Cellular Organelles Cell Membrane Cellular Organelles
advertisement

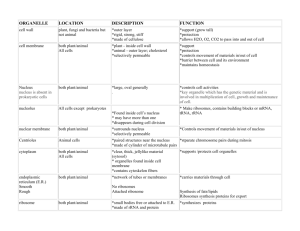
Cell Membrane • Also called Plasma Membrane • Controls what crosses membrane • Selectively PERMIABLE • Fluid Mosaic Model Cellular Organelles Cell Membrane and Organelles –Contains: proteins, phospholipids, Cholesterol, channels, pumps ... Cellular Organelles • Nucleus • Mitochondria –Nucleolus • Plastids • Ribosome • Vacuoles • Endoplasmic • Lysosomes Recticulum • Chloroplasts –Smooth & rough • Cilia, Flagella • Golgi • Other Structure of a Generalized Cell Cytoplasm Figure 3.2 • Cytoplasm – material between plasma membrane and the nucleus • Cytosol – largely water with dissolved protein, salts, sugars, and other solutes • Cytoplasmic organelles – metabolic machinery of the cell • Inclusions – chemical substances such as glycosomes, glycogen granules, and pigment 1 Cytoplasmic Organelles • Specialized cellular compartments • Membranous – Mitochondria Mitochondria, peroxisomes, peroxisomes lysosomes lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus • Nonmembranous – Cytoskeleton, centrioles, and ribosomes Nucleus • Nuclear membrane –controls movement –porous • Contains DNA & Nucleolus • Control Center Nucleus • Contains nuclear envelope, nucleoli, chromatin, and distinct compartments rich in specific p pprotein sets • Gene-containing control center of the cell • Contains the genetic library with blueprints for nearly all cellular proteins • Dictates the kinds and amounts of proteins to be synthesized 2 Nucleus Nuclear Envelope • Selectively permeable double membrane barrier containing pores y nucleoplasm, p which contains essential • Encloses jjellylike solutes • Outer membrane is continuous with the rough ER and is studded with ribosomes • Inner membrane is lined with the nuclear lamina, which maintains the shape of the nucleus Figure 3.28a Nucleoli • Dark-staining spherical bodies within the nucleus • Site of ribosome production • Pore complex regulates transport of large molecules into and out of the nucleus Chromatin • Threadlike strands of DNA and histones • Arranged in fundamental units called nucleosomes • Form condensed, barlike bodies of chromosomes when the nucleus starts to divide Figure 3.29 Endoplasmic Recticulum • Connects Nucleus to Golgi p of Chemicals • Internal transport • Rough - has ribosomes –Makes Protiens • Smooth - no ribosomes –makes lipids, Neutralizes toxins 3 Ribosome • Made of RNA • Make Proteins • Found in RER • Found in Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Ribosomes • • • • Granules containing protein and rRNA Site of protein synthesis Free ribosomes synthesize soluble proteins Membrane-bound ribosomes synthesize proteins to be incorporated into membranes Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Interconnected tubes and parallel membranes enclosing cisternae • Continuous with the nuclear membrane • Two varieties – rough ER and smooth ER Figure 3.18a and c Smooth ER Rough (ER) • Tubules arranged in a looping network • Catalyzes the following reactions in various organs of the body – In the liver – lipid p and cholesterol metabolism,, breakdown of glycogen and, along with the kidneys, detoxification of drugs – In the testes – synthesis of steroid-based hormones – In the intestinal cells – absorption, synthesis, and transport of fats – In skeletal and cardiac muscle – storage and release of calcium • External surface studded with ribosomes • Manufactures all secreted proteins • Responsible for the synthesis of integral membrane proteins and phospholipids for cell membranes 4 Signal Mechanism of Protein Synthesis Signal Mechanism of Protein Synthesis • mRNA – ribosome complex is directed to rough ER by a signal-recognition particle (SRP) • SRP is released and polypeptide grows into cisternae • The protein is released into the cisternae and sugar groups are added • The protein folds into a three-dimensional conformation • The p protein is enclosed in a transport p vesicle and moves toward the Golgi apparatus Signal Mechanism of Protein Synthesis Figure 3.19 Golgi Bodies • Shipping Warehouse p compounds p • wraps in membranes • Complex or apparatus Golgi Apparatus • Stacked and flattened membranous sacs • Functions in modification, concentration, and packaging of proteins • Transport vessels from the ER fuse with the cis face of the Golgi apparatus • Proteins then pass through the Golgi apparatus to the trans face • Secretory vesicles leave the trans face of the Golgi stack and move to designated parts of the cell 5 Role of the Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus Figure 3.20a Lysosomes Endomembrane System • Spherical membranous bags containing digestive enzymes • Digest ingested bacteria, viruses, and toxins • System of organelles that function to: – Produce, store, and export biological molecules – Degrade potentially harmful substances • Degrade nonfunctional organelles • Breakdown glycogen and release thyroid hormone • System includes: • Breakdown nonuseful tissue • Breakdown bone to release Figure 3.21 Ca2+ • Secretory lysosomes are found in white blood cells, immune cells, and melanocytes – Nuclear envelope, smooth and rough ER, lysosomes, vacuoles, transport vesicles, Golgi apparatus, and the plasma membrane Endomembrane System Peroxisomes • Membranous sacs containing oxidases and catalases • Detoxify harmful or toxic substances • Neutralize dangerous free radicals – Free radicals – highly reactive chemicals with unpaired electrons (i.e., O2–) Figure 3.23 6 Mitochondria • Has own DNA –maternal inheritance –evolutionary evolutionary thoughts • Powers the cell • Respiration –2 membranes - Inner folded Cristae (krebs Cycle here) Mitochondria Mitochondria • Double membrane structure with shelflike cristae • Provide most of the cell’s ATP via aerobic cellular respiration • Contain their own DNA and RNA Figure 3.17 Vacuoles - Storage tanks • Play large role in support for plants • Plastids - specialized vacuole in plant cells – Chromoplasts Ch l - store pigments i - color l storage – Leukoplasts - food storage - granules of starch Lysosome • lyse break down- some is body - digestive body • Only in animal cells • Break down dangerous & nonfunctional things 7 Chloroplast • • • • Only in Plants Energy converter Changes solar energy into chemical energy All energy for life comes from the sun Cytoskeleton Cell structure & support • • • • Microtubules - Hollow protein tubes Shape of cytoplasm, movement of organelles Form centrioles - only in animal cells Support for locomotion – Cilia - basil bodies - 9 triplets • tiny hairs that beat or wave – Flagella - 11 microtubules - 9 around 2 • Long whip like tail Cytoskeleton cont • Micro filaments - long thin fibers of actin • Actin is a protein found in muscles • Specialized for contraction • Movement of and in cytoplasm – Oranelle movement – cytoplasmic streaming 8 Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton • The “skeleton” of the cell • Dynamic, elaborate series of rods running through the cytosol • Consists of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments Figure 3.24 Microtubules • Dynamic, hollow tubes made of the spherical protein tubulin • Determine the overall shape of the cell and distribution of organelles Intermediate Filaments • Tough, insoluble protein fibers with high tensile strength • Resist pulling forces on the cell and help form desmosomes Microfilaments • Dynamic strands of the protein actin • Attached to the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane • Braces and strengthens the cell surface • Attach to CAMs and function in endocytosis and exocytosis Motor Molecules • Protein complexes that function in motility • Powered by ATP • Attach to receptors on organelles 9 Motor Molecules Motor Molecules Figure 3.25a Figure 3.25b Centrioles Centrioles • Small barrel-shaped organelles located in the centrosome near the nucleus • Pinwheel array of nine triplets of microtubules • Organize mitotic spindle during mitosis • Form the bases of cilia and flagella Figure 3.26a, b Cilia Cilia • Whiplike, p , motile cellular extensions on exposed surfaces of certain cells • Move substances in one direction across cell surfaces Figure 3.27a 10 Cilia Cilia Figure 3.27b Figure 3.27c Structure of a Generalized Cell Figure 3.2 11