Blood PowerPoint - Duluth High School
advertisement

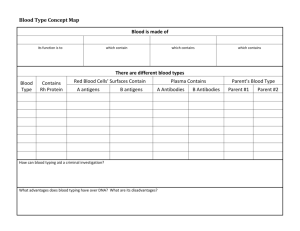
Forensic Serology What is Blood? Blood is a highly complex mixture of cells enzymes proteins inorganic substances. What is Blood? Fluid portion of blood is called plasma. Plasma is composed mainly of water and electrolytes nutrients vitamins hormones clotting factors proteins such as antibodies to fight infection. Accounts for 55% of blood content. What is Blood? Suspended in the plasma are solid materials, chiefly: Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets The solid portion of blood accounts for 45% of its content. What is Blood? Red Blood Cells (RBC) - Erythrocytes The most abundant cells in our blood; They are produced in the bone marrow They contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen to our cells. Red Blood Cell Journey What is Blood? White Blood Cells (WBC) - Leukocytes They are part of the immune system They destroy infectious agents called pathogens. Short video of a white blood cell chasing bacteria (no sound) What is Blood? PLATELETS (Thrombocytes) – The clotting factors that are carried in the plasma; They clot together in a process called coagulation to seal a wound and prevent a loss of blood. Serum The liquid that separates from the blood when a clot is formed. (pale yellowish color) What is Blood? Review Antigens Blood Typing Are usually a protein that stimulates the body to produce antibodies against it. Have nothing to do with oxygen transport Antigens with common traits are grouped into systems. Antigens Blood Typing 15 different systems have been identified. Most important system is A-B-O Blood Typing There are 3 alleles or genes for blood type: A, B, & O. Since we have 2 genes, there are 6 possible combinations. Blood Typing Notice Type A blood only contains B antibodies (or Anti-B) in the plasma. When Type A blood encounters A antibodies, agglutination will occur. Agglutination = clumping Type AB contains neither antibody and Type O contains both. Blood Typing The third antigen observed in the A-B-O system is the Rh antigen. Also known as: Rh Factor D antigen The presence of the Rh antigen found on a red blood cell would mean that the blood is Rh +. Blood Typing Population distribution of blood type varies with location and race throughout the world. According to your text: O = 43% A = 42 % B = 12% AB = 3% Which is the most common? Blood Typing - continued Serum is the part of the plasma that contains the antibodies. The Fundamental Principle of Blood Typing: For every antigen there is a specific antibody that will react with it to form clumps known as agglutination. Thus, if serum containing anti-B is added to red blood cells carrying B antigen, they will immediately react – meaning clumps will form. (Thus the blood will be Type B) Blood Typing - Continued Blood Transfusions - is a procedure in which blood is given to a patient through an intravenous (IV) line in one of the blood vessels. What could happen if a person receives blood that is incompatible? Agglutination or clumping = death Type O = universal donors Type AB = universal receivers Rh + Can receive + or - Rh - Can only receive - Blood Typing Game http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/landstei ner/index.html Actual Blood Typing Demo