9.4 The Byzantine Empire
advertisement

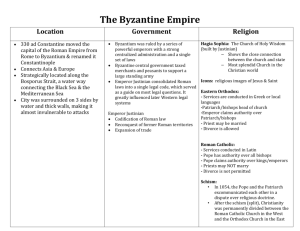
9.4 The Byzantine Empire Crossroads of Trade Heir to Rome Justinian • Corpus of Civil Law – “Justinian’s Code” • Commission appointed by Justinian • Preserved legal heritage Rome • Basis for European systems to come • Art & architecture achieve distinctive character Contribution to Western Civilization • early Middle Ages = a protective barrier between western Europe and hostile Persian, Arab, and Turkish armies. • major conduit of classical learning and science into the West down to the Renaissance. • cities of the Byzantine Empire provided them a model of a civilized society. Foundations: “Νέα Ῥώμη” • 330 Byzantium Constantinople • Peninsula • Europe & Asia meet • Control trade routes • Natural defense (Nea Romē) Constantinople Rebuilt after riots 532 Largest city Europe most of Middle Ages Architectural achievements Hagia Sophia Greatest commercial center til 12th cen Chinese Silk! Preserving Greco-Roman Culture Three “heirs” to Rome 1.Islamic Empires 2.Germanic Kingdoms 3.Byzantines (“Nea Roma”) Justinian’s Code Greek language Intact in east what was largely lost in west Not rediscovered until Crusades, 12th century Justinian • Ruler @ apex • Becomes emperor 527 • Wife = Theodora – Improve social standing women • Beat back Persian invaders Justinian • Justinian ordered collation and revision of Roman law. • Corpus Juris Civilis – “body of civil law” – little effect on medieval common law. – Renaissance foundation for most European law down to 19th century. Justinian • Wants to restore Roman Empire • The re-conquest = too expensive • Generation after Justinian’s death = lost all gains – Persians! The Byzantine empire in 565, at its largest expansion ever. Justinian’s legacy • Hagia Sophia remained seat of Eastern Christianity until Fall of Constantinople. • Corpus Iuris Civilis • 529 closed philosophical school of Athens, thus destroying last stronghold of paganism The Byzantine Empire 4min blended Greek, Roman, Persian and Middle Eastern styles. Church of Hagia Sophia whose name means “Holy Wisdom” Byzantine Religion • Byzantine emperors claimed to be God’s rep. on earth • Oath to defend Christian faith • 700s: icons an issue – Iconoclasts • 843 Eastern Church allows icons, but not statues in worship Independent Thinking Ideas thought to be heresies by the Roman Catholic Church received imperial support: – Arianism denied that Father and Son were equal and coeternal. – Monophysitism taught that Jesus had only one nature, a composite divine-human one. – Iconoclasm forbid the use of images (icons) because it led to idolatry. The Iconoclastic Controversy • Iconoclastic Controversy – movement that denied the holiness of religious images, – devastated much of empire for over a hundred years. • During the eighth and early ninth centuries use of such images was prohibited – icons were restored by 843. Byzantine Religion • Disagreements bt. East & West • Serious one: source of religious authority pope or patriarchs? • 1054 = schism with Roman Catholic Church The Great Schism • 1054 • First big split in Christian church since “orthodoxy” of Pauline Christianity established 4th century • Nicene creed – First ecumenical council, 325 – Similar to “Apostle’s Creed” – List of what Christian believes • Created “Roman Catholic” Church in the west and “Eastern Orthodox” in the east • The split still stands to this day Great Schism, 1054 Roman Catholic EASTERN ORTHODOX • • • • • • 5 patriarchs • No filioque • Married priesthood (but celibate bishops) • Leavened bread in Eucharist • Greek • Icons Pope “Filioque” “and the son” Celibate priesthood Unleavened bread in Eucharist • Latin • Iconoclast Byzantine Greek replaces Latin Eastern Orthodox Church Emperor = absolute, by divine right, church and state Believed God appointed them to defend true Christianity “Patriarchs” Byzantine Art & Learning • Forms adopted Eastern Europe • Religious subjects – Icons – Decorations • Scholars copy Greek and Roman docs • Monasteries serve important social functions • Missionaries go to neighbors Byzantine Art & Learning • Cyril & Methodius – Missionaries to the Slavs – Devised Cyrillic alphabet for Slavic languages (Russian) Byzantine artists … Mosaics often displayed religious themes. Decline and Fall • Justinian dies 565 • Invaders constant for centuries • Plague 700s • By 700 shrunk to just Greek areas • 1204 Crusaders loot the city! • 1453 Ottoman Turks seige and finally defeat Constantinople The Mediterranean Sea complex