Chapter 20 Review Worksheet—ANSWERS
advertisement
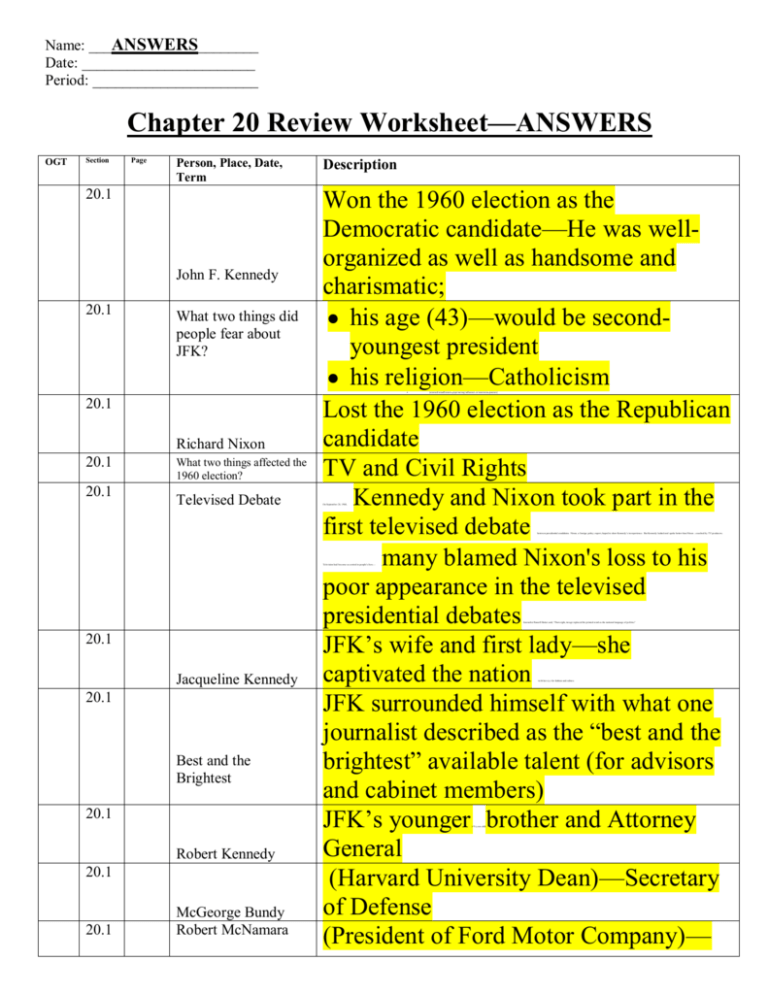
Name: ___ANSWERS________ Date: _______________________ Period: ______________________ Chapter 20 Review Worksheet—ANSWERS OGT Section Page Person, Place, Date, Term 20.1 John F. Kennedy 20.1 What two things did people fear about JFK? Description Won the 1960 election as the Democratic candidate—He was wellorganized as well as handsome and charismatic; his age (43)—would be secondyoungest president his religion—Catholicism Lost the 1960 election as the Republican candidate TV and Civil Rights Kennedy and Nixon took part in the first televised debate many blamed Nixon's loss to his poor appearance in the televised presidential debates JFK’s wife and first lady—she captivated the nation JFK surrounded himself with what one journalist described as the “best and the brightest” available talent (for advisors and cabinet members) JFK’s younger brother and Attorney General (Harvard University Dean)—Secretary of Defense (President of Ford Motor Company)— 20.1 Richard Nixon 20.1 20.1 What two things affected the 1960 election? Televised Debate (worried would lead to p ope having influence of American policies) On September 26, 1960, between presidential candidates. Nixon, a foreign policy expert, hoped to show Kennedy ’s in experience. But Kennedy looked and spo ke better than Nixon —coached by TV producers. Television had become so central to people's lives— . Journalist Russell Ba ker said, “That n ight, image replaced the printed word as the natio nal language of po litics” 20.1 Jacqueline Kennedy 20.1 Best and the Brightest 20.1 with her ey e for fashion and culture. (35-y ear-old) Robert Kennedy 20.1 20.1 McGeorge Bundy Robert McNamara 20.1 Dean Rusk 20.2 New Frontier 20.2 Mandate 20.2 Recession 20.2 Deficit spending 20.2 Peace Corps 20.2 Alliance for Progress 20.2 Secretary of Defense (President of the Rockefeller Foundation)—Secretary of State name given to Kennedy’s domestic policies clear voter support for his agenda (margin in which you win election) a moderate slowdown of the economy spending more money than the government collects in order to stimulate growth volunteers assist developing nations of Asia, Africa, and Latin America offered economic and technical assistance to Latin American countries Kennedy sought to surpass the Soviets—main goal was send a man to the moon (before the Soviets did) Americana’s space agency—National Aeronautics and Space Administration American, first man to walk on the moon Book by Michael Harrington that brought attention to poverty in the U.S. The official plane of the president, where Johnson was sworn Ex-Marine and communist supporter who killed Kennedy nightclub owner who shot Oswald to help keep countries from loo king at Communism as an option saw the space race as a challenge and Race to the Moon 20.2 NASA 20.2 Neil Armstrong 20.2 The Other America 20.2 Air Force One 20.2 Lee Harvey Oswald 20.2 20.2 20.2 Jack Ruby Zapruder Film Warren Commission in as president fo llow ing the ass ignation of Kennedy in front of a live television aud ience investigated the assassination and 2 (NASA) 20.2 20.3 20.3 House Select Committee on Assassinations (HSCA) Lyndon B. Johnson “LBJ Treatment” 20.3 Civil Rights Act 1964 concluded that Oswald had indeed acted alone 1979— concluded that Oswald assassinated President Kennedy as a result of a probable conspiracy ability to persuade senators to support his bills prohibited discrimination based on race, color, religion or national origin, and granted the federal government new powers to enforce the law voting rights for all Americans prohibited literacy tests or other discriminatory practices for voting insured consistent election practices The act 20.3 20.3 Voting Rights Act “war on poverty” Economic Opportunity Act (EOA) 20.3 Job Corps Youth Training Program 20.3 The act LBJ’s declare that caused him to pass EOA approved nearly $1 billion for youth programs, antipoverty measures, smallbusiness loans, and job youth training program (vocational training and job search skills) help find long-term solutions to the problems caused by urban and rural poverty for underprivileged preschoolers with a focus on helping develop the early reading and math skills encouraged poor people to participate in public-works programs LBJ won reelection in a landslide—for places individuals with community -based agencies to VISTA 20.3 an education program special PROJECT HEAD START 20.3 Community Action Program 20.3 1964 Election 3 20.3 many Americans it was an antiGoldwater vote Republican nominee for 1964 Presidential Election—Senator of Arizona LBJ’s domestic policy aimed at ending poverty and discrimination PRO WAR AGAINST WAR provided $1 billion to schools for textbooks, library materials, and special education funded scholarships and low-interest loans for college students created to financially assist painters, musicians, actors, and other artists provided hospital insurance and lowcost medical care to the elderly provided health benefits to the poor created to administer federal housing programs—improve urban conditions ends quotas (1920’s National Origins Acts) based on nationality Book by Rachel Carson’s that exposed the dangers of pesticides and other harmful environmental threats required states to clean up their rivers and lakes Book by Ralph Nader that detailed resistance by car manufacturers to the Barry Goldwater Barry Goldwater 20.3 Great Society 20.3 20.3 “hawk” “dove” 20.3 Elementary and Secondary Education Act 20.3 Higher Education Act 20.3 National Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities 20.3 Medicare 20.3 20.3 Medicaid Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) 20.3 Immigration Act of 1965 20.3 Silent Spring 20.3 Water Quality Act of 1965 20.3 Unsafe at Any Speed o pposed L BJ ’s social legis lation (believed government should not solve social and economic issues) and alienated vo ters by suggestin g the use of n uclear weapons in Cuba and N orth Vietnam specifically related to low-income housing and thus o pened the door for many non-European immigrants to settle in the U. S. 4 introduction of safety features, set federal safety standards for the auto and tire industries required states to set up highway safety programs required that states have inspection programs "equal to" that of the federal government set standards for labeling consumer products Supreme Court under Chief Justice Earl Warren—took an activist stance on the leading issues of the day way states redraw election districts by population districts must have approximately equal population—“one person, one vote” illegally seized evidence cannot be used in court like seat belts, and their general reluctance to spend money on improving safety 20.3 National Traffic and Motor Vehicle Safety Act 20.3 Highway Safety Act 20.3 Required new safety features such as: head rests, energy-absorbing steering wheels, s hatter-resistant win dshields, safety belts, etc Roads were improved by better delineation of curves (edge and center line stripes and reflectors), use of breakaway sign and u tility poles, improved illuminatio n, addition of barriers separating oncoming traffic lanes, and guardrails, etc. Also called "Eq ual To" law, Wholesome Meat Act 20.3 Truth in Packaging Act 20.3 Warren Court 20.3 Reapportionment 20.3 states redraw election districts by population, court rules Baker v. Carr (1962) and Reynolds v. Sims (1964) 20.3 20.3 Mapp v. Ohio (1961) Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) 20.3 Escobedo v. Illinois (1964) 20.3 Miranda v. Arizona (1966) —led to a shift in political p ower from rural to urban areas courts must provide legal counsel to poor accused has the right to have an attorney present when questioned by police all suspects must be read their rights before questioning 5 Chapter 20 Focus (plus additional items): SECTION 1: Peace Corps mandate New Frontier hot line Bay of Pigs Berlin Wall Fidel Castro flexible response John F. Kennedy Richard M. Nixon massive retaliation Nikita Khrushchev Cuban Missile Crisis Limited Test Ban Treaty SECTION 3: Baker v. Carr The Warren Court Civil Rights Act reapportionment Miranda v. Arizona Gideon v. Wainwright Medicare and Medicaid Immigration Act of 1965 Economic Opportunity Act Brown v. Board of Education Elementary and Secondary Education Great Society SECTION 2: Alliance for Progress Lee Harvey Oswald Warren Commission Jack Ruby 6











