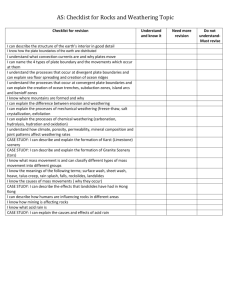
AS Rocks and Weathering Section B all questions
advertisement

AS Paper 1: Rocks and Weathering - SECTION B Full list of 2010-2015 Rocks and Weathering questions from Section B (45 minutes) Summer 2010 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the weathering terms exfoliation and crystal growth (salt). [4] (ii) Describe the process of freeze-thaw weathering. [3] (b) Explain the influences upon weathering of: (i) rock type and structure, (ii) vegetation. [8] (c) Explain how plate tectonics can be used to account for the development of ocean ridges and ocean trenches. [10] Winter 2010 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms pressure release (dilatation) and crystal growth (salt crystalisation) as they apply to rock weathering. [4] (ii) Briefly describe spheroidal weathering. [3] (b) Using diagrams, explain the operation of one type of slide and one type of flow on slopes. [8] (c) Explain how chemical weathering is influenced by climate, rock type and rock structure. [10] Summer 2011 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms oxidation and freeze thaw. [4] (ii) Explain the process of exfoliation. [3] (b) Explain how the differences in the chemical composition of limestone and granite lead to differences in the ways they are weathered. [8] (c) With the aid of diagrams describe and explain the formation of landforms found near convergent plate boundaries. [10] Winter 2011 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms flow and slide as they apply to mass movements. [4] (ii) Briefly describe how a rock slide can affect the shape of a slope. [3] (b) With the use of a diagram or diagrams, show how ocean trenches and island arcs may develop at a convergent plate margin. [8] (c) Explain how human activities can both increase and decrease mass movements on slopes. [10] Summer 2012 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms continental plate and oceanic plate. [4] (ii) Briefly describe the formation of a mid-ocean ridge. [3] (b) With the help of a diagram, explain the formation of landforms at the destructive plate margin formed by the meeting of two oceanic plates. [8] (c) Describe the physical factors that can make a slope become unstable. To what extent can human activities affect slope stability? [10] Winter 2012 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms ocean ridges and island arcs. [4] (ii) Briefly describe the process of subduction. [3] (b) With the help of diagrams, explain how fold mountains are formed at tectonic plate margins. [8] (c) Explain how mass movements can affect the development of slopes. [10] Summer 2013 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms humic acid and chelation. [4] (ii) Briefly explain how hydration weathers rock. [3] (b) With the aid of diagrams show how: (i) rock slides and (ii) mud flows occur and can affect the shape of slopes. [8] (c) Explain to what extent climate, vegetation and relief influence the weathering of limestone. [10] Winter 2013 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms salt crystal growth and hydration. [4] (ii) Briefly describe the process of exfoliation. [3] (b) Explain how human activities may affect the nature and intensity of weathering. [8] (c) With the aid of diagrams, explain how the movement of tectonic plates leads to the formation of mid-ocean ridges and island arcs. [10] Summer 2014 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms heave and slide as they apply to mass movements. [4] (ii) Describe how a mud flow occurs. [3] (b) With the aid of diagrams explain how ocean ridges and ocean trenches are formed. [8] (c) To what extent do rock type, vegetation and human activities affect the shape of slopes? [10] Winter 2014 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define the terms chelation and hydrolysis. [4] (ii) Briefly describe the process of pressure release (dilatation). [3] (b) Explain how vegetation, gradient and aspect may affect the nature and intensity of weathering. [8] (c) To what extent is mass movement on slopes the result of human activities rather than natural processes? [10] Summer 2015 9696/11 9 (a) (i) Define sea floor spreading and ocean ridge. [4] (ii) Describe an island arc. [3] (b) Draw a labelled diagram showing the convergence of an oceanic plate and a continental plate. Explain the processes occurring and the types of landforms produced. [8] (c) Explain the factors and processes that are most effective in the weathering of granite and limestone. [10]