Population Ecology
advertisement

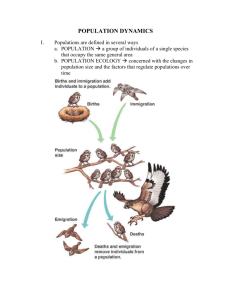
2/22/15 Population Ecology Density dependence, regulation and the Allee effect ESRM 450 Wildlife Ecology and Conservation Wildlife Populations Groups of animals, all of the same species, that live together in a particular area and reproduce Gotelli, N.J. (1998) A Primer of Ecology 1 2/22/15 Population Growth • Populations increase in proportion to their size • e.g., at a 10% annual rate if increase – a population of 100 adds 10 individuals in one year – A population of 1000 adds 100 individuals in one year • Allowed to grow unchecked, populations growing at a constant rate will rapidly approach infinity… Exponential Growth Nt = N0ert 2 2/22/15 Exponential Growth Model – A Cornerstone of Population Ecology • All populations have potential for exponential growth – Exponential models valuable because they recognize the multiplicative nature of population growth (positive feedback yields accelerating growth) • Realistically describes growth of many populations in the short term – i.e., resources are often temporarily unlimited (pest outbreaks, weed invasions, humans) Wildlife Populations Have Great Capacity for Growth • e.g., population growth of the ring-necked pheasant (Phasianus colchicus) – 8 individuals introduced to Protection Island, Washington, in 1937, increased to 1,325 adults in 5 years: • 166-fold increase! 3 2/22/15 Wildlife Populations Have Great Capacity for Growth • e.g., population growth of the ring-necked pheasant (Phasianus colchicus) – 8 individuals introduced to Protection Island, Washington, in 1937, increased to 1,325 adults in 5 years: • 166-fold increase! • Aside - Unforgiven Film set in 1881; includes scene with pheasants being shot from a train Pheasants not imported from China until 1890s Yet, Infinite Population Sizes Not Observed • Despite potential for exponential increase, most populations remain at relatively stable levels or fluctuate around equilibria – Paradox noted by Malthus and Darwin – for population growth to be checked, a decrease in the birth rate or an increase in the death rate (or both) must occur as overall population size gets large – What causes these changes in birth and death rates? 4 2/22/15 Crowding • As populations grow, crowding… – Reduces access to food (other resources) for individuals and their offspring – Aggravates social strife – Promotes the spread of disease – Attracts the attention of predators • As a result, population growth slows and eventually halts • Process known as DENSITY DEPENDENCE – decreasing per capita growth rate* with increasing population size * Individual contribution to population growth (survival and reproduction) The Logistic Growth Model • Populations with density dependence (decreasing per capita growth rate with increasing population size) modeled using the logistic growth equation • Logistic model incorporates idea that populations tend to level off at carrying capacity (K) • K: population size at which no more individuals can be supported over long time periods 5 2/22/15 The Logistic Growth Model Density dependence K/2 No density dependence Logistic Growth Curve • Graph of population size (N) versus time (t) for logistic growth features S-shaped curve (sigmoid growth) – Populations below K increase – Populations above K decrease – Populations at K remain constant • Inflection point at K/2 separates accelerating and decelerating phases of growth 6 2/22/15 Not All Factors Cause Populations to Level Off at K • Those that do are called Density-dependent factors – Effects increase in intensity with crowding – Prevent populations from growing larger in process called REGULATION – e.g., food supply and places to live – Sometimes also: effects of predators, parasites, and diseases Owls in a tree cavity Not All Factors Cause Populations to Level Off at K • Density-independent factors may remove individuals from populations, thereby depressing numbers, but cannot regulate them – Also call limiting factors – Effects do not intensify with crowding; cannot check growth – e.g., temperature, precipitation, catastrophic events (sometimes predation and parasitism) – In some cases, can keep populations small if severe & common 7 2/22/15 Evidence for DensityDependence • Density-dependence difficult to demonstrate in field – Requires manipulation • Alter density, measure vital rates (fecundity and survival) – or Natural Experimentation • Take advantage of natural fluctuations in density (problem – exogenous factors) • Best evidence comes mainly from lab experiments – e.g., fruit flies: fecundity and life span decline with increasing density in laboratory populations Pearl (1927) Q Rev Biol Field Evidence • Island warbler populations underwent bottleneck mid-20th century, then recovered • Thus, researchers were able to measure population size and individual vital rates during recovery Seychelles Warbler (Acrocephalus sechellensis) – Island setting provided for replicates (multiple islands)… – …and minimized influence of exogenous factors like predators (i.e., islands acted as outdoor laboratories) Brouwer et al. (2009) Ecology 8 2/22/15 Overall Aride Breeding season Cousine Individual reproduction declined with increasing population size on 4 islands Populations leveled off in accord with projections based on density-dependent reproduction Field Evidence Bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis) Portier et al. (1998) J Zool 9 2/22/15 Offspring (lamb) survival plummeted with increasing density, especially during winter Portier et al. (1998) J Zool The Allee Effect • Under the density-dependent (logistic) growth model – Individuals in small populations should thrive; why? 10 2/22/15 The Allee Effect • Under the density-dependent (logistic) growth model – Individuals in small populations should thrive; why? – No crowding; plenty of resources • Thus, we expect high population growth rate for small populations The Allee Effect • Under the density-dependent (logistic) growth model – Individuals in small populations should thrive; why? – No crowding; plenty of resources • Thus, we expect high population growth rate for small populations • Sometimes, the opposite is observed - Low per capita growth rate at low population density - Allee effect - also called inverse density dependence or ‘depensatory’ growth 11 2/22/15 The Allee Effect • Causes? There are 6 that are widely recognized – (1) Difficulty finding mates (e.g., plants, broadcast spawners, also maybe some great whales) – (2) Cooperative defense – (3) Predator satiation (predation most effective at low prey density) – (4) Cooperative feeding – (5) Dispersal (high emigration at low density; animals more likely or better able to colonize occupied sites) – (6) Habitat alteration (presence of conspecifics increases recruitment to a population by altering biotic or abiotic conditions in a way that increases fitness of recruits) Kramer et al. (2009) Pop Ecol Evidence for Allee Effects Once widespread across Vancouver Island (31000km2) Now, only roughly 32 in wild (critically endangered) 170 captive in 4 breeding facilities Vancouver Island marmot (Marmota vancouverensis) Brashares et al. (2010 ) J Anim Ecol 12 2/22/15 Mechanisms? • VIM now lead solitary lives - - historically, as much as 90% of time spent within 20m of a conspecific Now, none • Also, VIM now range widely • Consequently – High energy expenditure (movement) – Higher predation mortality (greater exposure and fewer alarm calls) – Reduced foraging efficiency (more time devoted to vigilance) Brashares et al. (2010 ) J Anim Ecol Population Ecology and Conservation • An understanding of population growth, density dependence and the Allee effect has great applied value – Identify high and low quality habitat (e.g., comparison of growth rates) – Identify populations in trouble (sharp population declines); project future trajectories – Set appropriate harvest rates (crowded populations can be harvested sustainably due to compensatory growth) – Explain why small populations are not growing as expected (Allee effects) 13 2/22/15 Five Minute Paper Questions & Insights 14