Math Lesson Plan
advertisement

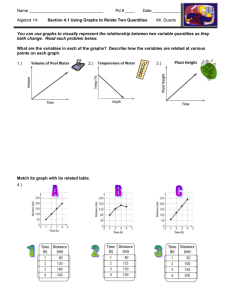
Math Lesson Plan Teacher Name: Rademacher Department: Science Name of Lesson: Kinetics Course: AP Chemistry Grade/Level: 11,12 Objective: To learn how to solve Kinetics (rates of reactions) problems using the data given to develop a graph, take a point from the graph and use that data to find the differential rate law, integrated rate law, the rate constant and the overall order of a reaction. Math Standard: Strand 2: Concept 1: PO 3: Display data as tables, lists. Strand 3: Concept 3: PO 1: Determine if a relationship is a function given a graph. Strand 3: Concept 3: PO 7: Express the relationship between 2 variables using graphs. Strand 3: Concept 3: PO 8: Interpret the relationship between data suggested by graphs. Math Concept (e.g. creating graphs, interpreting graphs, or problem solving): creating graphs interpreting graphs problem solving Anticipatory Set: Reactions can occur at very different rates. Name some that are very fast. (Food spoiling, combustion) Name some that are very slow. (Rusting, nuclear decay) We can determine the rate of a reaction between chemicals using the differential rate law, and the integrated rate law just by taking the information from a graph. Lesson/Activity/Instruction: Notes on the Differential rate law, Integrated rate law, finding the rate constant and the overall order of a reaction. Guided Practice: Book p. 604 #31 The rate of the reaction: NO2 (g) + CO (g) NO (g) + CO2 (g) depends only on the concentration of nitrogen dioxide below at 225C. At a temperature below 225C, the following data were collected. Determine the rate law, the integrated law and the value of the rate constant. Calculate the [NO2] at 2.70 x 104 s after the start of the reaction. Independent Practice: Book p. 604 #33 The decomposition of ethanol on an aluminum oxide surface was studied at 600 K. C2H5OH (g) C2H4 (g) + H2O(g) Concentration versus time data were collected for this reaction, and a plot of [A] versus time resulted in a straight line with a slope value of –4.00 x 10-5 mol/Ls. a) Determine the rate law, the integrated rate law and the rate law constant for this reaction. b) If the initial [C2H5OH] was 1.25 x 10-2 M, calculate the half-life for this reaction. Assessment: Go over the 2 problems and assign the book problems to be completed before the end of the hour. Check and go over the answers tomorrow. Question #3 from the 2003 AP Chemistry Exam - Free-Response section Closure: Continued tomorrow. Materials Needed, Resources, etc.: Textbook – Zumdahl, 5th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company, 2000.