Cytoskeleton and Extracellular Components Quiz.wpd
advertisement

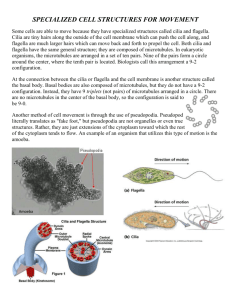
Cytoskeleton & Extracellular Quiz /41 Knowledge. Answer the following questions on foolscap where applicable. /3 1. Explain how motor proteins function. /6 2. Complete any 10 blanks in the following table on the quiz sheet. Property Microtubules Structure ! hollow tubes Diameter Protein Subunits ! dimer of alpha-tubulin and betatubulin (globular protein) 2 Specific Functions Name: Microfilaments ! 7 nm ! _________________________ _________________________ ! chromosome movement in cell division ! organelle movement such as guiding vesicles from the ER to the Golgi or Golgi to the membrane ! act as tension-bearing elements to maintain cell shape ! change cell shape ! muscle contractions ! cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells ! makes the outer portion of the cytosol, the cortex,__________ _________________________ ! amoeboid movement ! division of animal cells Intermediate Filaments ! fibrous proteins coiled into cables ! 8-12 nm ! several protein such as keratin of varying size ! act as tension-bearing elements to maintain cell shape ! anchors __________________ _________________________ ! formation of the nuclear lamina (a structure near the inner nuclear membrane and the peripheral chromatin) /2 /4 3.a) Explain how microtubules grow. b) Identify 2 ways basal bodies are more similar to centrioles than to flagella/cilia. /2 /6 /6 4.a) Identify 2 ways flagella and cilia are similar (aside from microtubule construction). b) Identify 3 ways flagella and cilia differ. c) Fully explain how flagella and cilia bend. /4 5. Identify 2 ways a primary cell wall differs from a cell membrane in plants. /6 6. For each of the following, identify the specific molecule of structure being described. a) the motor protein used for muscle contractions b) layer of pectin polysaccharide used to cement plant cells together c) type of cell wall made in several layers between the primary cell wall and cell membrane d) most abundant glycoprotein in the extracellular matric of animal cells e) a network of secreted proteins/carbohydrates embedding collagen fibres in the extracellular matric of animal cells f) attaches some animal cells to proteins in the extracellular matrix /6 7. Complete the following table on the quiz sheet. Property Main Function Basic Design Tight Junction Desmosome Gap Junction Cytoskeleton & Extracellular Quiz /41 /3 Knowledge. Answer the following questions on foolscap where applicable. 1. Explain how motor proteins function. ! ! ! ! ! ! /6 use ATP to energize the motor protein causing them to change shape to alter intermolecular attractions to other proteins then lose energy and change back to form new intermolecular attraction to the proteins the process is repeated 2. Complete any 10 blanks in the following table on the quiz sheet. Property Microtubules Microfilaments Structure ! hollow tubes ! two intertwined strands Diameter Protein Subunits ! 25 nm outside/15 nm inside ! dimer of alpha-tubulin and betatubulin (globular protein) ! 7 nm 2 Specific Functions ! provide compression resistance to maintain cell shape ! chromosome movement in cell division ! organelle movement such as guiding vesicles from the ER to the Golgi or Golgi to the membrane /2 ! act as tension-bearing elements to maintain cell shape ! change cell shape ! muscle contractions ! cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells ! makes the outer portion of the cytosol, the cortex, a more gellike consistency ! amoeboid movement ! division of animal cells ! act as tension-bearing elements to maintain cell shape ! anchors the nucleus and other organelles ! formation of the nuclear lamina (a structure near the inner nuclear membrane and the peripheral chromatin) one end, the plus end, can disassemble and reassemble tubulin dimers faster than the other end b) Identify 2 ways basal bodies are more similar to centrioles than to flagella/cilia. ! ! /2 ! actin (globular protein) Intermediate Filaments ! fibrous proteins coiled into cables ! 8-12 nm ! several protein such as keratin of varying size 3.a) Explain how microtubules grow. ! ! /4 Name: both centrioles and basal bodies have a (9 x 3) + 0 arrangement of microtubules; whereas, flagella/cilia have a (9 x 2) + 2 arrangement both centrioles and basal bodies serve as microtubule assembly regions; whereas, flagella/cilia beat to play some role in locomotion and movement 4.a) Identify 2 ways flagella and cilia are similar (aside from microtubule construction). any 2 of: ! both extend from cell membranes ! both can propel cells ! both can move fluid along the tissue surfaces ! both use the motor protein, dynein to walk between microtubules to create bending /6 b) Identify 3 ways flagella and cilia differ. any 3 of: ! cilia more commonly used to move fluid along tissue surfaces ! cilia more likely to occur in large numbers ! cilia tend to be shorter ! single non-motile cilia can act as a signal-receiving antenna to trigger internal cell activities ! cilia use rapid power stroke followed by a lax recovery stroke to beat; whereas, flagella undulate by beating strongly back and forth ! cilia typically create directional movement perpendicular to their axis of motion; whereas, flagella typically create directional movement in line with their axis of motion /6 c) Fully explain how flagella and cilia bend. ! ! ! ! /4 dynein proteins exist between microtubule doublets one foot of the dynein protein remains anchored while the other foot releases and reattaches further along the adjacent microtubule the anchoring microtubule for dynein is connected to the central pair by a radial spoke protein and in also connected to the microtubule dynein acts on by a flexible cross-linking protein to ensure that the microtubules can’t slide by each other as the dynein walks only one side of the circle of microtubules walks which forces flagella and cilia to bend 5. Identify 2 ways a primary cell wall differs from a cell membrane in plants. any 2 of: ! cell wall is the external most structure of a plant cell; whereas, the cell membrane is between the cell wall and the cytoplasm ! the cell wall may eventually have several layers; whereas, the cell membrane is only a bilayer ! the cell wall is much thicker ! the cell wall is made up of the polsaccharide cellulose; whereas, the cell membrane is largely made up of cholesterol, protein and phospholipids ! the cell wall is perforated by plasmodesmata channels for intercellular communication; whereas, the cell membrane uses transmembrane proteins for this purpose /6 6. For each of the following, identify the specific molecule of structure being described. a) the motor protein used for muscle contractions ! myosin b) layer of pectin polysaccharide used to cement plant cells together ! middle lamella c) type of cell wall made in several layers between the primary cell wall and cell membrane ! secondary cell wall d) most abundant glycoprotein in the extracellular matric of animal cells ! collagen e) a network of secreted proteins/carbohydrates embedding collagen fibres in the extracellular matric of animal cells ! proteoglycans f) attaches some animal cells to proteins in the extracellular matrix ! fibronectin /6 7. Complete the following table on the quiz sheet. Property Tight Junction Desmosome Gap Junction Main Function !tight barrier preventing leakage of extracellular fluid !anchor two cells together !intercellular communication Basic Design !branching network of sealing strands like stitching !rivet-like patches densely packed with keratin !transmembrane channels Prepared by K. Zuber