8th Earth Science Chapter 3 – Minerals
advertisement

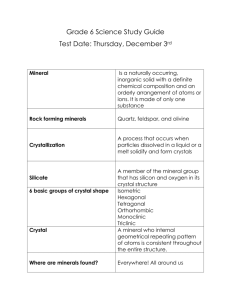
8th Earth Science Chapter 3 – Minerals Name ______________________ Section 1 – Minerals: Mineral About _________________ different minerals are found on Earth, but they all share four characteristics. 1.All minerals are formed by _________________ processes. These are processes that occur _______or _________________ Earth with no input from humans. 2.Minerals are _________________. This means that they _________________ made by life processes. 3.Every mineral is an _________________ or compound with a _________________ chemical composition. 4.Minerals are _________________ solids. All solids have a definite volume and shape. Only a solid can be a mineral, but not all solids are minerals. The word crystalline means that atoms are arranged in a _________________ that is _________________ over and over again. For example, graphite’s atoms are arranged in layers. Crystal: A crystal is a group of crystals that have _________________ atomic arrangements and therefore similar external crystal _________________. Not all mineral crystals have smooth surfaces and regular shapes. There are __________ major crystal systems, which classify minerals according to their crystal structures. Magma As magma cools, its atoms lose _________________ energy, move closer together, and begin to combine into compounds. Atoms of the different compounds arrange themselves into orderly, repeating patterns. The _________________ and _________________ of elements present in magma partly determine which minerals will form. When magma cools slowly the crystals that form are generally _________________ enough to see with the unaided eye. When magma cools quickly, the crystals that form will be _________________. Crystals also can form from minerals _________________ in water. When water evaporates, as in a dry climate, ions that are left behind can come together to form crystals. Or, if too much of a substance is dissolved in water, ions can come together and crystals of that substance can begin to form in the solution. Minerals can form from a solution in this way without the need for _________________. _______elements occur naturally in Earth’s crust. Approximately ______ percent (by weight) of the crust is made of only ________ of these elements. Most of the common rock-forming minerals belong to a group called the silicates Silicates: These two elements alone combine to form the basic _________________ blocks of most of the minerals in Earth’s _________________ and _________________. Section 2 – Mineral Identification: _________________ and _________________ are two obvious clues that can be used to identify minerals. Some other properties to study include how _________________ a mineral is, how it breaks, and its _________________ when crushed into a powder. Hardness: Sometimes the concept of hardness is confused with whether or not a mineral will _________________. It is important to understand that even though a _________________ is extremely hard, it can _________________ if given a hard blow in the right direction along the crystal. In 1824, the Austrian scientist Friedrich _________ developed a list of common minerals to compare their hardness. This list is called ________ scale of _________________. Luster: Luster can be _________________ or _________________. Minerals with a metallic luster _________________ like metal. When a mineral does not shine like a metal, its luster is nonmetallic. Terms for nonmetallic luster include _________________, pearly, _________________, and glassy. Specific Gravity: Specific gravity is expressed as a _________________ (with no unit following). Streak: When a mineral is rubbed across a piece of unglazed _________________ tile, a streak of powdered mineral is left behind. The streak test works only for minerals that are _________________ than the streak plate. Some soft minerals will leave a streak even on _________________. The last time you used a _________________ to write on paper, you left a streak of the mineral _________________. Cleavage: Cleavage is determined partly by the arrangement of the mineral’s atoms. Not all minerals have _________________. Fracture: _________________ is a mineral with fracture. Some minerals have unique properties. _________________ is attracted to magnets. Light forms two separate rays when it passes through _________________ causing you to see a double image when viewed through transparent specimens. Section 3 – Uses of Minerals: Gems: Most gems are special varieties of a particular minerals. They are _________________, brighter, or more _________________ than common samples of that mineral. Sometimes a gem has a crystal structure that allows it to be ______ and _________________ to a higher quality than that of a non-gem mineral. All gems are prized, but some are truly spectacular and have played an important role in _________________. The _________________ diamond, found in South Africa in 1905, was the largest _________________ diamond ever discovered. The Cullinan diamond was cut into _____main stones and ______ smaller ones. The largest of these is called the Cullinan 1 or Great Star of Africa and it is now part of the British monarchy’s _________________ _________________. Another well-known diamond is the blue _________________ diamond. The Hope diamond has gained a reputation for bringing its owner _____ luck. The Hope diamond’s mass is 45.52 _________________. Currently, it is displayed in the _________________ Institute in Washington, D.C. Diamonds have a hardness of ______ on Mohs scale. They can _________________ almost any material—a property that makes them useful as industrial _________________ and _________________ tools. Other useful gems include _________________, which are used to produce specific types of _________________ light. _________________ crystals are used in electronics and as timepieces. Most industrial diamonds and other gems are _________________ which means that _________________ make them. _________________, used in everything from frying pans to ships, is obtained from its ore, hematite. A mineral or rock is an _________________ if it contains a useful substance that can be mined at a profit. Aluminum sometimes is refined, or purified, from the ore _________________. In the process of refining aluminum, aluminum oxide powder is separated from unwanted materials that are present in the original bauxite. After this, the aluminum oxide powder is converted to molten aluminum by a process called _________________. Under certain conditions, metallic elements can _________________ in fluids. These fluids then travel through weaknesses in rocks and form mineral deposits. Mineral deposits left behind that fill in the open spaces created by the weaknesses are called _________________ mineral deposits. _________________ is a _________________, _________________, metallic element derived from minerals that contain this metal in their crystal structures. Two minerals that are sources of the element titanium are ilmentite and rutile. Titanium is used in automotive body parts, such as connecting rods, valves, and suspension springs and in _________________.