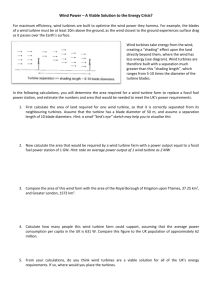
Module Name - WFL Academy
advertisement
Wind Farm Design Principles Module 2.2 – Lesson 001 Tutor: John Stavenuiter PhD Version: February 2015 1 Wind Energy Content & Features Intended Learning Outcomes The student has/can/is: • knowledge and understanding of relevant terminology • look through the organizational structure, processes and design aspects, of the asset (Wind Farms) related to expected problems in Wind farm Design • able to define a Wind Farm Design approach • able to describe and execute several techniques used within Wind Farm Design activities • understand the necessity of appropriate methods and techniques • awareness of future threats and opportunities. 2 Wind Energy Context & Features http://www.wwindea.org/webimages/WWEA_half_year_report_2014.pdf 3 Global wind map, installed capacity and production for lead countries (data from 2013) KEY POINT: good wind resources are found in many regions, notably in the United States, Europe and China, which lead the global market. Estimated Renewable Energy Share of Global Final Energy Consumption, 2012 [Renewables 2014 GLOBAL STATUS REPORT, page 21] Fossil, the lowest cost of electricity? How should you calculate? 6 [GWEC Global Wind Report 2014] Pollution from Electric Power Example from the US Sulfur Dioxide 70% Carbon Dioxide 34% Nitrous Oxides 33% Particulate Matter 28% Toxic Heavy Metals 23% 0% 20% 40% 60% Percentage of U.S. Emissions Source: Northwest Foundation, 12/97 Electric power is a primary source of industrial air pollution 7 80% Wind Farm Design Principles 2 examples Offshore Wind Farm Horns Ref, Denmark, 2002 80 Vestas V80-2.0 MW units, in total 160 MW installed Onshore Wind Farm Anacacho, Texas, 2012 55 Vestas 1.8 MW WT in total 100 MW installed 8 Conservative, Moderate, and High Renewables Scenarios to 2050 9 [Renewables GLOBAL FUTURES REPORT 2013] Wind Energy History • 1 A.D. • Hero of Alexandria uses a wind machine to power an organ • ~ 400 A.D. • Wind driven Buddhist prayer wheels • 1200 to 1850 • Golden era of windmills in western Europe – 50,000 • 9,000 in Holland; 10,000 in England; 18,000 in Germany • 1850’s • Multiblade turbines for water pumping were made • 1882 • Thomas Edison commissions first commercial electric generating stations in NYC and London • 1900 • Competition from alternative energy sources reduces windmill population to fewer than 10,000 • 1850 – 1930 • Heyday of the small multiblade turbines • As many as 6,000,000 units installed in US • 1936+ • US Rural Electrification Administration extends the grid to most formerly isolated rural sites • Grid electricity rapidly displaces multiblade turbine uses 10 Wind Turbines Power for a House or City 11 Significant Power Source coal coal petroleum petroleum natural gas natural gas nuclear nuclear hydro hydro other renewables other renewables wind wind Wind currently (2014) produces less than 1% of the world power. Source: Energy Information Agency 12 Wind could generate 6% of worlds electricity by 2020. Global Wind Energy Outlook (2014) Three visions of the future: 1. IEA New Policies Scenario (The baseline scenario obtained by the International Energy Agency) 2.GWEO Moderate Scenario 3.GWEO Advanced Scenario The Moderate and Advanced scenario’s are evolved over the years as a collaboration between the Global Wind Energy Council, Greenpeace International and the German Aerospace Centre. 13 [GLOBAL WIND ENERGY OUTLOOK 2014] Global Cumulative Wind Power Capacity Note: As wind power plays a more and more central role in our electricity system, the various scenarios from industry, the IEA, NGOs and others all begin to converge. 14 [GLOBAL WIND ENERGY OUTLOOK 2014] Wind Power Share of Global Electricity Demand 15 [GLOBAL WIND ENERGY OUTLOOK 2014] Investment and Employment 16 [GLOBAL WIND ENERGY OUTLOOK 2014] Service Team at Work 17 [GLOBAL WIND ENERGY OUTLOOK 2014] Benefits of Wind Power • Environmental • Economic Development • Fuel Diversity & Conservation • Cost Stability Wind Farms: Are All the Best Spots Taken? Source: Vestas 18 How much Power a Wind Turbine can generate? Note: Power is the rate of producing energy. Power is measured in kiloWatts (kW) or MegaWatts (MW). Energy is what is used to do work and is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) or Megawatt-hours (MWh) 19 [Wind Learning Centre, 2015] How much Energy a Wind Farm Turbine can generate? Notes; 1. Some of turbines in the table are not suitable for ‘class 1’ sites with annual average wind speeds above 8.5 m/s, hence are shown as n/a. Where there is a figure provided for 9 m/s, this will be a special ‘class 1 variant’ which generally has a smaller rotor and shorter tower to limit the extreme loads on the turbine. 2. The Enercon E82 comes in three variants with maximum power outputs of 2, 2.3 and 3 MW depending on the average wind speed at the site. In the table we have selected the most appropriate variant. 20 [Wind Learning Centre, 2015] Wind Turbine Annual Energy Production for a range of Annual Mean Wind Speeds 21 [Wind Learning Centre, 2015] How much money would a farm wind turbine provide? Each of these components is described in more detail here along with information on how they can affect the overall value of the energy generated. If you want a simple answer, then assuming 100% of the generated energy was exported with an export rate of 5 p/kWh, then the value of the electricity generated, per kWh, for the wind turbine sizes shown below would be: 22 [Wind Learning Centre, 2015] How much does a (small) farm wind turbine cost? 23 [Wind Learning Centre, 2015] Reading Literature • Renewables 2014 GLOBAL STATUS REPORT, • Market and Industry Trends, page 30-57 • Policy Landscape, page 74-86 • GWEC-Global-Wind-Report_9-April-2014 • REDEFINING THE COST DEBATE – THE CONCEPT OF SOCIETY’S COST OF ELECTRICITY, page 6-9 • A RENEWABLE ENERGY FUTURE, page 10-15 • GLOBAL WIND ENERGY OUTLOOK 2014 • The Global Wind Energy Outlook Scenarios, page 8-24. 24 Assignment for Lesson M2.2-001 As assignment for this lesson you have to answer 8 multiple choice question at the WFL academy site. You have passed this lesson when you have a 100% score of right answers. Success by doing the Question Quiz! 25