Comparative Advantage
advertisement

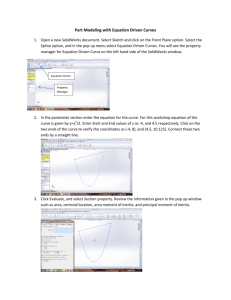
AGEC 652 – Lecture 6 COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE - OFFER CURVES A difference in relative autarky commodity prices between two countries is a reflection of their comparative advantage and forms the basis for mutually beneficial trade. Offer curves are a more rigorous, theoretical yet intuitive method of determining the equilibrium relative commodity price with trade Definition: the locus of supplies available for export of one commodity and quantities desired for import of another commodity at various relative price levels for the two commodities. Alternatively: the offer curve shows how much of one commodity a nation desires to import to be willing to export various amounts of another commodity in return. NATION A – OFFER CURVE Y Y P2 y4-y0 E y4 H y3 y2 P0 A y1 E’ P1 F G y0 B C P1 H’ y3-y1 P0 P2 C’ G’ 0 X3 X0 X1 X2 X4 X 0 X4-X2 X3-X1 Price ESX EDy Pt. on O.C. P0 0 0 0 P1 F – G = (X3-X1) H – G = (y3-y1) H’ P2 B – C = (X4-X2) E – C = (y4-y0) E’ X NATION B – OFFER CURVE Y P’1 P’2 Y P’0 D F’ D-L J’ I-K I F L B U2 J K B B U1 X 0 F-L J-K Price ESy EDX Pt. on O.C. P’0 0 0 0 P’1 I-K J-K J’ P’2 D-L F-L F’ X WORLD PRICE AND TRADE EQUILIBRIUM P’1 P’0 A Y F’ L’ E’ K’ p2 = p’2 B J’ p1 H’ p0 G’ C’ 0 X 1. Equilibrium Price at P’2 = P2 2. World Trade Nation A exports 0C’ of X to Nation B Nation B exports 0L’ of Y to Nation A 3. Why are offer curves bowed outward? EXCESS SUPPLY AND DEMAND CURVES P (=P /P ) P’0 x y Nation A Nation B Nation A Nation B ES AX EDBX ES AX EDBX 100 150 P’1 P2=P’2 P1 P0 P’0 World Market for Good X P’1 P2 = P’2 P1 P0 50 200 250 Qx FORMAL GEOMETRIC DERIVATION OF OFFER CURVE – Nation A Y W B Z A C Y0 XC0 Commodity X A’ Consumption Production C Trade (=Prod-Cons) X X C 0 X0 0 Y Y C 0 Y C 0 0 FORMAL GEOMETRIC DERIVATION OF OFFER CURVE (cont’d) Y W B Z A C Y1 ● Y 1t Commodity X C1 A’ Consumption Production t t B’ (X 1 ,Y 1 ) X 1t t X X C 1 X Y Y C 1 Y 1 - Y1 X Trade (=Prod-Cons) t C 1 + X1 X1 C t - Y 1t FORMAL GEOMETRIC DERIVATION OF OFFER CURVE (cont’d) TI0 W Y B Z W’ A B’ A’ X Z’ 1. A whole family of Trade Indifference curves can be derived for each country 2. Note: The slope of the TI curves are equal to those of the U curves at corresponding points FORMAL GEOMETRIC DERIVATION OF OFFER CURVE (cont’d) Y P6 Nation A Offer Curve P5 P4 P3 P2 TI6 TI5 P1 TI4 TI3 TI2 TI1 P0 0 X TWO COUNTRY GENERAL EQUILIBRIUM TRADE MODEL Nations A and B Y A U0 PA PA = PB Nation A OCA OCB PB 0 X Nation B U B 0