Nasal cavity
advertisement
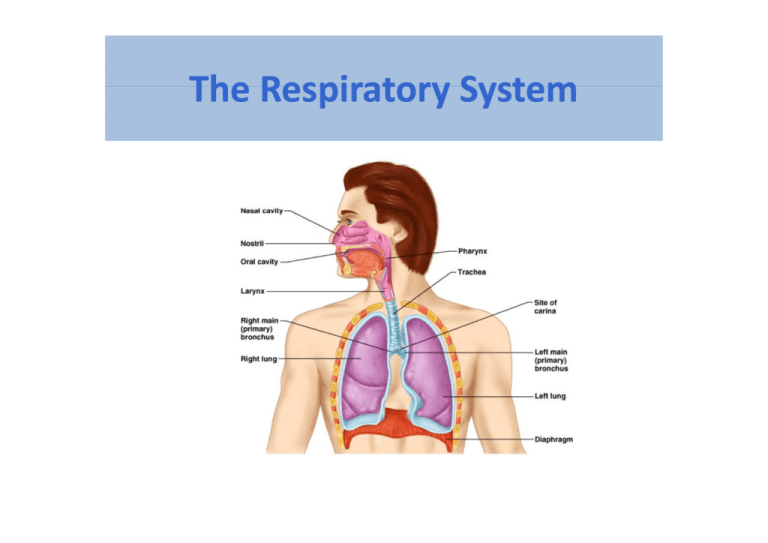
The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Functions of the Functions of the Respiratory System • • • • Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Filters inspired air C t i Contains receptors for smell t f ll Enable speech p production p Respiration p Includes • Pulmonary ventilation – Air moves in and out of lungs – Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) • External respiration – Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli – O2 (oxygen) in air diffuses into blood – CO2 (carbon dioxide) in blood diffuses into air • Transport of respiratory gases – Between the lungs and the cells of the body – Performed by the cardiovascular system – Blood is the transporting fluid • Internal respiration p – Gas exchange in capillaries between blood and tissue cells – O2 in blood diffuses into tissues – CO2 waste in tissues diffuses into blood 3 Pathway of Respiratory System • Upper respiratory tract (Conducting zone) – nose, mouth, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx and trachea nose, mouth, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx and trachea • Lower respiratory tract ‐ bronchial tree and lungs (Respiratory zone) 鼻腔 喉 鼻 口 氣管 支氣管 小支氣管 肺泡 肺臟 Mouth & Nose • Brings air into the body • Nasal hairs in nostrils trap dust 鼻骨 上頷骨 側鼻軟骨 間隔軟骨 翼軟骨 Nasal cavity鼻腔 Nasal cavity鼻腔 • Warms & moistens air a s & o ste s a • nasal septum & conchae 鼻中膈 & 鼻甲 (bone & cartilage) (bone & cartilage) Nasal Conchae 鼻甲 •Inferior to each is a meatus 鼻道 •Increases turbulence of air I b l f i : ↑air time ↑ i i •3 scroll‐like structures 7 8 Nasal cavity 鼻腔 Nasal cavity • Warms & moistens air • nasal septum & conchae nasal septum & conchae • mucous membrane 黏膜: mucus; cilia; olfactory receptors – traps dust, pollen, and other materials that were p ,p , not trapped by nasal hairs – cilia sweep mucus and trapped material to the cilia sweep mucus and trapped material to the back of the throat where it can be swallowed 痰 Olfactory Epithelium 嗅覺上皮 Olfactory Epithelium Nasal cavity 鼻腔 Nasal cavity • Warms & moistens air • nasal septum & conchae nasal septum & conchae • mucous membrane 黏膜: mucus; cilia; olfactory receptors – traps dust, pollen, and other materials that were p ,p , not trapped by nasal hairs – cilia sweep mucus and trapped material to the cilia sweep mucus and trapped material to the back of the throat where it can be swallowed • Nasal sinus N l i 鼻竇 Paranasal sinuses 副鼻竇 – Frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid and maxillary bones – Open into nasal cavity Open into nasal cavity – Lined by same mucosa as nasal cavity and perform same functions f ti : moisture, warm, expel it l – Also lighten the skull – Can get infected: sinusitis 蝶竇 額竇 蝶竇 篩竇 上頷竇 12 Pharynx 咽 • Tube‐like passageway used by food, liquid, and air Nasopharynx 鼻咽 : pharyngeal tonsils, 耳咽管 oropharynx 口咽 h 口咽 : palatine tonsils, digestion/ air transduction l i il di i / i d i laryngopharynx喉咽: larynx, common passage Larynx 喉 • • • • Transmit canal from the pharynx pg 會厭 Epiglottis 喉壁由九塊軟骨構成支架 “Voice Voice box box”音箱 音箱 ; vocal cords 聲帶 ; vocal cords 聲帶 Epiglottis pg 會厭 • At the lower end of the pharynx is a flap of tissue – covers covers the trachea during swallowing so that food does the trachea during swallowing so that food does not enter the lungs 食道 Nine cartilages 軟骨 不成對 • Epiglottis 會厭 – (1) elastic cartilage • thyroid cartilage 甲狀– (1) Adam’s apple, anterior attachment of vocal folds, folds testosterone increases size after puberty 喉結 • cricoid cartilage 環狀– (1) ring-shaped, 成對 • arytenoid cartilages 杓狀– (2) • cuneiform cartilages 械狀- (2) • corniculate cartlages – 角狀(2) • • • • • • Epiglottis 會厭 – (1) elastic cartilage thyroid cartilage 甲狀– (1) anterior attachment of vocal folds cricoid cartilage 環狀– (1) ring-shaped, arytenoid cartilages 杓狀– (2) posterior attachment of vocal folds, Movement/ vocal fold 震動 cuneiform cartilages 械狀- (2) corniculate cartlages – 角狀(2) Larynx 喉 • • • • Transmit canal from the pharynx pg 會厭 Epiglottis 喉壁由九塊軟骨構成支架 “Voice Voice box box”音箱 音箱 ; vocal cords 聲帶 ; vocal cords 聲帶 24 04 24_04 聲帶(鬆,外開) 聲帶(緊,內收) Voice Production Voice Production i). Vibration Air passing over the vocal folds causes vibrations ii). Pitch Length and tension of the vocal folds is controlled by muscle iii) Loudness iii). Loudness depends on the force with which air is exhaled through the cords through the cords iv). Muscles of the face, tongue, and lips help with enunciation of words enunciation of words v). resonating chambers : nasal sinus 發炎 / 腫大 : 聲帶收縮受阻/無法震動 : 沙啞/失聲 Trachea 氣管 • • • • Air‐conducting tube y Connects the larynx with the bronchi Lined with mucous membranes and cilia Contains strong cartilage rings (C 型) Contains strong cartilage rings (C 型) Cartilage C til : prevention ti off the th collapse of trachea and air can pass Pathway of Respiratory System • Upper respiratory tract – nose, mouth, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx and trachea nose, mouth, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx and trachea • Lower respiratory tract ‐ bronchial tree and lungs 支氣管 & 肺 Bronchi 支氣管 • • • • Two short tubes that branch (T4;T7 ?) C Carry air into the lungs i i t th l Respiratory epi. p y p Bronchial Tree The bronchi sub divide into The bronchi sub divide into 2nd and 3rd bronchials and then continue to subdivide then continue to subdivide 23 pairs of branching passageways • Rid Ridge on internal aspect of last tracheal of last tracheal cartilage • Point where trachea branches • Mucosa highly M hi hl sensitive to irritants: cough irritants: cough reflex Carina* * 25 Bronchial Tree 分枝 lung 24_06a 氣管 初級支氣管 次級支氣管 三級支氣管 小支氣管 末小支氣管 會厭 甲狀軟骨 右 高, 短, 右: 易阻塞 氣管 左初級支氣管 左次級支氣管 左三級支氣管 小支氣管 Bronchioles 小支氣管 • Tiny branches of air tubes in the lungs • Connect bronchi to alveoli Connect bronchi to alveoli 肺泡 • • • • 偽複層纖毛上皮→單層立方上皮 Cartilage no↓; smooth muscle ↑; Cartilage no↓; smooth muscle ↑; 呼吸 氣喘 氣管 初級支氣管 次級支氣管 三級支氣管 小支氣管 末小支氣管 肺泡囊 Alveoli 肺泡 • Tiny, thin‐walled, grapelike clusters at the end of each bronchiole • Singular ‐ alveolus • Surrounded by capillaries Surrounded by capillaries • Where carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange take place Pulmonary Circulation 肺循環 肺動脈CO2 全身 氣體交換 肺靜脈 O2 左心房/室 31 Pulmonary arteries and veins Pulmonary vein (intersegmental) Pulmonary artery Pulmonary artery 肺動脈 (缺氧) 肺靜脈 (充氧) 32 Lungs • Thoracic cavity 胸腔 • Left & right Lung • Pleurae 胸膜 Pleurae 胸膜:: visceral pleura & parietal pleura 臟膜 壁膜 頸部 中膈 肋 橫膈 34 Thoracocentesis 胸腔穿刺 9th intercostal space in the MAL ((midaxillaryy line)) 抽肺積水或肺積血 血胸 Hemothorax H th MCL Scapular line MAL 胸肋膜陷窩 12th rib 35 10th rib 右 3 左 2 上葉 斜裂 斜裂 水平裂 中葉 下葉 下葉 心臟壓跡 B Breathing hi • Breathing (pulmonary ventilation) consists of two cyclic phases: 氣體交換 • inhalation, inhalation, also called inspiration also called inspiration ‐ draws gases draws gases into the lungs.吸氣 • exhalation, exhalation also called expiration ‐ also called expiration forces gases forces gases out of the lungs.呼氣 呼吸之肌肉變化 吸氣 肋間肌收縮 呼氣 Neural Control of Ventilation • Reticular formation in medulla – Responsible for basic rate and rhythm Responsible for basic rate and rhythm – Can be modified by higher centers • Limbic system and hypothalamus, e.g. gasp with certain emotions • Cerebral cortex – C b l conscious control i l • Chemoreceptors detect the chemistry change of blood pH detect the chemistry change of blood, pH – Central – in the medulla – Peripheral: • Aortic bodies on the aortic arch • Carotid bodies : monitor O2 and CO2 tension in the blood and help regulate respiratory rate and depth regulate respiratory rate and depth The carotid sinus (dilated area near fork) helps regulate blood pressure and can affect the rate (stimulation during carotid massage can slow an and can affect the rate (stimulation during carotid massage can slow an abnormally fast heart rate) 41 Peripheral chemoreceptors regulating respiration • Aortic bodies* – On aorta – Send sensory info to medulla through X (vagus n) + • Carotid bodies+ * – At At fork of common carotid fork of common carotid artery – Send info mainly through IX Send info mainly through IX (glossopharyngeal n) 42