide contain smooth muscle mostly. 3. Submandibular gland (glandula submand., sl.n. 20) section., H&E stain. This mixed-secretion producing (seromucous secretion with prevalence of the serous component) gland is located in the tissue under the mandible. Practically everywhere you can locate both, the serous alveoli (these prevail, arrow) and some mucous tubules (arrowhead) containing pale-stained cells. Locate some serous demilunes at the terminal portions of mucus tubules. Note the arrangement of the glandular tissue into lobules and the presence of several ducts there. 4. Sublinqual gland (glandula sublinqualis, sl.n. 21) sect., H&E stain. This mixed secretion-producing gland (sero mucous secreti on with preva lence of the mucous component) is located in the tissue under the tongue. Find the lobule where the mucous tubules prevail (arrow) and study the mucous cells and serous demilunes. Compare these with the other lobules where the serous cells are in majority. 5. Trachea (trachea, sl.n. 34) t.s., H&E stain. In transverse section of the trachea, find the inner surface of this tube and locate the pseudostratified columnar epithelium with kinocilia. Note, that the kinocilia are absent on the surface of pale or empty-looking cells, called goblet cells. At high power lens, locate one of these cells and study its shape and location of its nucleus. This is an example of the 2 intraepithelial single-cell gland. What is the quality of its product? Internal layers of the trachea in this slide also contain some other glands. Evaluate the quality of their product. B. ENDOCRINE GLANDS 6. Suprarenal gland (Nadledvinka, sl.n. 15) section., H&E stain. This is a section of the suprarenal gland that is the example of the endocrine gland with fascicular arrangement of secretory epithelial cells. Locate the cords of cells in the superficial layers of this section (arrow). Note the absence of ducts. What is the way the secretory cells release and distribute their product to their body targets? How we call these products? 7. Thyroid gland (glandula thyroidea, sl. n. 13) sect., H&E stain. Thyroid gland is an endocrine gland with follicular arrangement of secretory epithelial cells. The follicles are lined mostly with simple cuboidal endocrine cells that surround the central area filled with an acidophilic material called colloid (arrow). Study the shapes of epithelial cells and note the absence of ducts. Within the connective tissue septa, between lobules of the secretory parenchyma, there are several blood vessels and some adipose tissue cells. 3 8. Identify as many structures in this picture as you can. …………………… …………………… …………………… …………………… …………………… …………………… 11. In your selfstudy, revise the ultrastructure of specialized protein synthesizig and mucus secreting epithelial cells. (Use the recommended textbook and atlas with CD-ROM) Websites: http://www.kumc.edu/instruction/medicine/anatomy/histoweb/glands/glands.htm http://www.anatomyatlases.org/MicroscopicAnatomy/Section02/Plate0226.shtml http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/MedEd/Histo/frames/h_frame1.html http://www.path.uiowa.edu/cgi-bin-pub/vs/vl_browse.cgi?cat=h_epithelium http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/default.htm 4-EpithGland Practical.doc dk-3/2009 4