7th Grade Social Studies
advertisement

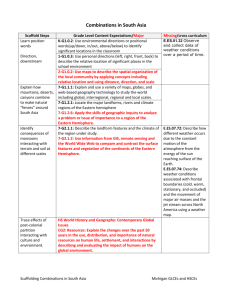
7th Grade Social Studies Weeks Curriculum Units Essential Questions Updated April 2014 Lesson Sequence (hover over link to access resources) 3 weeks 7 weeks 4 weeks 5 weeks 4 weeks 4 weeks 5 weeks Vocabulary/Key Concepts Unit 1: Geography of 1.What are the significant physical and human 1:Exploring Maps of the Eastern Hemisphere climate, fundamental themes of the Eastern Hemisphere characteristics of the Eastern Hemisphere? 2:Landforms, Bodies of Water and Vegetation of the Eastern geography, geographic tools and 2.How is the geography of the Eastern Hemisphere technologies, human characteristics, Hemisphere different from the geography of the 3:Climate Regions of the Eastern Hemisphere human/environment interaction, Western Hemisphere? How is it alike? 4:Human Characteristics of the Eastern Hemisphere physical characteristics, population 3.How have humans used, adapted to, and 5:Population Patterns of the Eastern Hemisphere patterns, region modified different environments in the Eastern 6:Human/Environment Interaction in the Western Hemisphere Hemisphere? 7:Putting it All Together: Geography of Planet Earth 1.Why is it important to treat maps and "history" 1. What are Maps? Unit 2: An close-reading, contextualizing, as accounts? 2. What Can a Map Tell Us? Introduction to corroborating, event, evidence, 2.How do historians know and create accounts about 3. What Does History Mean? World History framing, geographic features, the past? 4. How Do Historians Create Accounts of Past Events historical argument, historical 3.Why might historians have different and 5. What Process Do Historians Use to Investigate the Past? problem, history sometimes conflicting versions of the same event? 6..Tools to Organize and Analyze the Past-Establishing perspective, primary sources, Significance representations/accounts, 7. Tools to Organize and Analyze the Past - Using Social secondary sources, significance, Institutions 8. Tools to Organize and Analyze the Past - Using Temoral Frames social institutions, sourcing, spatial scales, temporal frames 9:.Tools to Organize and Analyze the Past - Using Spatial Scales (time) 10. History as a Discipline 11. Challenging the Power the Authority of the History Textbook 1. Introducing Reading Strategies Unit 3: Beginnings 1.How do we learn about humans and human adaptation, agriculture, 2. The Study of Prehistory of Human Societies ancestors in pre-historic times, before there was 3. Anthropology and Early Humans domestication, evidence, writing? evolution, foraging, meta 4. The Peopling of the Earth 2.How and why did humanity spread across the 5. The Paleolithic Age cognition, migration, Neolithic earth? Era, Paleolithic Era, settlement, 6. The Agricultural Revolution 3.How did the natural environment shape the social, institutions, 7. Neolithic Settlement, Surplus, Specialization, and Social ways people lived in the Paleolithic Era? specialization, world history Institutions 4.How and why did many humans begin to shift 8. Global Patterns of Early Human Settlement from full-time foraging to living in settled villages? 1.What are Civilizations? 2.The Early River Valley Civilizations 3.What Were Early Civilizations Like? 4.How did Intensification Lead to the Development of Writing,Laws, and Centralized Governments in Early Civilizations? 5.Who Were the Nomadic Pastoralists and How Did They Live? 6.The Technology of Era 2... Spinning the Wheels of the Bronze Age 7.Interaction in Era 2 – Conflict and Cooperation The Human Story Outside of Afroeurasia - Historical Patterns in 8.Different World Zones 1.Unit Overview: From Early Civilizations to Empires 1.Why did some civilizations develop into largeUnit 5: The Rise of 2.What is the recipe for empire? A comparative analysis of Era 3 scale empires while others did not? Classical Empires 2.How and why did changes in social institutions empires and ... (Era 3) 3.How did empires wield power and authority? change how people lived in large-scale empires? 4.Social Hierarchy and Slavery in the age of Empires 3.How did empires change exchanges between 5.The Emergence and Spread of World Religions peoples across large expanses of territory? 4.How did the emergence of world religions both 6.From Religious Tolerance to Book Burning - Leadership in the Empires influence and reflect the rise of empires? 7.Connections and Contacts in Era 3: Exchanging ideas, technologies, and goods in the age of empire 8.Empire... what it is, and what it is not: Using non-examples to refine the concept 1.How did the interaction between empires affect 1. The Han Dynasty: The rise of a Chinese Empire, 206 BCE to Unit 6: Interactions, 220 CE the Fall of Empires & their growth and development? 2.What were the most significant factors that 2. The Glory of Rome - The Roman Empire at its Height Other... enabled empires to stay in power and why did these 3. The Kushan Empire: A Nomadic Empire at the Crossroads empires eventually fall? 4. The Mayans – A different global pattern 3.What other patterns of human societies and 5. The Golden Age of the Gupta: Why and to what extent was it organization were in place during this era and why “Golden”? did they not become empires or parts of empires? 6. Why do empires collapse? - A comparative case study of the decline and fall of Era 3... 7. Turning Points and Other Stories: The World at the End of the Age of Empire 1.Why did the Civil Rights Movement intensify 1. The Prologue to Brown: Life Under Plessey Unit 7: Era III: World after World War II? 2. The Influence of World War II, Cold War, and Television Religions 2.How did individuals and groups use political, 3. Brown v. Board of Education legal, and social means to strive for freedom and 4. The Civil Rights Movement: Leadership and Organizations equality? 5. Coming to a Boil - White Resistance 3.How successful was the Civil Rights movement? 6. Legislating Civil Rights 7. Comparing Ideals - The Declaration of Independence and Civil Rights Movement Unit 4: Early Civilizations & the Emergence of ... 1.How did geography shape the way in which people lived in various world zones during Era 2? 2.How and why did civilizations develop during Era 2? 3.What new problems and solutions emerged from living in civilizations during Era 2? 4.What role did cultural diffusion play during Era 2? cities, civilization, conflict and cooperation, cultural diffusion, evidence, geographic luck, intensification, nomadic pastoralism, power and authority, river valley civilizations, social hierarchy, specialization, technology, world zones, writing bureaucracy, collective learning, cultural diffusion, democracy, empire / emperor, leadership, militarism, monarchy, nonexamples, philosophy, power and, authority, religious tolerance, republic, right to rule (divine right, inherited power), rise and fall of empires, Silk Roads, slavery, social, hierarchy/class, social inequality, society, specialization of labor, trade networks, world religions causes and consequences, citystate, civil service, civilization, Confuscianism, cultural diffusion, dynasty, empire, environmental circumstances/geographic luck, fall or decline of empires, Golden Age, historical significance, innovation, patriarchy, social hierarchy, class system, trade networks, turning point civil disobedience, civil rights, equality, federalism, idealism, individual freedom, protest movements, resistance, segregation, suffrage ASSESSMENTS: Formative: responding to essential questions, short articles, and in-class debates Summative: Common Assessment given at the end of each unit (combination of multiple choice, infographics, short answer , and essay based on reading passage or focus question.