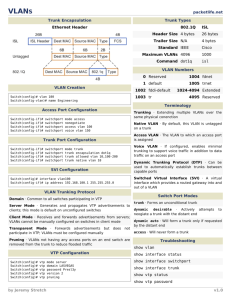
CCNA—Cisco Certified Network Associate
advertisement

CCNA—Cisco Certified Network Associate z Agenda – Dag 14 z z Kap 8 LAB By default z Switches break up collision domains z Routers break up broadcast domain VLAN Basics z Short for virtual LAN, a network of computers that behave as if they are connected to the same wire even though they may actually be physically located on different segments of a LAN. VLANs are configured through software rather than hardware, which makes them extremely flexible. One of the biggest advantages of VLANs is that when a computer is physically moved to another location, it can stay on the same VLAN without any hardware reconfiguration. VLAN Basics VLAN Basics Brodcast to all All users can see all devices by default VLAN Basics z There are several ways that VLANs simplify network management: – – – – – Network adds, moves, and changes are achieved by configuring a port into the appropriate VLAN. A group of users needing high security can be put into a VLAN so that no users outside of the VLAN can communicate with them. As a logical grouping of users by function, VLANs can be considered independent from their physical or geographic locations. VLANs can enhance network security. VLANs increase the number of broadcast domains while decreasing their size. Switching vs Hub z Brodcast Control: – Broadcasts occur in every protocol, but how often they occur depends upon three things: z z z Type of protocol The application(s) running on the internetwork How these services are used Switching vs Hub z EX. – – – – Bandwidth abusers are multimedia applications that use broadcasts and multicasts extensively. Faulty equipment. Inadequate segmentation, and Poorly designed firewalls only serve to compound the problems that these broadcast-intensive applications create. Switching vs Hub z z All devices in a VLAN are members of the same broadcast domain and receive all broadcasts. The broadcasts, by default, are filtered from all ports on a switch that are not members of the same VLAN. This is great because it offers all the benefits you gain with a switched design without the serious anguish you would experience if all your users were in the same broadcast domain! Security z z A flat internetwork's (connecting hubs and switches together with routers). Router’s jobb to maintain security. To bad!!!!!!!! – Anyone connecting to the physical network could access the network resources located on that physical LAN. Security z To bad!!!!!!!! – – All anyone had to do to observe any and all traffic happening in that network was to simply plug a network analyzer into the hub. users could join a workgroup by just plugging their workstations into the existing hub. Switching vs Hub z This is why VLANs are so cool. By building them and creating multiple broadcast groups, administrators can now have control over each port and user! Flexibility and Scalability z z z VLANs creating smaller broadcast domains at layer 2. Add only the users you want into that broadcast domain regardless of their physical location. When a VLAN gets too big, you can create more VLANs to keep the broadcasts from consuming too much bandwidth. Switching vs Hub VLAN Memberships z VLAN 1? – That VLAN is an administrative VLAN, and even though it can be used for a workgroup, Cisco recommends that you use this for administrative purposes only. You can't delete or change the name of VLAN 1, and by default, all ports on a switch are members of VLAN 1 until you change them. VLAN Memberships z Static VLANs – Created by an administrator, who then assigns switch ports to each VLAN. VLAN Memberships z z z Dynamic VLANs Are created through the use of software packages such as CiscoWorks 2000. With a VLAN Management policy Server (VMPS), you can assing switch ports to VLANs dynamically based on the source MAC address of the device that is conected to the port VLAN Memberships • Dynamic VLANs Identifying VLANs z As frames are switched throughout the network, switches must be able to keep track of all the different types, plus understand what to do with them depending on the hardware address. And remember, frames are handled differently according to the type of link they are traversing. Identifying VLANs z There are two different types of links in a switched environment: – – Access links Trunk links Access links z This type of link is only part of one VLAN, and it's referred to as the native VLAN of the port. Any device attached to an access link is unaware of a VLAN membership—the device just assumes it's part of a broadcast domain, but it has no understanding of the physical network. Access links z Switches remove any VLAN information from the frame before it's sent to an access-link device. Access-link devices cannot communicate with devices outside their VLAN unless the packet is routed. Trunk link z A trunk link is a 100- or 1000Mbps point-topoint link between two switches, between a switch and router, or between a switch and server. These carry the traffic of multiple VLANs—from 1 to 1005 at a time. Trunk link z z Trunking allows you to make a single port part of multiple VLANs at the same time. Another benefit to trunking is when you're connecting switches. Trunk links can carry some or all VLAN information across the link, but if the links between your switches aren't trunked, only VLAN 1 information will be switched across the link by default. Frame Tagging how it works z Each switch that the frame reaches must first identify the VLAN ID from the frame tag, then it finds out what to do with the frame by looking at the information in the filter table. If the frame reaches a switch that has another trunked link, the frame will be forwarded out the trunk-link port. Frame Tagging z Once the frame reaches an exit to an access link matching the frame's VLAN ID, the switch removes the VLAN identifier. This is so the destination device can receive the frames without having to understand their VLAN identification. VLAN Identification Methods z It's how switches identify which frames belong to which VLANs – – – Inter-Switch Link (ISL)* IEEE 802.1Q Inter-Switch Link (ISL) Protocol* VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) z The basic goals of VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) are to manage all configured VLANs across a switched internetwork and to maintain consistency throughout that network. VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) z VTP allows an administrator to add, delete, and rename VLANs—information that is then propagated to all other switches in the VTP domain. VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) z Benefits VTP has to offer: – – Consistent VLAN configuration across all switches in the network VLAN trunking over mixed networks, such as Ethernet to ATM LANE or even FDDI VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) z Benefits VTP has to offer: – – – Accurate tracking and monitoring of VLANs Dynamic reporting of added VLANs to all switches in the VTP domain. Plug-and-Play VLAN adding VTP Modes of Operation VTP Modes of Operation z Server – This is the default for all Catalyst switches. You need at least one server in your VTP domain to propagate VLAN information throughout the domain. VTP Modes of Operation z Server – – The switch must be in server mode to be able to create, add, or delete VLANs in a VTP domain. Changing VTP information must also be done in server mode, and any change made to a switch in server mode will be advertised to the entire VTP domain. VTP Modes of Operation z client – – In client mode, switches receive information from VTP servers, and they also send and receive updates. But they can't make any changes. Plus, none of the ports on a client switch can be added to a new VLAN before the VTP server notifies the client switch of the new VLAN VTP Modes of Operation z Transparent – – Switches in transparent mode don't participate in the VTP domain, but they'll still forward VTP advertisements through any configured trunk links. These switches can't add and delete VLANs because they keep their own database—one they do not share with other switches. VTP Pruning z VTP provides a way for you to preserve bandwidth by configuring it to reduce the amount of broadcasts, multicasts, and unicast packets. This is called pruning. VTP pruning only sends broadcasts to trunk links that truly must have the information.