CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
advertisement

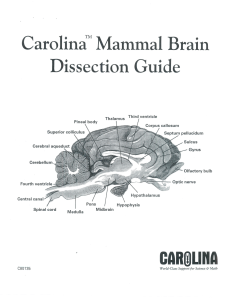
Nervous System Study Guide Yoga Sundram CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM BRAIN and SPINAL CORD BRAIN Protected by: Outer duramater (tough layer) Middle arachnoidmater Inner piamater (thin but vascular layer) Cerebrum Anterior (Larger part) Cerebellum Posterior (Smaller part) Brain Stem Posterior ventral (continues as spinal cord) Cerebrum: Frontal lobe, Parietal lobes, Temporal lobes, Occipital lobe Left and right hemispheres; these are connected by Corpus Callosum Thalamus and Hypothalamus Gyri (gyrus); ridges Sulci (sulcus); grooves Fissures deep grooves - separate the lobes Ventricles: (cavities) 1st ventricle; left cerebral hemisphere 2nd ventricle; right cerebral hemisphere 3rd ventricle; center 4th ventricle; brain stem Cerebral cortex and white matter Cerebellum: Cerebellar cortex Arbor vitae Peduncles Brain Stem: Mid brain Pons Medulla oblongata Brain Functions: Cerebrum: Interpretation Memory storage and retrieval Reasoning Starting muscle activity Intelligence and personality Sensory Areas of Cerebrum Primary somatosensory : Posterior frontal Somatosensory Association: Posterior frontal Visual: Posterior occipital Auditory: Superior temporal Olfactory: Medial temporal Gustatory: Medial temporal - Insula Visceral: Posterior temporal Vestibular: Posterior insula Fall / 09 Left Hemisphere: Language, Math, Logic Right Hemisphere: Insight, Visual, Intuition, Artistry Thalamus & Hypothalamus Brain stem Mid Brain Homeostasis: Temperature and Pressure regulation Head and Eye movement Posture Pons Regulates breathing Medulla oblongata Controls heart and lungs Cerebellum Controls body position Limb movements SPINAL CORD: Extends from foramen magnum (end of brain stem) to Cauda Equina (at 2nd / 3rd lumbar vertebrae Cervical enlargement: supplies upper limbs Lumbar enlargement: supplies lower limbs Gray and white matter Gray matter Butterfly shaped, Anterior horns, posterior horns, lateral horns Contains interneurons Posterior Horn (dorsal root): Sensory fibers: impulses travel towards spinal cord Anterior Horn (ventral root): Motor fibers: impulses travel away from spinal cord PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM CRANIAL NERVES and SPINAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVES (12 nerves) sensory (s), motor (m) or both (b) i ii iii iv v vi vii viii ix x xi xii Olfactory: Smell (s) Optic: Sight (s) Occulomotor: Eye muscles (m) Trochlear: Smallest cranial nerve: Fifth pair of eye muscle, (m) Trigeminal: Largest cranial nerve: Eye, Maxilla, Mandible, (b) Abducens: Eye muscle (m) Facial: Taste, facial expression, salivary and tear glands (b) Vestibulocochlear: Hearing, balance (s) Glossopharyngeal: Swallowing (b) Vagus: Speech, swallowing, heart, other organs in thorax and abdomen (b) Accessory: Muscles of palate, pharynx, trapezius, sternocleidomastoid (m) Hypoglossal: Tongue (m) Nerves i, ii and viii Mainly Sensory Nerves iii, iv, vi, xi and xii Mainly Motor Nerves v, vii, ix and x Both Some Say Money Matters, But My Brother Says Bigger Brains Matter Most SPINAL NERVES (31 nerves) Cervical (C1 to C8) : Total 8 Thoracic (T1 to T12) : Total 12 Lumbar (L1 to L5) : Total 5 Sacral (S1 to S5) : Total 5 Coccygeal (Co) : Total 1 Somatic and Autonomic nervous systems Somatic Pathway : Voluntary, involves skeletal muscles Sense Organ Sensory Neuron Dorsal Root Ganglion Interneurons (In brain or spinal cord) Motor Neuron Skeletal Muscle Autonomic Pathway : Involuntary, involves viscera, heart, glands, other internal organs Sense Organ Sensory Neuron Dorsal Root Ganglion Interneurons (in brain or spinal cord) Preganglionic Fiber Autonomic Ganglion Postganglionic Fiber Viscera Autonomic nervous system ---- Sympathetic system ( Action, emergency, fear, excitement) (Fight or Flight mode) Arises from thorax and lumbar regions (thoraco-lumbar) Adrenergic (Norepinephrine) Parasympathetic system ( Restores back to resting conditions, (visceral activity) Arise from brain stem and sacrum (cranio-sacral) Cholinergic (Acetylcholine) Pain: Acute pain conducted through A Delta fibers : Thick Myelinated (faster) Chronic pain conducted through C fibers : Thin, Unmyelinated (slower) Referred Pain: Feeling of pain at a different location than from the real source (visceral organs)