Answers
advertisement

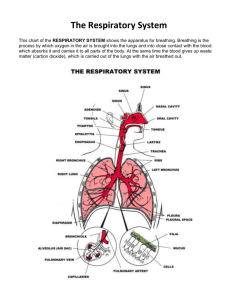
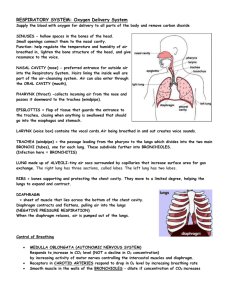
Summary of the Respiratory System Organ Structure Function Air Conducting Nasal Cavity Lined with mucus membranes Contains tiny hairs that act as a filtering system Filters and warms and moistens air Transports air to pharynx Oral Cavity normally moist, and is lined with a mucous membrane Transports air to pharynx; warms and moistens air, helps produce sounds Pharynx muscular tube section between the mouth/nasal cavity and the larynx/esophagus Transports air to larynx Epiglottis Flap like structure that covers the opening of the trachea Covers the opening of the trachea during swallowing Larynx Made up mainly of cartigles. It includes the vocal cords which are responsible for speech Trachea Series of cartilage rings that keep the trachea open Warms and moistens air; transports air to lungs; filters incoming air Bronchi Air ways that contain cartilage rings for structure Warms and moistens air; transports air to lungs; filters incoming air Smaller airways with smooth muscle walls Controls air flow in the lungs; transports air to alveoli Tiny sac and the end of bronchioles measured between 0.1 and 0.2 micro meters Provides area for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide Bronchioles Produces sounds; transport air to tracheal; helps filter incoming air; warms and moistens incoming air Gas exchange Alveoli