Computer Program Programming language Programming
advertisement
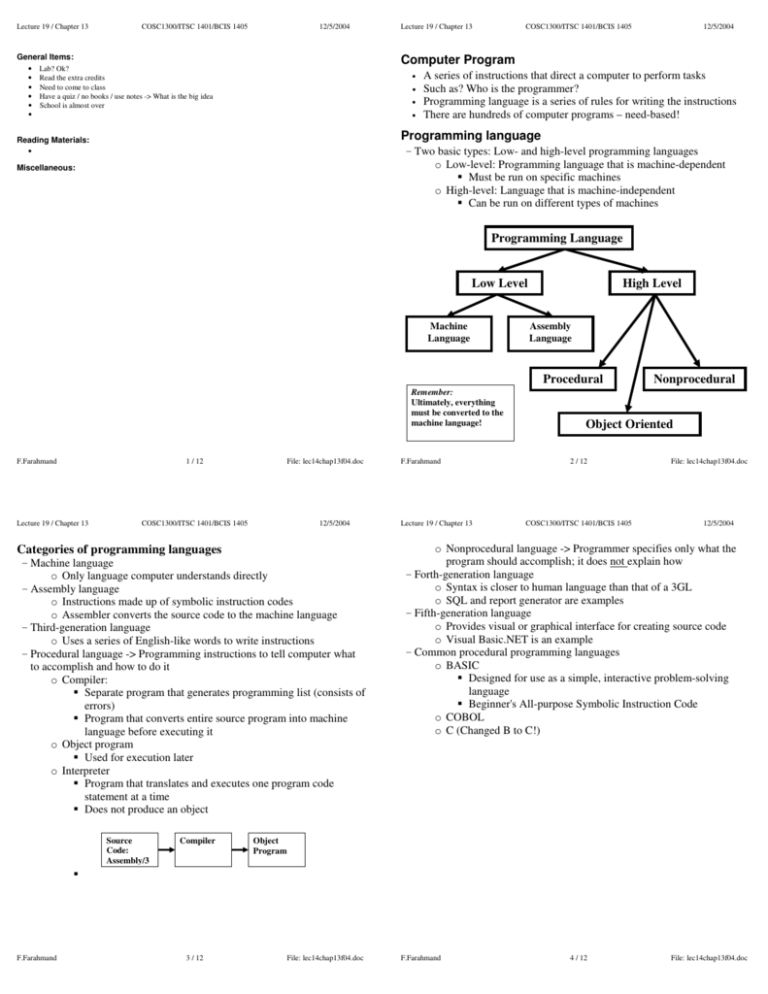
Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 12/5/2004 General Items: • • • • • • Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 12/5/2004 Computer Program Lab? Ok? Read the extra credits Need to come to class Have a quiz / no books / use notes -> What is the big idea School is almost over • • • • A series of instructions that direct a computer to perform tasks Such as? Who is the programmer? Programming language is a series of rules for writing the instructions There are hundreds of computer programs – need-based! Programming language Reading Materials: - Two basic types: Low- and high-level programming languages o Low-level: Programming language that is machine-dependent Must be run on specific machines o High-level: Language that is machine-independent Can be run on different types of machines • Miscellaneous: Programming Language Low Level Machine Language Remember: Ultimately, everything must be converted to the machine language! F.Farahmand Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 1 / 12 File: lec14chap13f04.doc COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 12/5/2004 Categories of programming languages - Machine language o Only language computer understands directly - Assembly language o Instructions made up of symbolic instruction codes o Assembler converts the source code to the machine language - Third-generation language o Uses a series of English-like words to write instructions - Procedural language -> Programming instructions to tell computer what to accomplish and how to do it o Compiler: Separate program that generates programming list (consists of errors) Program that converts entire source program into machine language before executing it o Object program Used for execution later o Interpreter Program that translates and executes one program code statement at a time Does not produce an object Source Code: Assembly/3 F.Farahmand Compiler 3 / 12 F.Farahmand Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 High Level Assembly Language Procedural Nonprocedural Object Oriented 2 / 12 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 File: lec14chap13f04.doc 12/5/2004 o Nonprocedural language -> Programmer specifies only what the program should accomplish; it does not explain how - Forth-generation language o Syntax is closer to human language than that of a 3GL o SQL and report generator are examples - Fifth-generation language o Provides visual or graphical interface for creating source code o Visual Basic.NET is an example - Common procedural programming languages o BASIC Designed for use as a simple, interactive problem-solving language Beginner's All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code o COBOL o C (Changed B to C!) Object Program File: lec14chap13f04.doc F.Farahmand 4 / 12 File: lec14chap13f04.doc Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 12/5/2004 Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 12/5/2004 Object-oriented (OO) approach o The structured programming does not explain how to keep the data and program together o Eliminates redundant programming o No more spaghetti code o Programmer can package data and program (or procedure) into a single unit, called an object (uses the OO approach) o OOP is event-driven o Checks for and responds to set of events o C++ is a complete object-oriented language OO Programming languages Hundreds of programming languages exist – They are different in flexibility, user interface, and functionality o C++ : Classes and events o Java and Java applets: Small Java program that runs inside another program such as a Web browser o Visual Programming Language Windows-based application that assists programmers in developing event-driven Windows-based applications Fifth – generation language • Allows drop and drag of objects • Easy to use Examples: • Visual Basic • Visual Studio/Visual C++/Visual C# .NET o Run over the Internet o Easier programming development o Suitable for large/small – scale applications F.Farahmand Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 5 / 12 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 File: lec14chap13f04.doc 12/5/2004 Web page program development tools o Tools used to create web pages o Adding special effects and forms to a Web page Examples: Cookies, Shopping cards, Games, and many other multimedia effects Script: Interpreted program that runs on client Applet: Also usually runs on client, but is compiled – runs faster than script Servlet: Applet that runs on server ActiveX control: Small program that runs on client o HTML Hypertext Markup Language – set of special codes used to create web pageNot a programming language – Page formatting language Uses tags an must be kept as an ASCII file o Dynamic HTML: Allows you to include more graphics and interactivity on Web page (pointing to a text changes the shape) Animations, Interactions, Scroll bar, pop-up windows o XML: eXtensible Markup Language Allows Web page developers to create tags that describe data passed to a client so client, rather than server, can process data – different platforms can display the same XML o XHTML: eXtensible HTML Includes features of HTML and XML o WML Wireless Markup Language Allows Web page developers to design pages specifically for micro-browsers Uses the wireless application protocol (WAP) o Web page authoring: Dreamweaver MX, FrontPage, Flash F.Farahmand 7 / 12 File: lec14chap13f04.doc F.Farahmand Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 6 / 12 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 File: lec14chap13f04.doc 12/5/2004 o Common Gateway Interface Program (CGI) Used for sending and receiving information over the web Basic Idea: • Resides in the server • When a search is requested the it is sent to the CGI program • The CGI contacts the database and requests the information • The CGI receives the information from the database and shows it in HTML format and it is sent to the web browser F.Farahmand 8 / 12 File: lec14chap13f04.doc Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 12/5/2004 System development life cycle 9 / 12 Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 o o o o F.Farahmand COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 File: lec14chap13f04.doc 12/5/2004 • Flowchart (Graphically shows logic in a solution algorithm) • Pseudocode (Uses condensed form of English to convey program logic) Code programs Translating solution algorithm into a programming language Entering programming language code into the computer Test programs Goal is to ensure program runs correctly and is error free Three types of errors • Syntax • Logic • Run time Debugging: Process of locating and correcting syntax and logic errors in program Formalize solution Programmer performs two activities • Reviews program code • Reviews documentation Maintain program Identify errors Identify enhancements Involves modifying existing programs to improve their functionality 11 / 12 COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 12/5/2004 Program development life cycle - A system is a set of components that interact to achieve a common goal - System development life cycle generally has 5 phases: o Planning o Analysis o Design o Implementation o Support F.Farahmand Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 File: lec14chap13f04.doc - A computer program is a set of instructions that directs computer to perform tasks - A programming language is a set of words, symbols, and codes that enables a programmer to communicate instructions to a computer - PDLC is a steps followed to build computer programs o Analyze problem Review program specifications package Meet with systems analyst and users Identify each program’s input, output, and processing components o Design problems Grouping program activities to modules (top-down design) Providing a solution algorithm for each phase and testing it (structured design) Top-down design: Focuses on what program should do Structured design: Focuses on how to build program based on requirements (Creating a hierarchical chart) • Uses a technique that builds all program logic by combining three control structures: o Sequence control structure (Input, Process, Output) o Section control structure (if-then-else) o Repetition control structure (do-while) Writing proper programs: • No-dead codes • No infinite loops • One entry point • One exist point (no spaghetti code – not structured) Using design tools (graphical or written description of each module) F.Farahmand Lecture 19 / Chapter 13 10 / 12 File: lec14chap13f04.doc COSC1300/ITSC 1401/BCIS 1405 12/5/2004 QUIZ What is a computer program? Why do we use Object-oriented programming language? Name 3 programming languages. Name 2 web page development techniques. What is HTML? F.Farahmand 12 / 12 File: lec14chap13f04.doc