The Power of Thinking Big or Small.RTF
advertisement

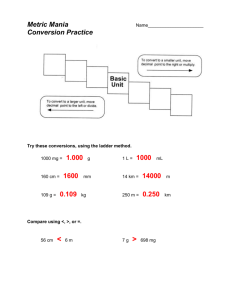
The Power of Thinking Big, … or Small Objectives • Students know their own measurement system (English and metric). • Students have a solid point of reference of their own size, use various methods to help determine the size of macro and micro systems and how big or small they actually are. Suggested Grade Level 9 Subject Area Math Physical Science Timeline Two 55-minute periods Background Students need to know the English system of measurement as well as the metric scale. Materials Meter stick Tape measure Computer and internet access Worksheets on metric and English measurement conversions Lesson First, present a review on the English system of measurement in comparison to the metric system to make students comfortable with their own measurement system. Present the metric system. Do a worksheet to convert measurements in the metric system from one unit to another. Metric System Km Hm Dm m,l,g dm cm mm µm nm .001 .01 .1 1 10 100 1000 1,000,000 1x10¯ ³ 1x10¯ ² 1x10¯ ¹ 1x10º 1x10¹ 1x10² 1x10³ 1,000,000,00 0 1x109 1x106 View the Powers of 10 video on the internet which shows a simulation on size comparisons. Find the distances of the planets from the sun in kilometers. Make a chart like the one below to record the information. Once the distances are recorded, convert these distances to meters, yards and miles. Planet/star or Distance Distance from Distance Distance from Scale model atom from the Sun the Sun (m) from the Sun the Sun distance (yds) (km) (yards) (miles) Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto Oort Cloud Alpha Centauri A Hydrogen atom Now make a scale to allow the planets to fit into one length of a football field. In this system, the sun is at one end of the football field and the edge of the solar system (the Oort Cloud) is at the other end. Find this distance. Find the distance in the scale model of each planet from the Sun and record. Hint: you must know the length in yards of a football field. Also, make a proportion comparing real distances to scale in order to find scale model distances. Use this measurement to place the planet on the football field. Research the distance to the nearest star. How many football fields would you need to place alpha Centauri in the solar system model using the created model? Research the size of an atom. Include the diameter of the hydrogen atom and the size of its nucleus. How would this be placed on the same solar system model? Calculate distance in nanometers and meters. Extensions Make up your own scale of measurement. Calculate the distance to each planet from Earth. Calculate the distance to each planet from Earth using light years and parsecs. Evaluation •Students will know how to convert from English to metric units as well as metric to metric units. •Students know their own measurement system (English and metric). •Students have a solid point of reference of their own size, use various methods to help determine the size of macro and micro systems and how big or small they actually are. Resources Space Foundation Biological, Physical Science notes and handouts. Algebra: Explorations and Applications by McDougal Littell. Powers of 10 website. Worksheets on conversions of units. Algebra: Explorations and Applications, Evanston, Illinois, McDougal Littell, 1998, 0-395-86297-3. http://www.powersof10.com Addendum Metric Mania Name_________________________ English or Metric? Use the chart and a calculator to convert each measurement. Be sure to show your work. Round answers to the nearest hundredth if needed. To go Multiply To go Multiply To go Multiply from To by from To by from To by ml -> fl oz 0.0338 cm -> in 0.3937 g -> oz 0.0353 fl oz -> ml 29.575 in -> cm 2.54 oz -> g 28.35 l -> gal 0.2642 m -> ft 3.2808 kg -> lbs 2.2046 gal -> l 3.785 ft -> m 0.3048 lbs -> kg 0.4536 km -> mi 0.6214 mi -> km 1.609 1) 16 in = _______ cm 2) 345 lbs = _______ kg 3) 56 g = _______ oz 4) 450 km = _______ mi 5) 1200 ml = _______ fl oz 6) 40 m = _______ ft 7) 4 gal = _______ l 8) 12 fl oz = _______ ml 9) 50 kg = _______ lbs 10) Penny has a pencil that is 19 cm long. How long the pencil in inches? 11) Macho Mel can lift 200 kilograms with ease. How much is this in pounds? 12) The distance between Happyville and Giggleland is 60 miles. How far is this in kilometers? 13) A can of Cheap-O soda holds 355 ml of soda. How many milliliters would be in 2 cans of soda? 14) A cookie recipe calls for 1 pound of butter. How many grams of butter would be needed for 3 batches? T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/ English or Metric Worksheet - ANSWER KEY 1. 40.64 cm 2. 156.49 kg 3. 1.98 oz 4. 279.63 mi 5. 40.56 fl oz 6. 131.23 ft 7. 15.14 l 8. 354.9 ml 9. 110.23 lbs 10. 7.48 in (19 x .3937) 11. 440.92 lbs (200 x 2.2046) 12. 96.54 km (60 x 1.609) 13. 710 ml (355 x 2) 14. 1360.8 g (1 lb -> 16 oz x 28.35 x 3) T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/ Name_________________________ Metric Mania Conversion Practice To convert to a smaller unit, move decimal point to the right or multiply. Basic Unit To convert to a larger unit, move decimal point to the left or divide. Try these conversions, using the ladder method. 1000 mg = _______ g 1 L = _______ mL 160 cm = _______ mm 14 km = _______ m 109 g = _______ kg 250 m = _______ km Compare using <, >, or =. 56 cm 6m7g 698 mg T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/ Metric Mania Conversion Practice To convert to a smaller unit, move decimal point to the right or multiply. Basic Unit To convert to a larger unit, move decimal point to the left or divide. Kilo 1000 units Hecto 100 units Deka 10 units Deci 0.1 units Centi 0.01 units Milli - 0.001 units Overhead Copy Try these conversions, using the ladder method. 1000 mg = _______ g 1 L = _______ mL 160 cm = _______ mm 14 km = _______ m 109 g = _______ kg 250 m = _______ km Compare using <, >, or =. 56 cm 6m7g 698 mg T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/ Metric Mania Name_________________________ Conversion Challenge Write the correct abbreviation for each metric unit. 1) Kilogram _____ 4) Milliliter 7) Kilometer 2) Meter 5) Millimeter 8) Centimeter 3) Gram 6) Liter 9) Milligram Try these conversions, using the ladder method. 1) 2000 mg = _______ g 6) 5 L = _______ mL 11) 16 cm = _______ mm 2) 104 km = _______ m 7) 198 g = _______ kg 12) 2500 m = _______ km 3) 480 cm = _____ m 8) 75 mL = _____ L 13) 65 g = _____ mg 4) 5.6 kg = _____ g 9) 50 cm = _____ m 14) 6.3 cm = _____ mm 5) 8 mm = _____ cm 10) 5.6 m = _____ cm 15) 120 mg = _____ g Compare using <, >, or =. 16) 63 cm 6 m 17) 5 g 508 mg 18) 1,500 mL 1.5 L 19) 536 cm 53.6 dm 20) 43 mg 5 g 21) 3.6 m 36 cm T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/ Metric Mania Answer Keys Conversion Practice NOTE: See overhead copy for the stairstep boxes. 1000 mg = 1 g 160 cm = 1600 mm 109 g = 0.109 kg 1 l = 1000 ml 14 km = 14000 m 250 m = .250 km 56 cm < 6 m 7 g > 698 mg Conversion Challenge 1. kg 2. m 3. g 4. ml 5. mm 6. l 7. km 8. cm 9. mg 1. 2 g 2. 104000 m 3. 4.8 m 4. 5600 g 5. .8 cm 6. 5000 ml 7. 0.198 kg 8. 0.075 l 9. 0.5 m 10. 560 cm 11. 160 mm 12. 2.5 km 13. 65000 mg 14. 63 mm 15. 0.12 g 16. < 17. > 18. = 19. = 20. < 21. > T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/