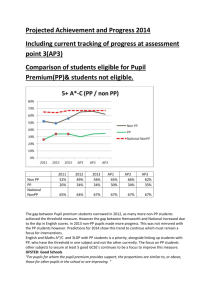
National Labor Relations Act _enforcement
advertisement

Urban Political Machines C19 America’s wealthiest men studies C19 Gilded Age political parties C20 Sherman Silver Purchase Act C20 Zimmerman Telegram C23 Andrew Johnson’s flaws C16 Sinking of the Maine C22 Referendum, recall, initiative etc. C21 Fed Reserve Act of 1913 C21 Hazen S. Pingree C19 Latin American policy C22 Federal Trade Commission C21 Rock Springs massacre C22 Mass transit in cities C19 Women’s fashions C18 Election of 1896 C20 Grant and presidency C16 Society of American Indians C21 Businesspeople and foreign expansion C22 Election of 1888 C20 Emergency Banking Relief Act C25 Urban school systems C25 AAA C25 1 Johnson and Reconstruction C16 American entertainment C19 Ku Klux Klan C16 American business in 1929 C24 POUR C25 Newlands Reclamation Act C17 Problems with pools C18 Latin American countries early 1900s C22 Great Plains migration C17 Universal Negro Improvement Association C24 Open-range ranching C17 Francis Perkins C25 Factions C20 Underwood tariff C21 Standardization of time C17 Pullman Strike C18 Bryan resignation C23 Mexican workers C25 National Industrial Recovery Act C25 Frederick W. Taylor C18 Geary Act C19 Issue focused politics C21 American sport C19 2 Cattle industry C17 New Deal success/failure C25 Dawes Severalty Act C17 Sharecropping C16 Railway strike of 1877 C18 The long drive C17 Cyrus Field C24 Sewards Folly C22 Anti-imperialists C22 Womens Christian Temperance Union C24 1890’s depression C20 Jim Crow laws C20 Ku Klux Klan C24 Open Door policy C22 Venezuelan and Cuban crisis C22 Settlement workers C19 Justice Department in 1920’s C24 African American migrants C19 Edward Bellamy C18 Cattle and sheep C17 1868 indictment/AJ C16 National Labor Relations Act _enforcement C25 The rise of organized sport C19 3 Senate defeat of Treaty of Versailles C23 First Reconstruction Act C16 Underconsumption C24 Scalawag C16 William Jennings Bryan & Treaty of Paris C22 Second Hundred and business C20 Lochner vs New York C21 Women’s Suffrage Amendment C20 Social Gospel C21 New Consumerism C24 Calvin Coolidge and price supports C24 Northern African Americans & Republicans C25 National Recovery Administration C25 Haymarket Bombing C18 Utah Statehood C17 Criticism of trusts C18 Welfare Capitalism C24 National labor Relations Act C25 Open Door notes (1899-1900) C22 New Deal programs and women C25 Wilsonianism C23 Roosevelts court packing C25 Pensions for former union soldiers C20 4 Hoover and the crash of “29” C24 Conservation movement C17 NAACP C21 The Wade-Davis Bill C16 Charles Beard C21 Ethnic neighborhoods C19 Wilson and exports to allies C23 Politics in the late 19th century C20 George Westinghouse C18 Steel workers strike of 1919 C23 U.S. acquisition of Philippines C22 American Labor Force 1890-1920 C18 Father Charles Coughlin C25 The Bonus Expeditionary Force C25 Congress’s First Reconstruction Plan C16 Theodore Roosevelt and conservation C21 Farmers in the southern backcountry C20 Western Indians most common crop C17 “rum, Romanism, and rebellion” C20 American workers diets (late 19th, early 20th) C18 American farmers and low prices (1929-1933) C25 U.S. enters WWI….why? C23 Eugenicists C21 5 New Nationalism C21 WWI & American women C23 National Consumers League C21 Great Depression (end of) C25 United Mine Workers Strike (1902) C21 Baily v. Drexel Furniture Company C24 Schenck vs. U.S. C23 Prospecting precious metal C17 Growth of suburbs C24 National Industrial Recovery Act (end of) C25 Corporations and the 14th amendment C18 African Americans (3/5) C16 Roosevelt and business consolidation C21 U.S. declares war on Spain (1898) C22 Populist Party in 1896 C20 Influx of Puerto Ricans to U.S. in 1920’s C24 Birth of a Nation C19 The following is a study sheet for the chapter-25 questions that will appear on the midterm exam. Chapter-25 Study Guide Depression: Family life; farmers; African American workers; Mexican born workers; Women workers in the 1930’s; Response to by prominent business leaders Urban schools in the 1930’s Hoover’s response to, and philosophy of dealing with the depression 6 Hawley-Smoot Tariff; POUR Reconstruction Finance Corp; Farmers Holiday Association; Bonus Expeditionary Force; National Industry Recovery Act; NIRA and Roosevelt administration; National Recovery Administration; NIRA and the Public Works Administration; end of industrial recovery program; Agricultural Adjustment Act – purpose and consequences; American Liberty League; Social Security Act of 1935; National Labor Relations Act (Wagner) Causes of depression; Causes of banking crisis (1929); Emergency Banking Relief Act The First Radio “Fireside Chat” – purpose, occasion; New Deal laws and programs and women; New Deal and unemployment; Father Charles Coughlin; Dr. Frances E. Townsend ; Huey Long and the Share Our Wealth Society; Francis Perkins; John Collier and his beliefs; The Federal Writers Project; Second Hundred Days & Big Business; African American voting; wealthy business and the New Deal; Business and labor during the worst years; Industrial unions in the 1930’s; Congress of Industrial Organization; 1936 United Auto Workers Strike; Large multi-purpose dams and the federal government; Tennessee Valley Authority; effects of the radio; Effects of Roosevelt’s court-packing plan; his economic policies at beginning of his 2nd term; 1937-1939 recession and his response; decision to seek 3rd term; and African Americans; and the presidency; and Hoover; Non-white Americans under the New Deal (limited gains); What finally ended the depression 7