Evolution Worksheet: Natural Selection & Evidence
advertisement

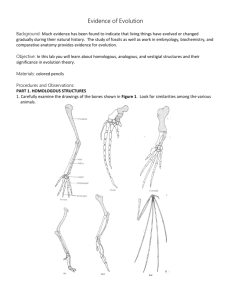
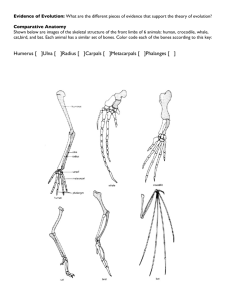
STAAR: EOC Biology – RC 3 - Evolution Read the following situations below and identify the 5 points of Darwin’s natural selection. In ostriches, there are 2 types: ones that run fast and those that run slowly. The fast birds can reach up to 40 miles an hour. Jackals love to eat ostrich, and they can reach speeds of up to 35-40 miles per hour. A flock of ostrich will lay ~ 10 eggs (each mother only lays 1), but many rodents break into the eggs and eat the fetus before they hatch. 1. What ostrich will be selected AGAINST? _________________ FOR? _______________ 2. Darwin's 5 points: Identify the parts of the scenario that match Darwin’s 5 criteria for natural selection: Population has variations. _________________________________________________________________ Some variations are favorable. _____________________________________________________________ More offspring are produced than survive._________________________________________________ Those that survive have favorable traits. ____________________________________________________ A population will change over time. ________________________________________________________ 2) Bob believes that giraffes have long necks because they have stretched their necks to try and reach food that is high in trees. Since the parent had stretched its neck, it passed the long neck on to its offspring. Ryan believes that giraffes have long necks because the ones with long necks were able to reach the food, and those with short necks could not and died. The long necked giraffes reproduced, and soon all of the giraffes had long necks. a. Which student thinks like Darwin? Justify your answer. EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION 1 Describe the function of each set of bones below: ANIMAL FUNCTION Human Whale Bat Are the bones arranged in a similar way in each animal? These structures are formed in similar ways during embryonic development and share like arrangements: however, they have somewhat different forms and functions. They are called homologous structures. BUTTERFLY WING AND BIRD WING. What function do these structures share? Do birds and insects share any structural similarities that would suggest they are closely related? form. These structures are called analogous structures. VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES (cave fish /minnow) Explain why eyesight is not an important adaptation to life in a cave. Organs or structures that lost their function in the organism and become reduced in size (because of efficiency) are called vestigial structures. Human vestigial organs are well documented. Read the list of human vestigial structures shown below. Suggest a possible function for each structure and explain why it became vestigial. STRUCTURE PROBABLE FUNCTION WHY VESTIGIAL? Appendix Coccyx (tail bones) Muscles that move ears ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATIONS 10. Explain why the homologous structures of the bones are evidence of evolutionary relationships. 11. Explain the evolutionary relationship between the fin of a fish and the flipper of a whale. EVIDENCE FROM EMBRYOLOGY 13. How does a comparison of the embryos provide evidence of evolution? 14. Which of the organisms would be most biochemically similar to humans: fish or pig? 2 Some COMPLETE THE CHART by checking the kind of evidence described. Kind of Evidence Evidence Homologous Structures Analogous Structures 20. A modified structure seen among different groups of descendants 21.In the earliest stages of development, a tail and gill slits can be seen in fish, birds, rabbits, and mammals. 22.Examples of forelimbs of bats, penguins, lizards, and monkeys The forelimbs of flightless birds 23.DNA and RNA comparisons may lead to evolutionary trees 24.Bird and butterfly wings have same function but different structures. 25.A body structure reduced in function but may have been used in an ancestor 3 Vestigial Embryological Structures Development Genetic Comparisons