CL4
advertisement

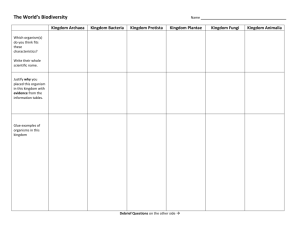
Name: _______________________________________________ SCIENCE – CLASSIFICATION CL-4 March 15, 2007 Section #/color: ____ / ___________ SCIENCE – CLASSIFICATION How do scientists classify living things? What are the characteristics of the kingdoms of living things? PLANTAE ANIMALIA KINGDOM 5 KINGDOMS CHART The way it gets its food (Hetero or autotroph? If auto, chemo or phosynthesis?) Heterotrophs Autrotrophs (photosynthetic) and a few Heterotrophs (some parasitic) Organization (Uni or multicellular? Eukaryote or prokaryote?) Mullticellular, Eukaryotic Unicellular (e.g. algae) and multicellular, Eukaryotic Importance and role in our world Example organism (give common name, scientific name, description, and picture) Extra Facts Crown-of-thorns (Acanthaster planci) is a Consumer (i.e a hetertrophic organism that eats The largest animal ever to starfish that lives in other organisms or organic waste) in food chains believed to have existed was Australia. It feeds off the coral polyps of the Can be a herbivore, carnivore, or omnivore. the blue whale. coral reef. Surprisingly, it eats one of When too many of Serves as a food source and provides assistance, the smallest organisms, Them are present, they transportation, recreation, and companionship. phytoplankton (from kingdom can destroy a reef; Can be a source of as well as a solution for Protista)! they are second only to humans in destroying environmental problems. reef habitat! The Venus Fly Trap Plants can be found in the ( (Dionaea muscipula), water (algae) and on land (e.g. even though it eats moss and ferns). insects, can survive without Serves as a food and medicinal source; used as them because it uses sunlight for its food Plants can be vascular (have dyes, in building material, and as the component also. Scientists believe it evolved the ability tissues for transporting of some fuels. to “eat” insects in response to the fact that its materials through its structure habitat is void in proper nutrients and – e.g. fern) and nonvascular sunlight (it lives in a bog/marsh ecosystem). (no tissue for transporting materials – e.g. algae and moss). KINGDOM MONERA Autorophs (Photosynthetic) and Hetrotrophs (absorb or engulf their food) FUNGI Heterotrophs and Autotrophs (Chemo and Photosynthetic) PROTISTA The way it gets its food (Hetero or autotroph? If auto, chemo or phosynthesis?) Heterotrophic (parasitic or absorb food from environment) Organization (uni or multicellular? Eukaryote or prokaryote?) Unicellular (filamentous or colonial), ALL prokaryotic Uni and multicellular, some colonial and filamentous, ALL eukaryotic Importance and role in our world Example organism (give common name, scientific name, description, and picture) Extra Facts Some strains of the bacteria Important in ALL food chains, help Escherichia Coli are harmless; maintain supply of nutrients by decomposing however, others are not. wastes, some produce oxygen, used in antibiotics, important part of human/animal One strain of E. Coli is responsible for the flu-like intestines (help break down food), also used symptoms that result when undercooked meat is in cleaning up environmental problems like contaminated with it. oil spills. Bacteria were the first form of life on Earth. Some Monera are Algae (e.g. cyanobacteria/blue-green algae). Antibiotics come from chemicals that certain bacteria produce; these help to weaken or kill bacteria and fight infection and disease! Paramecia (Paramecium Caudatum) are protists that have tiny hairs (cilia) Important producer in aquatic food chains, on the outside of their body that they food source for many organisms, one species use to move through the water. They also helps to produce oxygen. Some may be use these hairs to “push” food towards their oral parasitic and cause sickness. grooves (i.e. a tiny mouth). Paramecia live in pond ecosystems. Some protists are plant-like and others are very animal-like…these differing characteristics were collectively one of the reasons why scientists decided to abandon the two kingdom system of Aristotle! Decomposer (decays/breaks down wastes, dead materials – prevents build up of wastes Uni and from living things), produces antibiotics, used multicellular, some filamentous, to make bread and alcohol, damages crops ALL eukaryotic (parasitic). The Portobella Mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus) is the mushroom that we grill as a low-cal replacement of meat…hence “agaricus” means grilled! It is the most commonly grown mushroom in the States! A Honey Mushroom (Amillaria Ostoyae) in a forest in Oregon is believed to be the world’s largest living organism. It is about 8,500 years old and covers nearly 10 square kilometres of forest floor – i.e. an equivalent to about 1,600 football fields. Some forms of fungi are used in medicines to fight infection (e.g. penicillin). Most fungi are made up of tubular structures called HYPHAE. PART DIRECTIONS: Fill in the chart below using your 5 KINGDOMS CHART. # CATEGORY 1 Kingdom(s) that have organisms that do NOT have nuclear membranes in their cells 2 Kingdom(s) that have ONLY unicellular species 3 Kingdom(s) that have species which make or synthesize their food using light or chemicals 4 Kingdom(s) that have species that are eukaroytic 5 Kingdom(s) that have species that help cure diseases 6 Kingdom(s) that have ONLY multi-cellular species 7 Kingdom(s) that have prokaryotic species 8 Kingdom(s) that have species which help to clean up the environment 9 Kingdom(s) that have species which cause disease 10 Kingdom(s) that have organisms that DO have nuclear membranes in their cells 11 \ Kingdom(s) that have BOTH multi-cellular and unicellular species 12 Kingdom(s) that can be broken up into two groups: VASCULAR and NON-VASCULAR 13 Kingdom(s) that make O2 for the Earth 14 Kingdom(s) that contain the organism ALGAE 15 Kingdom(s) that species that feed off of other organisms (dead or alive) 16 Kingdom(s) that have specie with cilia or flagella that help them to move or grasp onto materials in their environment. 17 Kingdom(s) that contain producers (organisms that use sunlight or chemicals to make energy and serve as a food source for consumers). 18 Kingdom(s) that contain organisms that may destroy habitats. KINGDOM(S) # CATEGORY 19 Kingdom(s) that are helpful to the environment. 20 Kingdom(s) that serve as a food source for other kingdoms. 21 Kingdom(s) that contain decomposers (organisms that break down wastes). 22 Kingdom(s) that contain species that are parasites (organisms that live at the expense of another organism). 23 Kingdom(s) that have species made up of tubular structures called hyphae. 24 Kingdom(s) that contain species that are microscopic. 25 Kingdom(s) that contain some species that are plant—like and some species that are animal-like. KINGDOM(S)