Feudalism and Manorialism
advertisement

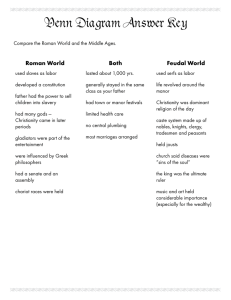
Global History and Geography I Feudalism and Manorialism Name: ___________________ Under feudalism, the king owned all the land. But he needed loyal nobles to serve him. He needed nobles to provide armies. The king gained loyalty by giving nobles land. The nobles could then give land to other people and ask for their loyalty. Since warfare increased, armies were essential. The kings and nobles who gave land were called lords. The nobles who received land were called vassals. Vassals promised loyalty to their lords. They promised to serve their lords and help them in battle. This system of exchanging land for military service was called feudalism. It existed in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The Middle Ages began with the fall of Rome and lasted for approximately 1,000 years. It is important to remember that a central government did not exist in Western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. It is also important to remember that warfare between the many kingdoms of Western Europe was frequent and that in a time of war, armies are important. Questions: 1- Who owned all the land? ________________________________________________________ 2- What did the owner of all the land need? _____________________________________________________________________________ 3- How did he gain loyalty? ________________________________________________________ 4- Who were lords? _______________________________________________________________ 5- Who were vassals? _____________________________________________________________ 6- Define feudalism. ______________________________________________________________ 7- When did feudalism exist in Western Europe? _____________________________________________________________________________ 8- What no longer existed after the fall of Rome? _____________________________________________________________________________ 9- Why was warfare frequent during the Middle Ages? _____________________________________________________________________________ 10- What is important during a time of war? _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ The lord gave his vassal a fief. A fief was a piece of land, and the peasants farmed on it. To protect his fief, each vassal needed his own soldiers. The vassal had much land, but little money. The vassal offered land to men who agreed to be his vassals. The lords and vassals kept dividing the land into smaller and smaller pieces. Questions: 11- What was a fief? ________________________________________________________ 12- What did a vassal need to protect his fief? ______________________________________________________________________ 13- What did the vassal have in great quantities and what did the vassal have in lesser quantities? ______________________________________________________________________ 14- How did the vassal get what he needed? ______________________________________________________________________ 1 The Middle Ages was a time of thousands of small wars. Knights did most of the fighting. Only the son of a noble could become a knight. A young noble started training to be a knight by first becoming a page. He learned religion, manners, obedience, and loyalty. When he was about 15 years old, the page became a squire. Then he learned to ride a horse and use weapons. At age 21, most squires became knights. Questions: 15- Who did most of the fighting during the Middle Ages? ____________________________________________________________________ 16- Define knight. ________________________________________________________ 17- Who could become a knight? ________________________________________________________ 18- Who was a page and what did a page learn? ________________________________________________________ 19- Who was a squire and what did a squire learn? ________________________________________________________ 20- When did most young men become knights? ________________________________________________________ About ninety percent of the people who lived during the Middle Ages were peasants. Peasants were small farmers or farm laborers. A few peasants were free, but most peasants were serfs. Serfs were not free, but they were not slaves either. No one could buy or sell them. But they had to stay on the manor on which they had been born. Serfs worked on the manor farms from early in the morning until late at night. They did the farm work, cut wood, and built fences. Female serfs worked in the fields, cooked, made clothing, and cared for the house. About 60 percent of what each serf raised went to the lord of the manor and to the church. Life was difficult for serfs. After meeting their responsibilities, little remained for themselves and their families. However, lords protected serfs during a time of warfare. Questions: 21- Who were the majority of people during the Middle Ages? ________________________________________________________ 22- Define serf. _______________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ 23- What did serfs do? ________________________________________________________ 24- What percentage of their produce went to the lord of the manor and to the church? ________________________________________________________ 25- What did serfs receive in exchange for their labor? ________________________________________________________ During the Middle Ages, most people lived on manors. A manor consisted of the lord’s house and the peasants living around it. Each manor produced its own food, clothing, and shelter. Serfs gave their lord part of their harvest in return for the use of land and other services they needed. In exchange, the lord protected the serfs from attacks by outsiders. Each lord had complete power over the serfs who lived on his manor. Serfs were bound to the land (could not leave their lords’ land) and had no voice in most matters. A manor was self-sufficient because the people who lived on it grew, raised, or made nearly everything that they needed. They rarely traded. They made their own clothing, cut their own wood, and raised all the food that they ate. The lord of the manor bought only a few things – like salt and iron – from the outside world. Given the dangers of travel and trade during 2 this time of increased fighting, the self-sufficiency of the manor was critical. The economic system of the Middle Ages was called Manorialism because life in the Middle Ages centered on the manor. Questions: 26- What was a manor? ________________________________________________________ 27- Provide examples of the manor’s self-sufficiency. _______________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ 28- Who did the lord have complete power over? ________________________________________________________ 29- Why was a serf “bound to the land”? ________________________________________________________ 30- Why did trade decrease during the early Middle Ages? _______________________________________________________________________________ 31- Define Manorialism. ________________________________________________________ The Age of Faith During the Middle Ages, the Roman Catholic Church was the single most powerful organization in Western Europe. There were many reasons for its power. First, people during the Middle Ages were very religious. They believed that the Roman Catholic Church represented God on Earth and held the power to send a person to Heaven or Hell. In addition, many nobles left land to the Church when they died hoping to gain entry into heaven. Therefore, the Church became Western Europe’s largest landowner. Church wealth also increased through tithes or church taxes which all Catholics were required to pay. Finally, the Church was the main center of learning. Church officials were usually the only people who could read and write. Rulers often relied on Church officials, since they were the most educated people during the Middle Ages. While Western Europeans were divided into small kingdoms, the one institution that united people during the Middle Ages was the Roman Catholic Church. Questions: 1- What was the single most powerful organization in Western Europe during the Middle Ages? ________________________________________________________ 2- Why was the Roman Catholic Church the most powerful institution in Western Europe during the Middle Ages? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3- Why was the Roman Catholic Church the largest landowner during the Middle Ages? _____________________________________________________________________________________ What is a tithe and how did tithes increase Church wealth? _____________________________________________________________________________________ Why did rulers rely on Church officials? _____________________________________________________________________________________ Why did the Roman Catholic Church unite people during the Middle Ages? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 3 During the Middle Ages, monks and nuns copied books from the past to make more copies. They did this by hand because no one in Europe had invented a machine to copy words. They decorated these books with bright colors and pictures. Over time, the largest monasteries (a place where monks live together) and convents (a place where nuns live together) became centers of learning. The monks and nuns kept alive learning from the past. Even though the central government collapsed with the fall of the Roman Empire, the Roman Catholic Church remained strong. Barbarians had converted to Catholicism. The Roman Catholic Church always had a tradition of the monastic life or a person devoting his or her life to the Church by forsaking marriage and family. Monks and nuns promised to never marry, to never own property, and to never disobey their superiors in the Church. They spent their lives praying, studying, and working. So, as education outside of the Church declined due to the dangers of travel, education within the Church remained strong as monks and nuns preserved some of the knowledge of the past. In addition, in the Byzantine Empire, the preservation of Greek and Roman ideas occurred. It is important to remember that the Barbarians destroyed Rome and that many of the great Greek and Roman works were destroyed in Rome. However, the Byzantine Empire was the former Eastern Roman Empire and it was able to preserve or keep many of the great Greek and Roman works. Questions: 4- What did monks and nuns do that greatly benefited the people of Western Europe? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5- What did monks and nuns promise to do? _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 6- Why did the Roman Catholic Church remain strong after the fall of Rome? _______________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ 7- Who else was responsible for the preservation of Greek and Roman ideas after the fall of Rome? Why? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ The Roman Catholic Church was the single, largest unifying institution in medieval Europe. It touched everyone's life, no matter what their rank or class or where they lived. With the exception of a small number of Jews, everyone in Europe was a Roman Catholic Christian during the Middle Ages from the richest king down to the lowest serf. From the moment of its baptism a few days after birth, a child entered into a life of service to God and God's Church. As a child grew, it would be taught basic prayers, would go to church every week barring illness, and would learn of its responsibilities to the Church. Every person was required to live by the Church's laws and to pay heavy taxes to support the Church. In return for this, they were shown the way to everlasting life and happiness after lives that were often short and hard. The head of the Church was called the Pope. As God's representative on Earth, the Pope had a great amount of power to influence kings and their advisors. If someone went against the Church, the Pope had the power to excommunicate them. This meant that the person could not attend any church services or receive the sacraments and would go straight to hell when they died. At a time when everyone believed in heaven and hell and all belonged to the Church, this was an awful punishment. Questions: 8- Why was the Roman Catholic Church so powerful during the Middle Ages? _______________________________________________________________________________ 4 9- Who was the head of the Roman Catholic Church and why was he so powerful during the Middle Ages? _______________________________________________________________________________ 10- What was excommunication and why was it a powerful punishment during the Middle Ages? _______________________________________________________________________________ Is religion a powerful force in the world today? Explain your answer. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ “All things were under its domain...its power was such that no one could hope to escape its scrutiny.” Which European institution during the Middle Ages is best described by this statement? 1. the Guild 2. Knighthood 3. the Church 4. the nation-state The Middle Ages in Western Europe was characterized by 1. the manor system and the importance of land ownership 2. absolute monarchies and strong central governments 3. decreased emphasis on religion in daily life 4. extensive trade with Asia and the Middle East Feudal societies are generally characterized by 1. an emphasis on social order 2. a representative government 3. many economic opportunities 4. the protection of political rights The art, music, and philosophy of the medieval period in Europe generally dealt with 1. human scientific achievements 2. religious themes 3. materialism 4. classic Greek and Roman subjects In Europe during the Middle Ages, the force that provided unification and stability was the 1. central government in Rome 2. military alliance between France and Germany 3. federation of the craft guilds 4. Roman Catholic Church Which is a characteristic of a feudal society? 1. rapid social change 2. high literacy rate 3. industrial-based economy 4. rigid class structure 5