Study Guide - Science With Ms. Ortiz
advertisement

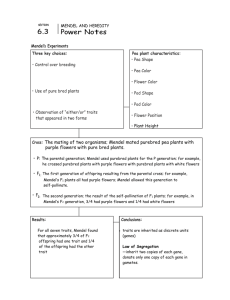
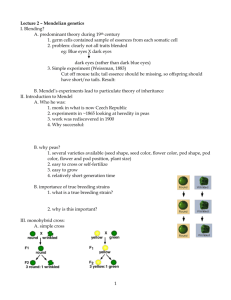
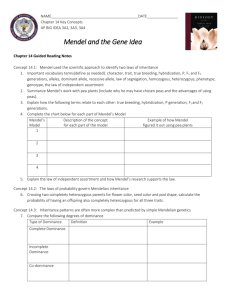
sEcït0N 6.3 MENDEL AND HEREDITY Study Guide KEY CONGEPT VOCABULARY Mendel's research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. tra it MAIN IDEA: Mendel laid the groundwork for pu c AW of seg re g genetics. l. What is genetics? 2. Whose early work is the basis for much of our current understanding of genetics? 3. How did Mendel's 0n r0ss views on inheritance difîer from the views of many scientists of his time? that m MAIN IDEA: Mendel's data revealed patterns of inheritance. In designing his experiments, Mendel made three important choices that helped him see patterns of inheritance. In the table below, list Mendel's tlree choices and write an example ofhow he put each ofthese choices into action. c> o À E o (J Mendel's Choices 4. Control over breeding removed the stamens and fertilized pistilwith from a pea plant of his choice 5. Use of purebred plants used'self-poll ínating , purebred pea plants .E E c o o) l Example Io õ E I o o) 6. studied "either-or" traíts f o ôo not ate characteristics such as pea shape, pea color, color, pod shape, pod color, flower position, and @ ,9 À oo 7. Why did Mendel use pea plants? Unit 3 Resource Book McDougal Littel Biology Srudy Guide 9 Name Period STUDY GUIDE, CONTINUED 8. Fill in the sequence diagram below to summarize Mendel's experimental process. rs in F, generbtion with dominant phenotype. to self-pollinate. a e 9. Mendel concluded that traits are inhçrited as "disorete units." What do we call these discrete units today? i *' C o o E ô , O ,s 1O. What two conclusions make up Mendel's law of segregation? E c o f each gene in their gametes. =o) - -o Vocabulary i Check :' E .ti I @ E 11. Segregation means "separation." What is "segregated" in Mendel's law of segregation? f o ôo @ 12. What does "purebred" o) mean? 'È à O 10 Study Guide Unit 3 Resource Book McDougal Littell Biology