Lab Packet - eacfaculty.org
advertisement

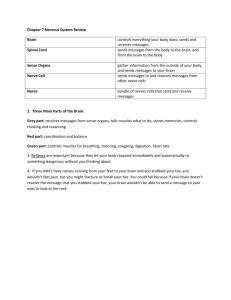
Thursday Lab Human Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory The laboratory portion of Biology 201 is a very important aspect of the course. It is here that you will make the observations and identifications of structures discussed and relating to concepts covered in lecture. It is extremely important that you study in advance for your weekly laboratory experience and that you stay current on your laboratory preparations and homework. The laboratory portion of your grade will amount to roughly a third of the points that are possible in the class. A portion of these points come from completion of the lab exercises which are due at the beginning of each lab. The answers will be found in your lab manual and corresponding chapters from the textbook. The rest of the points will come from weekly quizzes and the two lab practicals. The quizzes will be given at the beginning of each laboratory period (with the exception of the first lab period and the two lab periods when the practicals are given). Your lowest quiz score will be dropped from your grade prior to the calculation of your quiz percentage. If you miss a quiz (due to absence or tardy) you will receive a zero on that quiz. THERE WILL BE NO MAKE-UP QUIZZES. Please let me know if at any time you do not feel comfortable with some aspect of the class (specimens, cadaver, etc.). I understand that some religious and cultural beliefs may oppose some of the things which occur in class. However, at the same time, the things we do in class may continue on in your chosen career and may be unavoidable. I will try to do my best to accommodate you (within certain limits). Good luck and enjoy the semester. A final note: You will be required this semester and next to memorize a large number of unfamiliar terms. Your success will come only if you review these terms often. Studying five minutes before a quiz will not be enough—I guarantee you! Decide now that you will study with a study group and meet at least once a week. Thursday Lab Week #1 Body Landmarks Lab Exercise 1, p. 11-14 Abdominal Axillary Brachial Carpal Cervical Femoral Frontal Inguinal Nasal Oral Orbital Patellar Pelvic Pubic Sternal Tarsal Thoracic Umbilical Cephalic Gluteal Lumbar Occipital Otic Plantar Popliteal Sacral Scapular Vertebral Organ System Overview Lab Exercise 2, p. 25-26 Parts of Cell Lab Exercise 4, p. 49-52 Cell or plasma membrane Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Rough Smooth Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Mitochondria Centrioles Cytoskeleton Nucleus Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Chromatin Nuclear pores Cell Transport Lab Exercises 5A, p. 64, and 5B, p. PEx 17-19 Passive Transport Concentration Gradient Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion Filtration Active Transport Phagocytosis Endocytosis Exocytosis Cellular environments Isotonic Hypotonic Lysis Hypertonic Crenation Thursday Lab Week #2 Classification of Tissues Lab Exercise 6A, p. 85-90 Epithelial tissue Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Connective tissue Loose connective Areolar Adipose Reticular Dense connective Dense irregular Dense regular Cartilage Hyaline Elastic Fibrocartilage Others Bone Blood Muscle tissue Skeletal Cardiac Smooth Nervous tissue Integumentary system Lab Exercise 7, p. 101-104 Epidermis Keratinocytes Melanocytes Layers of Epidermis Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum Dermis Papillary layer Dermal papillae Reticular layer Appendages of Skin Hair Follicle Arrector pili muscle Nails Sebaceous glands Eccrine glands Apocrine glands Thursday Lab Week #3 Axial Skeleton: Skull Lab Exercise 10, p. 139-144 Skull Cranium Face Sutures Fontanels Bones of the skull and associated structures Frontal Parietal Coronal suture Sagittal suture Temporal Squamosal suture Zygomatic arch Mandibular fossa External acoustic meatus Mastoid process Carotid canal Jugular foramen Occipital Lambdoidal suture Foramen magnum Occipital condyle Sphenoid Sella turcica Pterygoid processes Optic foramen Ethmoid Perpendicular plate Crista galli Cribriform plate Maxilla Palatine process Hard palate Palatine Zygomatic Lacrimal Nasolacrimal canal Nasal Vomer Mandible Body Ramus Mandibular condyle Mandibular foramen Alveoli Hyoid Thursday Lab Week #4 Vertebral column and associated structures Intervertebral discs Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and pelvic curves Curvature disorders Scoliosis Kyphosis Lordosis Vertebra Body Vertebral foramen Intervertebral foramina Spinous process Transverse processes Articular processes Cervical vertebrae (7) Transverse foramina Atlas Axis Odontoid process (dens) Thoracic vertebrae (12) Facets Lumbar vertebrae (5) Sacrum (5 fused) Auricular surface Coccyx (4 fused) Sternum and rib cage Sternum Manubrium Body Xiphoid process Ribs Costal cartilage True ribs False ribs Floating ribs Head Tubercle Histology Lab Exercise 9, p. 119-122 Compact bone Spongy bone Osteon (Haversian system) Osteoblasts Osteoclasts Perforating canal Central canal Lamella Lacuna Canaliculi Thursday Lab Week #5 Classification of Bones Long Epiphysis Diaphysis Articular cartilage Epiphyseal plate Yellow marrow Red marrow Periosteum Endosteum Short Flat Irregular Bone markings (see p. 113, tab. 9.1) Upper Appendicular Skeleton Lab Exercise 11, p. 157-163 Pectoral girdle Clavicle Scapula Spine Supraspinous fossa Infraspinous fossa Glenoid cavity Coracoid process Subscapular fossa Acromion process Humerus Head Greater tubercle Lesser tubercle Deltoid tuberosity Capitulum Trochlea Coronoid fossa Olecranon fossa Ulna Trochlear notch Coronoid process Olecranon process Radius Head Radial tuberosity Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges (phalanx = sing.) Pollex Thursday Lab Week #6 Lower Appendicular Skeleton Pelvic Girdle Os coxa Symphysis pubis Acetabulum Ilium Iliac crest Greater sciatic notch Auricular surface Ischium Ischial tuberosity Obturator foramen Pubis Lower Appendicular Skeleton (cont) Femur Head Greater trochanter Lesser trochanter Medial and lateral condyles Intercondylar fossa Patellar surface Lateral and medial epicondyles Patella Tibia Medial and lateral condyles Intercondylar eminence Tibial tuberosity Anterior crest Medial malleolus Fibula Head Lateral malleolus Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Hallux Articulations Lab Exercise 13, p. 183-186 Synarthrosis Suture Synchondrosis Amphiarthrosis Symphysis Syndemosis Diarthrosis/Synovial Joint Structure of diarthrosis Joint capsule Synovial fluid Synovial membrane Articular cartilage Meniscus Bursa Types of diarthroses Gliding/plane Hinge Pivot Condyloid Saddle Ball-and-socket Body Movements Flexion Extension Hyperextension Dorsiflexion Plantar flexion Abduction Adduction Rotation Circumduction Supination Pronation Inversion Eversion Protraction Retraction Week #7: Lab Practical #1 Thursday Lab Week #8 Microscopic Muscle Anatomy and Muscle Physiology Lab Exercise 14, p. 193-195; Ex. 16A, p. 253-256; Ex. 16B, p. PEx 33-35 Sarcolemma Myofibril Sarcoplasmic reticulum T tubule I band A band H zone M line Sarcomere Z disc Thick filament Myosin Thin filament Actin Tropomyosin Troponin Twitch Treppe Wave summation Multiple motor unit summation Tetanus Complete Incomplete Steps to Muscle Contraction Week #9: Spring Break No Lab!!!! Thursday Lab Week #10 Skeletal Muscles of the Upper Extremity Lab Exercise 15, p. 227-234 Muscles of Facial Expression Epicranius Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Levator labii superioris Zygomaticus Depressor labii inferioris Platysma Buccinator Muscles of Mastication Temporalis Masseter Medial/lateral pterygoid Muscles of the Neck Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Muscles that act on the Scapula Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Supraspinatus Levator scapulae Rhomboideus (major and minor) Muscles that move the Humerus Pectoralis major Latissimus dorsi Deltoid Infraspinatus Teres minor Teres major Subscapularis Muscles that act on the Forearm Brachioradialis Biceps brachii Brachialis Triceps brachii Muscles that move the Hand Supinator Pronator teres Palmaris longis Flexor carpi radialis Flexor digitorum superficialis Flexor carpi ulnaris Extensor carpi radialis Extensor digitorum Extensor carpi ulnaris Thursday Lab Week #11 Skeletal Muscles of the Lower Extremity Muscles of Abdominal Wall External oblique Internal oblique Transverse abdominis Rectus abdominis Muscles of the Vertebral Column Erector spinae Iliocostalis Longissimus Spinalis Muscles of the Hip Iliopsoas Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Gluteus minimus Tensor fasciae latae Muscles of the Thigh Sartorius Quadriceps femoris Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius Gracilis Pectineus Adductor longus Adductor magnus Hamstrings Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Muscles of the Leg Tibialis anterior Fibularis) muscles Extensor digitorum longus Gastrocnemius Achilles tendon Soleus Flexor hallicus longus Flexor digitorum longus Tibialis posterior Thursday Lab Week #12 Nervous Tissue and Physiology Lab Exercise 17, p. 265; Ex. 18A, p. 277; Ex. 18B, p. PEx 47-48 Neuroglial Cells Astrocytes Ependymal cells Oligodendrocytes Microglia Schwann cells Structures of a Neuron Nucleus Dendrites Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Synapse Types of Neurons Structural Unipolar Bipolar Multipolar Functional Sensory Motor Interneuron (association) Meninges Dura mater Arachnoid mater Pia mater Central Nervous System: Brain Lab Exercise 19, p. 299-302 Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres Longitudinal fissure Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Occipital lobe Gray matter (cortex) White matter (medulla) Gyri Sulci Cerebellum Arbor vitae Structures of Brain viewed in a midsagittal section Corpora quadrigemina Superior colliculi Inferior colliculi Pineal body Medulla oblongata Pons Corpus callosum Septum pellucidum Thalamus Hypothalamus Optic chiasma Pituitary gland Infundibulum Ventricles of the brain and cerebrospinal fluid CSF Choroid plexus Lateral ventricles Third ventricle Fourth ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Thursday Lab Week #13 Structure of the Spinal Cord, Reflexes, and Nerves Lab Exercise 19, p. 303-304; Ex. 21, p. 337-340; Ex. 22, p. 351; Gray matter Central canal Dorsal and ventral root Dorsal root ganglion Ulnar, radial, and median nerves Sciatic nerve Reflex Lab Components of a Reflex Arc Receptor Sensory (afferent) neuron Integration center Interneuron (association neuron) Spinal cord Motor (efferent) neuron Effector Cranial Nerves Olfactory nerve (I) Optic nerve (II) Oculomotor nerve (III) Trochlear nerve (IV) Trigeminal nerve (V) Abducens nerve (VI) Facial nerve (VII) Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) Vagus nerve (X) Spinal accessory nerve (XI) Hypoglossal nerve (XII) Autonomic Nervous System Thursday Lab Week #14 Exercise 24/25 – Sensory Organs Lab Exercise 23, p. 361-362; Ex. 24, p. 377-382; Ex. 25, p. 393-396; Ex. 26, p. 403-404 Associated structures of the Eye Palpebrae Levator palpebrae muscle Conjunctiva Lacrimal gland Nasolacrimal duct Extrinsic eye muscles Structure of the eyeball Sclera Cornea Choroid Ciliary body Iris Pupil Lens Retina Rods Cones Fovea centralis Macula lutea Optic disc Chambers of the eye Anterior segment Aqueous humor Posterior segment Vitreous humor Structure of the Ear Pinna (auricle) External acoustic meatus Ceruminous glands Tympanic membrane Ear ossicles Malleus Incus Stapes Oval window Round window Auditory (Eustachian) tube Bony and Membranous Labyrinth Perilymph Endolymph Vestibule Semicircular canals Cochlea Vestibular nerve Cochlear nerve Scala vestibuli Scala tympani Cochlear duct Vestibular membrane Basilar membrane Organ of Corti Tectorial membrane Hair cells Week # 15: Lab Practical #2