Thorax

Axial Skeleton 3
Thorax
Objectives
1. Identify the bones of the thorax
2. List the functions of the thorax
3. Identify the three regions of the sternum
4. Discuss the articulation of the sternum and ribs
5. Differentiate between the types of ribs
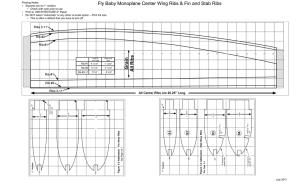
THORAX (Chest Region)
• Bony cage formed by the sternum, costal cartilage, ribs
& body of thoracic vertebrae
• Cone shaped ; superior end is narrow while inferior end is broad ; cage flattens toward the back
• Functions:
– Encloses & protects organs of thoracic cavity
– Supports bones of shoulder girdle & upper extremities
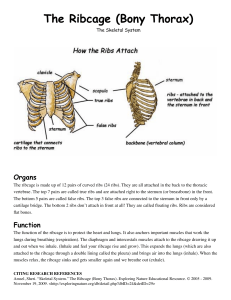
STERNUM
(hyaline cartilage until age 40)
1. Manubrium – triangular, superior portion
2. Body – intermediate, largest portion
3. Xiphoid Process – inferior, smallest portion
FEATURES OF MANUBRIUM
• Jugular or suprasternal notch – depression on superior surface
• Clavicular notch – lateral to jugular notch
& articulates with clavicle
ARTICULATION WITH RIBS
• Ribs 1 & 2 articulate with manubrium
• Ribs 3 – 10 articulate with the body of the sternum
• No ribs articulate with xiphoid processes
1
RIBS
• 12 pairs
• Increase in length from 1 – 7
• Decrease in length from 8 - 12
2. False ribs
– Ribs 8 – 12
– Vertebrochondrol – ribs 8, 9, 10 ; attached to each other & then to rib
7
– Indirect attachment
– Floating ribs – ribs
11 & 12; only attached posteriorly to the vertebrae
TYPES OF RIBS
1. True or vertebrosternal ribs
– ribs 1 – 7
– directly attached to sternum by strips of hyaline cartilage called costal cartilage
Between the Ribs
• Intercostal space – between ribs; filled with intercostal muscle which aids in expansion & contraction of rib cage when breathing http://mywebpages.comcast.net/wnor/respiratorymovements.htm
2