Igneous Rocks WS
advertisement

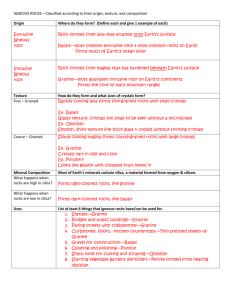
Name Date _ Class lgneous Rocks Guide for Reading I What characteristlcs are usedto classity igneous rocks? 132. F rock is anv rock that forms from magmaor lava.The name f Bneous I "igneous"comesfrom the Latin word ignis,tneaning"fire." Most igneousrocksare madeof mineralcrystals.The only exceptionsto this rule are the different types of volcanic glass-igneous rock that lacksa crystal structure. Igneous rocks are classified according to their origin, texture, and mineral composition. GeologistsclassiS'igneousrocks accordingto where they formed. Extrusive rock is igneous rock formed from lava that erupted onto Earth'ssurface.Basaltis the most common extrusiverock. Igneousrock that formed when magma hardenedbeneathEarth'ssurfaceis called intrusive rock. Graniteis the most abundantintrusiverock. The textureof an igneousrock dependson the sizeand shapeof its mineral crystals.Igneousrocks may be similar in mineral composition and yet havevery differenttextures.The texturemay be fine-grained, coarse-grained, porphyritic, or glassy.Rapid cooling lava forms finegrainedigneousrocks with small crystals.Slow cooling magma forms coarse-grainedrock with large crystals.Intrusive rocks have larger crystalsthan extrusiverocks.Some intrusiverocks have large crystals scatteredon a background of much smaller crystals,creating a porphyritic texture. Porphyritic rocks fbrm when magma cools in two stages, at first slowlyand then more rapidlyasthe magmamovesnearer to the surface.Extrusiverocks have a fine-grainedor glassytexture. Basalt,for example,is an extrusiverock whosecrystalsaretoo smallto be seenwithout a microscope. Lavathat is low in silicausuallyforms dark-coloredrocks,suchasbasalt. Magmathat is high in silicausuallyformslight coloredrock,suchasgranite. Granite,however,comesin manyshadesand colors,from dark to light gray, red,and pink. Its colorchanges alongwith its mineralcomposition.Granite that is rich in reddishfeldsparis speckledpink. Granite that is rich in hornblendeand dark micais a light graywith dark specks. Many igneousrocksare hard, dense,and durable.As a result,people havelong usedigneousrock for tools and building materials.Granite, one of the most abundantigneousrocks,hasa long historyasa building material.For example,ancientEgyptiansusedgranitefor statues.In the United Statesin the late 1800sand early 1900s,granitewaswidely used to build bridgesand public buildings.Igneousrocks such as basalt, pumice,and obsidianalsohaveimportant uses. TeachingResources InsideEarth o ! o = =. o T "g 5 Name Class lgneous Rocks o Understanding Main ldeas Fill in the lilanksin the tablebelow. Origin of lgneous Rock Resulting Texture Slowcoolingof magmafar beneath Earth'ssurface l. Magmacoolingin two stages, first slowlyand then quickly 2. Extremelyrapid coolingof lavain which no crystalsform 3. Rapidcoolingof lavain which tiny crystalsform 4, Answerthefollowingquesfiotts on a seporate sheetof paper. 5. Explainhow the silicacontentof molten materialaffectsthe color of ieneous rocks. 6. What qualitiesof igneousrockshavelong madethem usefulfor toolsand building materials? 7. Describeone useeachfor the igneousrocksgranite,basalt,and pumice. a Building Vocabulary Fill in tlrc blank to cornplete eachstatement. (d I q) 8. lgneousrock formedfrom lavaon Earth'ssurfaceis called E c O rock. L I 9. A rock with largecrystalsscattered on a backgroundof much smallercrystals hasa(n) texture. 10.Igneousrock formed from magmabelowEarth'ssurfaceis called rock. InsideEarth Teaching ResourcesF. 133