Earthquakes-causes and effects
advertisement

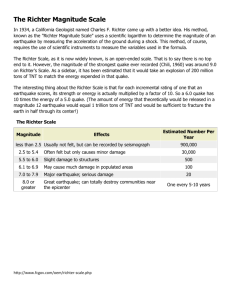
Such news items raises several questions like What are earthquakes? How do they occur? What are the causes and effects? Can we prevent them? Can we predict them? Earthquakes-causes and effects Prof. D Chandrasekharam Department of Earth Sciences Head, Centre of Studies in Resources Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Earth structure and Interior Continental drift Earth structure and Interior Plate boundaries Pacific ridge Indian Ocean Ridge Atlantic ridge 1 Plate boundaries Plate boundaries Constructive boundary Destructive boundaries Himalayas Sumatra Japan Continental crust California Ocean crust Types of collision tectonics Pakistan Earthquake 7.2M Subduction Continent-Continent Earthquake foci Earthquakes in 2005 Ring of Fire 2 Indian Ocean Floor Types of faults Mumbai 10 Ma Fracture 38 Ma 55 Ma 75 Ma Earthquake terms Locating an earthquake Seismograph USA Japan Bombay Arrival of “P” wave Tectonic map of India Arrival of “S” wave Seismic Profile 3 Earthquake Magnitude TNT Equivalent Richter TNT for Seismic Magnitude Energy Yield Earthquake Severity Richter Magnitude Earthquake Effects Less than 3.5 Generally not felt, but recorded. 3.5-5.4 Often felt, but rarely causes damage. 5.4 - 6.1 At most slight damage to well-designed buildings. Can cause major damage to poorly constructed buildings over small regions. 6.1-6.9 Can be destructive in areas up to about 100 kilometers across where people live. 7.0-7.9 Major earthquake. Can cause serious damage over larger areas. 8 or greater Great earthquake. Can cause serious damage in areas several hundred kilometers across. Sumatra -1.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0 6.5 7.0 6 ounces 30 pounds 320 pounds 1 ton 4.6 tons 29 tons 73 tons 1,000 tons 5,100 tons 32,000 tons 80,000 tons 1 million tons 5 million tons 32 million tons 7.5 8.0 8.5 9.0 10.0 12.0 160 million tons 1 billion tons 5 billion tons 32 billion tons 1 trillion tons 160 trillion tons Example (approximate) Breaking a rock on a lab table Large Blast at a Construction Site Large Quarry or Mine Blast Small Nuclear Weapon Average Tornado (total energy) Little Skull Mtn., NV Quake, 1992 Double Spring Flat, NV Quake, 1994 Northridge, CA Quake, 1994 Hyogo-Ken Nanbu, Japan Quake, 1995; Largest Thermonuclear Weapon Landers, CA Quake, 1992 San Francisco, CA Quake, 1906 Anchorage, AK Quake, 1964 Chilean Quake, 1960 (San-Andreas type fault circling Earth) (Fault Earth in half through center, OR Earth's daily receipt of solar energy) Volcanoes and earthquake foci-Indonesia 4 Can we predict an earthquake? Science has not reached that stage as yet!! Thank You 5