WH10 SAQ3 Chapter Prologue 3 Democracy Develops in England
advertisement
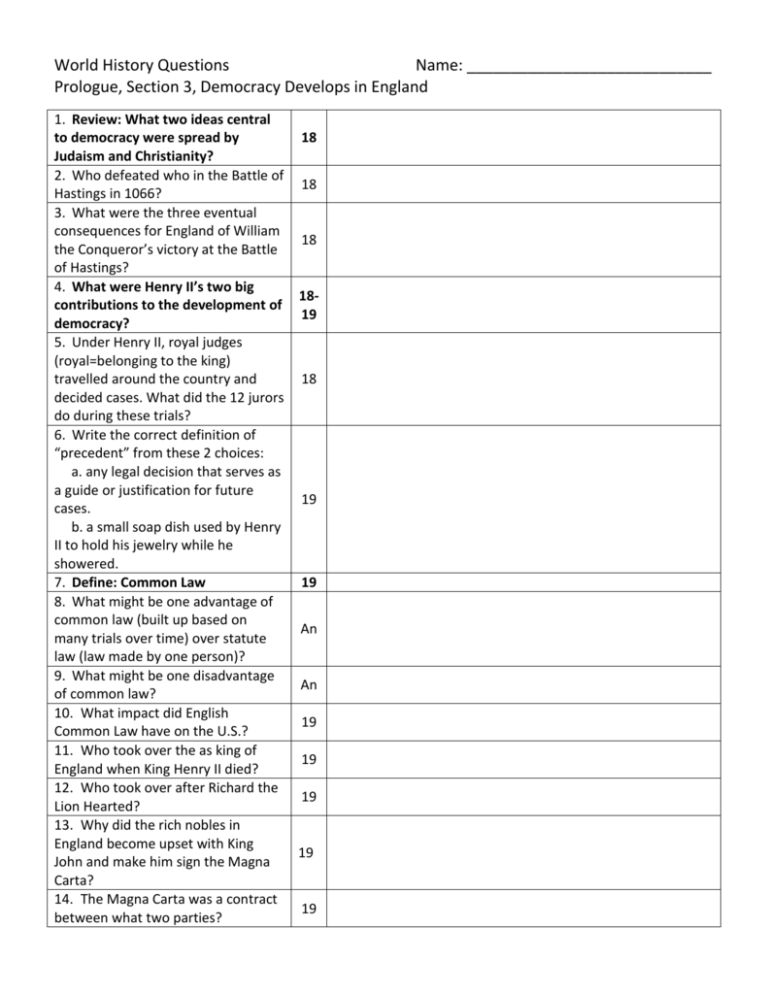
World History Questions Name: ____________________________ Prologue, Section 3, Democracy Develops in England 1. Review: What two ideas central to democracy were spread by 18 Judaism and Christianity? 2. Who defeated who in the Battle of 18 Hastings in 1066? 3. What were the three eventual consequences for England of William 18 the Conqueror’s victory at the Battle of Hastings? 4. What were Henry II’s two big 18contributions to the development of 19 democracy? 5. Under Henry II, royal judges (royal=belonging to the king) travelled around the country and 18 decided cases. What did the 12 jurors do during these trials? 6. Write the correct definition of “precedent” from these 2 choices: a. any legal decision that serves as a guide or justification for future 19 cases. b. a small soap dish used by Henry II to hold his jewelry while he showered. 7. Define: Common Law 19 8. What might be one advantage of common law (built up based on An many trials over time) over statute law (law made by one person)? 9. What might be one disadvantage An of common law? 10. What impact did English 19 Common Law have on the U.S.? 11. Who took over the as king of 19 England when King Henry II died? 12. Who took over after Richard the 19 Lion Hearted? 13. Why did the rich nobles in England become upset with King 19 John and make him sign the Magna Carta? 14. The Magna Carta was a contract 19 between what two parties? 15. What was the underlying principle (main idea) of the Magna Carta? 16. Which of the four quotes from the Magna Carta on page 19 is basically saying “no prison without a trial”? 17. Which of the four clauses from the Magna Carta on page 19 is basically the same as our 6th Amendment (right to speedy trial)? 18. Which of the four clauses from the Magna Carta on page 19 is basically saying “judges must know the law to serve as judges”? 19. Which of the four clauses from the Magna Carta on page 19 is basically saying: “no jail unless someone besides the police saw you do it”? 20. What did Clause 12 of the Magna Carta say the king had to do? 21. Define: due process of law 22. Define: Parliament 23. How did Edward I explain his action of calling together the Model Parliament in 1295? 24. How might it actually help a king to call together a parliament to approve his taxes, wars or other decisions rather than just force his will on the people? 25. Edward I allowed not only nobles but also knights and burgesses to be in his Model Parliament. Who were the burgesses? 26. By the mid 1300’s the parliament of England spit into one House for the knights and burgesses and one for the nobles and bishops. What were these two houses called? 27. Even though the vast majority of people had no part in Parliament, its existence was still important for what two reasons? 28. What power did the House of Commons have that gradually made 19 19 19 19 19 20 20 20 20 An 20 20 20 20 it as strong as the House of Lords? 29. Kings in Europe, including King James I, pushed back against the power of parliaments by claiming that they should have absolute (total) power because of “divine right” Define: divine right. 30. James I clashed with Parliament over what three things? 31. James I’s son, Charles I, agreed to sign the Petition of Right in exchange for money from Parliament. What four things did the Petition of Right seek to stop? 32. Did James I believe in the divine right of kings? 33. The English Civil war broke out in 1642. What were the two sides called and who did each support? 34. What happened to Charles I after the Antiroyalists won the English Civil War? 35. How was Oliver Cromwell’s rule like that of an absolute monarch? 36. Eleven years after Charles I was executed, his son, Charles II was restored as King of England. Why do you suppose Parliament restored the monarchy after all the trouble they had had with previous kings? 37. After 1679, if you were accused of a crime, the police had to bring you to court and tell a judge what you were accused of. What is this right, still in effect in the United States, called? 38. James II took over after Charles II. Why did the English people want James II’s daughter (Mary) and her husband (William) to take over after him instead of his son (James)? 39. What three great achievements of the Glorious Revolution? 40. Define: Constitutional Monarchy 41. Define: Bill of Rights 42. What were the four main contributions of England to the development of democracy? 20 21 21 21 21 21 22 An 22 22 Cl 22 23 Cl










