Fö11 Inför muntlig tentamen.pptx
advertisement

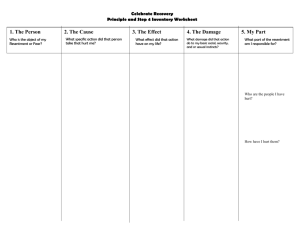
2013-12-06 THE ORAL EXAM Go to classroom R18, bring ID Come in good time! 45 min 15 minutes Test with 10 MC Questions 30 minutes preparation 3 questions Of these three one main question Fö 11 EXAM PREPARATION To examiner In groups of three Answer on main question Complement on the other two Three new questions Answer on main question Complement on the other two Jörgen Ljung (Nicolette Lakemond) Kursansvarig TGTU04 LEDARSKAP 45 min-1hour approximately Feedback and indication of grade 1 2 How can a question look like? Criteria for grading U (Fail) <10 Fails to provide an accurate answer 3 4 5 10-13 14-16 17-24 Provides an accurate answer on the question by describing and discussing the answer Provides an accurate answer by describing and discussing the answer, and linking it to its appropriate context in a reflection Provides an accurate answer by describing and discussing the answer, linking it to its appropriate context in a reflection, showing clearly how different models/ theories are connected to each other, and by providing an accurate example 3 You are a project manager of a product development project facing the termination of your project. With the same group you need to start development of a similar product based on a different technology. You fear that the group will resist. What approaches mentioned in Nahavandi could you use for dealing with this resistance? Discuss and explain these including their advantages and disadvantages. TEST YOURSELF: ARE YOU READY TO ANSWER THIS QUESTION? 4 Example answer • The questions asks for approaches for dealing with resistance to change – in essence the approaches are summarized in table 9-3 • Methods are – education and communication (+ facts, less resistance, - time consuming) – participation and involvement (+ commitment, richer ideas, - timeconsuming, implementation of inappropriate change) – facilitation and support (+ fear, - time-consuming, high risk failure= – negotiation and agreements (+ easy, balance power, - time consuming, expensive, further negotiation required) – Manipulation (+ quick, cheap, - mistrust, resentment) – explicit or implicit coercion (fast, effective short-term, - resentment, morale problems, not long-term 5 Example answer • The questions asks for approaches for dealing with resistance to change – in essence the approaches are summarized in table 9-3 • Methods are – – – – – – • education and communication (+ facts, less resistance, - time consuming) participation and involvement (+ commitment, richer ideas, - time-consuming, implementation of inappropriate change) facilitation and support (+ fear, - time-consuming, high risk failure) negotiation and agreements (+ easy, balance power, - time consuming, expensive, further negotiation required) Manipulation (+ quick, cheap, - mistrust, resentment) explicit or implicit coercion (fast, effective short-term, - resentment, morale problems, not long-term In this case – there is a lack of info a fear of unknown (new technology), your project team consists of experts and has power to block implementation, so the first two, and maybe even the third is most important (explain also why the others are less important) BEING ABLE TO EXPLAIN THESE METHODS, INCLUDING ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES AND WHY THEY FIT IN THIS SITUATION ENOUGH FOR A 3. 6 1 2013-12-06 Example answer But, we will check you understanding, - What is meant by facilitation and support? ACTIVE LISTENING Example answer 4 Listening and talking to a (group of) person(s) in a way that helps them understand the change and solve the problems related to the change reduces fear SUPPORTIVE COMMUNICATION - The proposed methods show clear support in Visionary leadership as well – empowerment, vision, teamwork And IN ADDITION, if you are able to show that you understand how different theories are connected to each other by e.g.: The proposed three are effective in dealing with all three groups of causes for resistance (individual, organizational, group), e.g. facilitation and support are effective in reducing fear, this method is especially appropriate when causes of resistance are related to the individual (e.g. fear of the unknown and fear of failure), maybe less applicable to organizational and group causes of resistance. or… connect approaches to visionary and exemplary leadership or… connect approaches to elements of learning organizations that facilitate changes (long-term) 5 + EXAMPLE how to use 7 8 Other example questions Other example questions • Throughout your education, and even in this course, you have been working in groups. In fact you could compare your group to a selfmanaged team. Discuss and explain the characteristics of self-managed teams and apply these to group work in your studies. • As a Swedish manager you are about to close a deal and order from a Chinese supplier. You are on the spot and ask if they are able to deliver the products on time. They answer: “Yes but it takes extra hard working and the traffic is terrible these days”. You get the feeling that you do not get the underlying message and come to think of Hall’s High-Context Low-Context model. Analyse the situation based on this model. 9 10 So, what other questions could you expect??? PUT YOURSELF IN THE ROLE OF THE TEACHER e.g. What are obstacles to effective leadership?, What is the trait era?, What are abilities and skills – do they differ?, What is charismatic leadership?, What is transactional leadership?, What are guidelines for good delegation?, What is visionary leadership?, What are methods for leadership development etc? IF YOU WERE ME; WHAT KIND OF QUESTIONS WOULD YOU HAVE ASKED? CREATE YOUR OWN DATABASE TEST YOURSELF! – GO THROUGH THE TABLE OF CONTENTS AND SEE IF YOU KNOW ABOUT ALL THE PARTS 11 12 2 2013-12-06 KNOWING THE ANSWER IN YOUR HEAD REMEMBER THAT WE WOULD MUCH RATHER LIKE TO SEE YOU PASS THAN FAIL! ≠ ARTICULATING OUT LOUD PRACTICE IN FRONT OF 13 14 ____ is change that occurs randomly and suddenly without the specific intention of addressing a problem. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 10 questions Minor influence on grade Increasing reliability Reducing blackout effects A. B. C. D. A. Planned B. Unplanned C. Revolutionary D. Evolutionary 15 16 Which of the following is NOT implied in the textbook’s definition of culture? (p. 34) The belief that leaders are born rather than made is part of which approach to leadership? (p. 67) Comprised of norms and values Culture is a perception There is a shared aspect of culture Individuals of a culture use dissimilar terms to describe it A. B. C. D. Scientific Contingency Case study Trait CULTURE CONSISTS OF COMMONLY HELD VALUES WITHIN A GROUP OF PEOPLE. A SET OF NORMS, CUSTOMS, VALUES, AND ASSUMPTIONS THAT GUIDES THE BEHAVIOUR OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE. … CULTURE IS SHARED BY THE MEMBERS OF A GROUP. 17 18 3 2013-12-06 Various definitions of leadership include all but one of the following: (p. 3) SO, ARE YOU PREPARED? A. Influence process B. Goal achievement C. Group phenomenon D. Control Good luck with studying! 19 20 4