Study Guide for Ancient Greece (test on Thursday, March 19, 2015)
advertisement

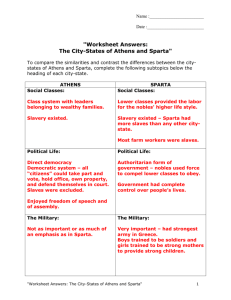
Study Guide for Ancient Greece (test on Thursday, March 19, 2015) Ancient Greece Geography a) Positive and negative impacts on the civilization Ex: Many islands lead to protection from invaders; difficult communication, separate city-states and little unification Mountainous land created a natural barrier of protection; allowed for little farmland b) Know these landforms and bodies of water in and around Greece * Islands, peninsula, mountainous land, Aegean, Ionic, and Mediterranean Seas Pericles/Golden Age a) Golden Agesarts and science thrive, literature, festivals, peace time, elaborate building and architecture, government b) Pericles Leader of Athens during the Golden Age c) Three Goals: Beautification, Protection, Democracy know examples of each Socrates/Plato/Aristotle/Philosophy a) Philosophy way of thinking about life b) Socratic Method questioning to come to answers c) Angered people of Athens because of his teaching methods d) Accused of corrupting and poisoning the minds of the youth and being disloyal to the gods and goddesses e) Plato students of Socrates, wrote the Republic to record Socrates’s writings, opened the Academy, taught Aristotle f) Aristotle taught Alexander the Great, believed in Constitutional Monarchy, used logical reasoning in his thoughts Alexander the Great a) Brave, loyal, courageous fighter; fought with his troops; spared innocent people in conquered lands b) Blended Greek culture with other cultures of lands he conquered (Hellenism) c) Worshiped as a god by Egyptians after liberating them from Persians; defeated the Persian Empire; expanded the Greek Empire into Asia d) Tutored by Aristotle; very educated man; interested in learning about all aspects of life: politics, literature, sports, combat Art and Architecture a) Architecture was viewed as a work of art; buildings reflect religious values b) Doric (simple), Ionic (curly part at top), Corinthian (highly decorative and detailed) c) Ancient Greeks were known for architecture with geometric designs (rectangle) Olympics a) Allowed various city-states to compete in sporting events; religious celebration b) Olympics were a religious festival to worship the gods c) Similarities and differences between the ancient and modern Olympics Religion/Literature/Theatre a) Literature and religion and theatre connection Myths were often performed as plays to worship the gods b) Religion was polytheistic myths of the gods of Mount Olympus c) Myths explained everyday occurrences Government a) City-state (polis); Acropolis city-state on a hill b) Different types of government: Monarchy, Tyranny, Oligarchy, Democracy (Direct and Representative) c) Athens (Democracy) Sparta (Oligarchy) Corinth (Monarchy) refer to chart on these three governments Athens vs. Sparta a) Know the daily life of Athenians and the daily life like of Spartans b) Athens: education, democracy; Sparta: military, war-like c) Delian League (Athens and its Allies); Peloponnesian League (Sparta and its Allies) d) Athenians develop a powerful navy due to location on the water; Sparta develops a strong army due to location in the middle of main peninsula Math and Science a) Advancements in Math: Geometry, Pythagoreans, Mechanics b) Herodotus: first historian, recorded history of events c) Hippocratic Oath for doctors; Birth of Science began looking for ways to explain the world without using the gods and religion IMPORTANT VOCABULARY TERMS!!! 1. City-state: region that governs itself 2. Polis: Greek word for city-state 3. Peninsula: land with water on 3 sides 4. Oligarchy: group of wealthy rule 5. Democracy: all citizens have a say 6. Tyranny: one ruler with absolute power 7. Monarchy: king or queen rules 8. Acropolis: city-state on a hill 9. Assembly: place for citizens to meet 10. Agora: open marketplace 11. Philosophy: way of life; behavior 12. Peloponnesian League: Sparta and allies 13. Delian League: Athens and allies 14. Hellenism: blending of Greek and non-Greek culture