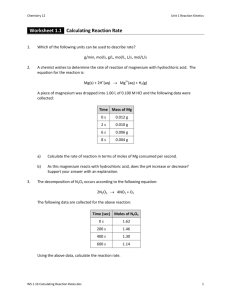
1. Prepare 500 mL of 0.5 M NaCl, MW (NaCl) = g/mol. (14.6 g of
advertisement

1. Prepare 500 mL of 0.5 M NaCl, MW (NaCl) = g/mol. (14.6 g of NaCl, add water to 500 mL) 2. Prepare 250 mL of 0.1 M HCl from stock 1 M HCl. (25 mL of 1M HCl, add water to 250 mL) 3. So that a 24-hour urine creatinine concentration could be assayed, the specimen had to be diluted 1:5 before measurement. Calculate the 24-hour excretion if the 24-hour urine volume is 1800 mL and the measuredcreatinine concentration is 260 mg/L. (2340 mg/24 hr) 4. Calculate the concentrations: a) 10 mM NaOH, which is diluted 1:20 (0.5 M) b) 2M HCl, which is diluted 1:5 (0.4 M) c) 1000 mg/L glucose, diluted 1:10 and than 1:2 (50 mg/l) 5. Calculate the amount of urea (mg/L and mmol/L) if a patient´s urea nitrogen level is 800 mg/L. The formula for urea is NH2CONH2 , and its molecular weight is 60 g/mol. Atomic mass (N) = 14. Normal level of urea in serum is 2 -8 mmol/L. (1712 mg/L = 28.5 mmol/L) 6. Concentrated HCl has a specific gravity of 1.25 g/mL and is assayed as being 38% HCl. a) What is the amount of HCl per milliliter (g/mL)? (0.475 g of HCl per mL) b) How many milliliters are needed to prepare 1 liter of 0.1 M HCl solution if the molecular weight of HCl is 36.5 g/mol? (7,68 mL) 7. How many grams of MgCl2 are there in 1 g of MgCl2 . 3 H2O? (0.637 g) 8. How much CuSO4 . 5 H2O must be weighted to prepare 1 liter of solution containing 80 mg of CuSO4? (125 mg) 9. If 24.5 g H2SO4 (MW = 98 g/mol) are dissolved in a 1 liter solution, what is its a) molarity, normality? (0,25 M, 0,5 N) 10. MW of CaCO3 is 100 g/mol and the atomic weight of calcium is 40 g/mol. How many grams are needed to prepare: a) 1 liter of 0,1 M CaCO3 (10 g/l) 2+ b) 100 mL of 10 mg/dL of Ca using CaCO3 (25 mg) c) 50 mg/L of CaCO3 (50 mg) 11. 3 M CaCl2 (MW = 111.1) = ? N CaCl2 (6 N) 2 N H3PO4 (MW = 98) = ? M H3PO4 (0.667 M) 2 M H2SO4 (MW = 98) = ? N (4 N) 12. 250 mL of 5% NaCl contains ? g of NaCl. (12.5 g) 13. If absorbance of an unknown is 0.25 and the concentration of standard is 4 mg/L with an absorbancy of 0.40, what is the concentration of unknown? (2.5 mg/l) 14. If the 1000 mg/L glucose standard reads 49% T, and the unknown reads 55% T, what is concentration of unknown? (839 mg/L) 15. The hemoglobin standard solution contains 200 g/l. What amounts would be used to prepare 6 mL of the following concentrations: 200 g/L, 150 g/L, 100 g/L, 50 g/L? (6 mL, 4.5 mL + 1.5 mL of diluent, 3.0 mL + 3 mL of diluent, 1.5 mL + 4.5 mL of diluent)