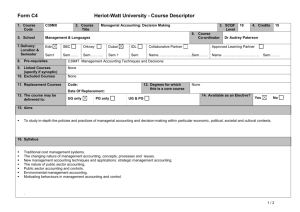
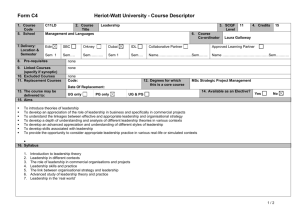
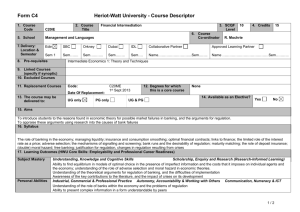
UNIX Semaphores
advertisement

Unix-Linux 4
Semaphores
Semaphore
data structure shared by multiple processes
normally used to synchronize access to a common, non-sharable resources
non-negative number stored in the kernel
semaphore system calls – atomic actions
o test
o decrement
o increment
o block invoking process
o notify queued, waiting process
Unix Semaphore Sets
System Semaphore Data Structure -- <sys/sem.h>
o struct semid_ds
{
struct ipc_perm
sem_perm; // permissions
struct sem
*sem_base // ptr to 1st semaphore in set
ushort_t
sem_nsems; // number of semaphores in set
time_t
sem_otime; // last semop time
long
sem_pad1; // time_t expansion reserve space
time_t
sem_ctime; // last modification time
long
sem_pad2; // time_t expansion
long
sem_pad3[ 4 ]; // reserve area
};
o
struct sem
{
ushort
pid_t
ushort
ushort
};
array of struct sem
semval;
sempid
semncnt;
semzcnt;
// semaphore value
// pid of last operation
// number of pid‟s waiting for semval > cval
// number of pid‟s waiting for semval = 0
Creating & Accessing Semaphore Sets
o int semget( key_t key, int nsems, int semflg );
key value is used by the system to generate by a unique semaphore identifier
nsems is the number of semaphores in the system;
it is used to allocate the array of sem structures
semflg is used to specify the access permissions &/or special
creation conditions; access permissions may be combined
with the IPC_CREAT and/or IPC_EXCL flags
o
semget system call
successful returns semaphore identifier (non-negative integer)
unsuccessful returns -1 & sets errno
key == IPC_PRIVATE
or
key does not have an associated
semaphore identifier
&&
IPC_CREAT has been specified
a new set of semaphores is created
the array of sem structures is not initialized
the semaphore set for the indicated key already exists
&&
IPC_CREAT has been specified
semget system call returns the associated semaphore identifier
When using semget to access an established semaphore set,
the value of nsems can be set to zero (don’t care value)
o
single character
key_t ftok( const char *path, int id );
path to an existing accessible file
successful returns a unique but reproducible key value
unsuccessful returns -1
int sem1, sem2, sem3;
key_t
ipc_key = ftok(“.”, „S‟);
if((sem1 = semget( ipc_key, 3, IPC_CREAT | 0666)) == -1 )
perror(“semget: IPC_CREAT | 0666):
creates set of three semaphores unless system limits have been reached
if((sem2 = semget( ipc_key, 3, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666)) == -1 )
perror(“semget: IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666):
attempts to create another set of three semaphores using the same key
value, and including the specification IPC_EXCL; the system call fails
if((sem3 = semget( IPC_PRIVATE, 3, 0666)) == -1 )
perror(“semget: IPC_PRIVATE):
creates set of three semaphores using IPC_PRIVATE instead of the ipc_key
the semaphore identifier generated will be private to the calling process
Semaphores need to be manually deleted by the user
$ipcrm semaphore_identifier
Semaphore Control
int semctl( int semid, int semnum, int cmd, /* union semun arg */ … );
semid – valid semaphore identifier
semnum – number of semaphore in semaphore set
cmd – integer command value -- <sys/ipc.h> <sys/sem.h>
/* union semun arg */ -- <sys/sem.h>
See Unix page 173-174 Linux pages 241-242
union semun
{
int val;
arg.array = my_very_own_array;
struct semid_ds * buf;
arg.buf = pointer_to_my_very_own_structure;
ushort *array;
};
int semctl( int semid, int semnum, int cmd, union semun arg );
union semun arg;
Semaphore Commands (cmd)
IPC_STAT
o
o
o
return current values of the struct semid_ds
requires a user-generated storage structure
requires read permission for the semaphore set
IPC_SET
o
o
if the effective ID of the accessing process is that of a
superuser, or
the same as the ID value stored in sem_perm.cuid or sem_perm.uid
then the following members of struct ipc_perm may be changed
sem_perm.uid
sem_perm.gid
sem_perm.mode
requires a user-generated structure of type semid_ds
the structure must be populated with the current values of the struct semid_ds
the desired values must be modified in the user-generated structure
the values may established via the IPC_SET command
IPC_RMID
o
remove the semaphore set associated with the semaphore identifier
GETALL
o
o
o
return the current values of the semaphore set
requires an struct sem[ sem_nsems ] array to be allocated
requires read permission for the semaphore set
SETALL
o
o
o
requires an struct sem[ sem_nsems ] array to be allocated & populated with values
initialize all semaphores in the set to values stored in that array
requires write/alter permission for the semaphore set
GETVAL
o
o
return the current value of the individual senum index
requires read permission for the semaphore
SETVAL
o
o
set the value of the individual semaphore referenced by the senum index
to the value specified in arg.val
requires write/alter permission for the specified semaphore
GETPID
o
o
return the process ID from the struct sem_perm within the struct semid_ds
requires read permission for the semaphore
GETNCNT
o
o
return # processes waiting for the semaphore
referenced by the semnum index to increase in value
requires read permission for the semaphore
GETZCNT
o
o
return # processes waiting for the semaphore
referenced by the semnum index to become zero
requires read permission for the semaphore
code
fragment
struct semid_ds
{
struct ipc_perm
sem_perm; // permissions
struct sem
*sem_base // ptr to 1st semaphore in set
ushort_t
sem_nsems; // number of semaphores in set
time_t
sem_otime; // last semop time
long
sem_pad1; // time_t expansion reserve space
time_t
sem_ctime; // last modification time
long
sem_pad2; // time_t expansion
long
sem_pad3[ 4 ]; // reserve area
};
struct sem
{
ushort
semval; // semaphore value
pid_t
sempid // pid of last operation
ushort
semncnt; // number of pid‟s waiting for semval > cval
ushort
semzcnt; // number of pid‟s waiting for semval = 0
};
union semun
{
int
val;
struct semid_ds
*buf;
ushort
*array;
}
Initial values for the three semaphores
struct semid_ds
static ushort
union semun
sem_buf;;
sem_array[3] = {3, 1, 4};
arg;
sem_id = semget(ipc_key, 3, IPC_CREAT, | 0666);
// define arg.buf such that the current values in struct semid_ds are returned
arg.buf = &sem.buf;
semctl(sem_id, 0, IPC_STAT, arg);
// define arg.array such that the values in sem_array[3] = {3, 1, 4} are
changed
arg.array = sem_array;
semctl(sem_id, 0, SETALL, arg);
for(i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
Print the values for the three semaphores
{
sem_value = semctl(sem_id, i, GETVAL, 0);
printf( “Semaphore %d : value %d”, I, sem_value);
}
// remove the semaphore set
semctl(sem_id, 0, IPC_RMID, 0);
See Linux pages 177-178 for using dbx to view the content of sem_buf
Semaphore Operations
Individual Semaphores
int semop( int semid, struct sembuf *sops, size_t nsops );
pointer to an array of operations to be performed
<sys/sem.h>
o struct semid_ds
{
struct ipc_perm
struct sem
ushort_t
time_t
long
time_t
long
long
};
o
struct sem
{
ushort
pid_t
ushort
ushort
};
number of elements in the array
sem_perm; // permissions
*sem_base // ptr to 1st semaphore in set
sem_nsems; // number of semaphores in set
sem_otime; // last semop time
sem_pad1; // time_t expansion reserve space
sem_ctime; // last modification time
sem_pad2; // time_t expansion
sem_pad3[ 4 ]; // reserve area
array of struct sem
semval;
sempid
semncnt;
semzcnt;
// semaphore value
// pid of last operation
// number of pid‟s waiting for semval > cval
// number of pid‟s waiting for semval = 0
IPC_NOWAIT
semaphore operation fails return immediately
SEM_UNDO
if a blocked operation fails, allows an operation to be undone
process – number of resources currently held
system – number of resources currently free
sem_op value
negative process is attempting to
o decrement the semaphore
o record the acquisition of a resource affiliated with the semaphore
the acquiring process must have alter, i.e., write, permission on the semaphore set
semval >= abs(semop) semval = semval – abs(semop)
semval >= abs(semop) & SEM_UNDO set
semval = semval – abs(semop)
semadj = semadj + abs(semop)
semval < abs(semop) increment semncnt; block until
semval >= abs(semop)
adjust semncnt
semval = semval – abs(semop)
semid is removed
return -1
set errno to EIDRM
signal is caught
adjust semncnt
set errno to EINTR
semval < abs(semop) & IPC_NOWAIT is set
return immediately
set nerrno to EAGAIN
positive process is attempting to
o increment the semaphore
o record the release, i.e., return, of a resource affiliated with the semaphore
the acquiring process must have alter, i.e., write, permission on the semaphore set
semval = semval + sem_op
SEM_UNDO is set
semval = semval + sem_op
semadj = semadj – sem_op
sem_op == 0 (zero) test (semval == 0)
the accessing process must have read permission on the semaphore set
semval == 0 all resources are currently allocated
semval == 0 return immediately
semval != 0 & IPC_NOWAIT set return -1 & set errno to EAGAIN
semval != 0 increment semzcnt
block until
semval == 0 adjust semzcnt & return
semid is removed return -1 & set errno to EIDRM
signal is caught adjust semzcnt & set errno to EINTR
Producer-Consumer
argv[1] holds the # of seconds to sleep between consumer & producer cycles
Semaphore Section
#define BUFFER “./buffer”
// non-sharable resource
union semun
{
struct sembuf
int
val;
{
struct semid_ds
*buf;
ushort
sem_num;
ushort
*array;
short
sem_op;
}
short
sem_flg;
}
main (int argc, char *argv[ ])
{
sem_flg : SEM_UNDO allows rollback
FILE *fptr;
static struct sembuf acquire = {0, -1, SEM_UNDO}; // acquire operation defined
static struct sembuf release = {0, 1, SEM_UNDO); // release operation defined
static ushort start_val[2] = {1, 0};
sem_op : -1 decrements semaphore
pid_t c_pid;
1 increments semaphore
key_t ipc_key;
int
semid, producer = 0, i, n, p_sleep, c_sleep;
union semun arg;
enum{READ, MADE};
ipc_key = ftok(“.”, „S‟);
sem_num = 0; placeholder, dynamic change
indicates which semaphore is being referenced
first pass – producer : semaphore set is created
if(( semid = semget(ipc_key, 2, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666_)) != -1)
{
producer = 1;
provides initial values or the two semaphores
arg.array = start_val;
if ( semctl(semid, 0, SETALL, arg ) == -1 ){perror … exit(1); }
}
else if (( semid = semget(ipc_key, 2, 0)) == -1){perror … exit(2);}
}
second pass – consumer : gain access to the semaphore set
Producer Section
switch(producer)
{
case 1:
p_sleep = atoi(argv[1]); // producer sleep time
srand((unsigned) getpid( )); // determine seed value for random generator
for( i = 0; I < 10; i++)
struct sembuf
{
{ ushort sem_num;
sleep(p_sleep);
short sem_op;
n = rand( ) % 99 + 1;
short sem_flg;
printf(“A. Number [%2d] generated by producer\n”, n); }
acquire.sem_num = READ;
static struct sembuf acquire = {READ, -1, SEM_UNDO};
if ( semop(semid, &acquire, 1) == -1)
{ perror(“ waiting for consumer “); exit(3);}
if (( fptrf = fopen(BUFFER, “w”)) == NULL ) {perror(BUFFER); exit(4);}
fprintf(fptr, “%d\n”, n);
fclose(fptr);
release.sem_num = MADE;
static struct sembuf release = {MADE, 1, SEM_UNDO};
printf(“b. Number [%2d] deposited by producer\n”, n);
if (semop(semid, &release, 1) == -1) { perror(“ … “); exit(5);}
}
sleep(5); // waiting for final consumption to occur
if (semctl(semid, 0, IPC_RMID, 0) == -1 (perror(“ … “); exit(6);}
printf(“Semaphore Removed\n”);
break;
}
Consumer Section
case 0;
c_sleep = atoi(argv[1]); // consumer sleep time
c_pid = getpid( );
while (1)
{
sleep(c_sleep);
acquire.sem_num = MADE;
if ( semop(semid, &acquire, 1) == -1)
{perror(“waiting for item to be produced”); exit(7);}
if (( fptr = fopen(BUFFER, “r”)) == NULL) {perror(BUFFER); exit(8);}
fscanf(fptr, “%d”, &n);
fclose(fptr);
release.sem_num = READ;
if (semop(semid, &release, 1) == -1) {perror(“ … “); exit(9);}
printf(“C.
Number [&2d] obtained by consumer %6d\n”, n, c_pid);
}
}
exit(0);
}
Entry
Critical
Exit
Acquire READ
Release MADE
Producer
READ
MADE
1
0
0
0
0
1
Consumer
READ
MADE
0
1
0
0
1
0
Acquire MADE
Release READ