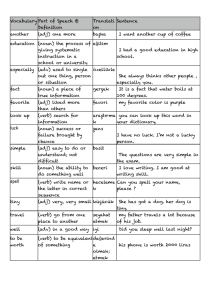
Social Science Vocabulary List
advertisement

GLOSSARY OF KEY SOCIAL SCIENCE “WHY WORDS” These words can also be accessed on Quizlet at: https://quizlet.com/88225275/key-social-science-terms-flash-cards/ It will be useful to review with students the following words used in the definitions: SYNONYMS—words that mean roughly the same thing; ANTONYMS—words that mean the opposite; NOUN—person, place, or thing, logically preceded by an article such as “a,” “an” or “the” Example: DEMOCRACY. “We do not live in a DEMOCRACY,” or “She believes in DEMOCRACY.” ADJECTIVE— descriptive word, telling something about a noun. Example: DEMOCRATIC. “The United States is a DEMOCRATIC Republic”, or “He is very DEMOCRATIC.” Note: Words have many definitions; these are not all the definitions, only the ones commonly used by social scientists. ABSOLUTISM: The political doctrine and practice of unlimited, centralized authority and absolute sovereignty, as vested especially in a monarch or dictator. The essence of an absolutist system is that the ruling power is not subject to regularized challenges or checks by any other agency, be it judicial, legislative, religious, economic, or electoral. ACCESSIBILITY: Openness to coming in or near. “Wheelchair ramps help give buildings the accessibility required by the Americans with Disabilities Act.” Syn: Availability Ant: Exclusivity. Adj: Accessible. ACCOUNTABILITY: Responsibility; liability; being answerable to others for one’s actions. “Government officials are accountable to the people they are supposed to serve” “Everyone is morally accountable for their actions.” Adj: Accountable. Antonym: Unaccountable. ANARCHY: The absence of government; chaos. Also (noun for a person): anarchist; adj: anarchic. ARISTOCRACY: Rule or government exclusively by an upper class or elite. Traditionally in history, this upper class was permanent, by inheritance from one’s father, and therefore unearned and not “meritocratic” (see MERITOCRACY). Syn: OLIGARCHY (rule or government by only a special few). Ant: DEMOCRACY (rule by all the people through voting.) Related: PLUTOCRACY (rule by a special few because they are the richest). Also related: MONARCHY—rule by a single chief executive who inherits the right to rule; related to EMPIRE, rule by an emperor. Note: a REPUBLIC, in the modern sense, is a semi-democratic government because we do not necessarily vote on all laws and policies, but rather elect REPRESENTATIVES who use their judgment to decide FOR us; thus, the Constitution of the U.S. sets up a REPRESENTATIVE DEMOCRACY, also known as a REPUBLIC. In 1787, this Republic was perhaps as aristocratic as it was democratic, but Constitutional Amendments (such as the 13th Amendment banning slavery and the 19th Amendment granting the vote to women), has made our nation less aristocratic and more democratic. A related noun form of aristocracy is ARISTOCRAT; an adjective form is ARISTOCRATIC. When spoken, the stress changes as follows: “A ri STOC’ racy” (stress on 3rd syllable), but “a RIST’ ocratic” (2nd syllable) Also related: SLAVOCRACY—an aristocracy ruled by slave owners (slavocrats) as in the pre-civil war South. ASSEMBLY: a public meeting of a group of people. Also used to mean a legislative (lawmaking) body in some states. Also a verb: “to assemble,” which is a Constitutional right under the First Amendment AUTHORITY: Power or right to make law & command obedience. Also, a person who commands. Syn: Rule, dominion. Ant: Usurper (one who tries to command but has no right to do so.) Verb: Authorize. AUTHORITARIANISM: The principle of blind submission to authority, as opposed to individual freedom of thought and action. In government, authoritarianism denotes any political system that concentrates power in the hands of a leader or a small elite that is not constitutionally responsible to the body of the people. Authoritarian leaders often exercise power arbitrarily and without regard to existing bodies of law, and they usually cannot be replaced by citizens choosing freely among various competitors in elections. Totalitarian regimes adhere to these principles. AUTOCRACY: Absolute authority of one person over all; dictatorship. Adj: autocratic. Noun: autocrat. AUTONOMY: Independence; authority over oneself; freedom from dictatorship. Adj: Autonomous BIGOTRY: Prejudice in any form, whether racial, religious, class, gender-based, or based on sexual orientation, etc. Adj: (a person might be) BIGOTTED; Noun: a prejudiced person is a BIGOT. CAPITALISM: An economic system by which the means of production are privately owned and production is guided and income distributed largely through the operation of markets. It’s also called a free market economy, or free enterprise economy, and is dominant in the Western world today. CIVILITY: Decency; politeness; courtesy; good manners Originally (still?) thought of as necessary to CIVILIZATION since a CIVILIZED person is courteous and kind, even to those with whom they differ. COMMUNITY: Society of people (such as a town or neighborhood) having common rights and privileges, and ties with each other. Syn: Commonwealth, commonweal. “The commons”: Shared areas. Related: integration (diverse peoples living in the same community with common rights & privileges); segregation (people living in separate areas to stress that they do not share common rights & privileges.) CONSERVATISM: A political and social philosophy that promotes retaining the traditional social order, traditional morality & hierarchies of authority. A person who follows the philosophies of conservatism is referred to as a traditionalist or conservative. Some conservatives seek to preserve things as they are, emphasizing stability and continuity, while others oppose modernism and seek a return to "the way things were." CONSTITUTIONALITY: The state of being consistent with or authorized by the state or national Constitution (or frame of government.) “The Supreme Court’s job is to rule on the constitutionality of disputed laws; they compare laws with the Constitution and can rule laws constitutional or unconstitutional.” Note: this responsibility of the Supreme Court is known as “judicial review.” CREDIBILITY: Believability; trustworthiness. Adj: Credible. Ant: Incredible “Not every internet source has credibility; we must think about what gives a source credibility so we aren’t misled.” DEMOCRACY: Rule by all the people through voting. DEMOGRAPHY: The study of statistics such as births, deaths, income, or the incidence of disease, which illustrate the changing structure of human populations. It also can be used in a broader sense as the composition of a particular human population. DEPENDENCY: Reliance on others for support, aid or existence. Ant: Independence, or the “spirit of rugged individualism” (Herbert Hoover.) “Morality may require we assist the needy, but if possible it is best to avoid permanent dependency.” See also INDIVIDUALITY DIVERSITY: Variety, and the value of seeing different kinds of people in a society as positive. “There is a great diversity of races and religions in a free country.” Adj: Diverse. Related: Heterogeneous (having great diversity) and homogeneous (having just one kind of person and no diversity.) Also, heterogeneity and homogeneity (diversity and the lack of diversity.) Related: PLURALISM: the belief that diversity is desirable; and its opposite, PREJUDICE—the assumption that differences are not good and the tendency to “pre-judge” people who are different as bad. The adjective form of PREJUDICE, to describe a biased or bigoted person, is PREJUDICED (note the “ed”) “A civilized, democratic person values DIVERSITY, but bigots are prejudiced.” Also related: “E PLURIBUS, UNUM”—Latin, “From Many, One [Nation]” ECOLOGY: Study of the relationship between humans and other living organisms; also, healthy environmental practices in the management of natural resources. ECONOMY: System of producing, distributing & consuming wealth. Adj: ECONOMIC ECONOMIC IS NOT a synonym of “ECONOMICAL,” which means inexpensive or “cheap”) (NOTE, EFFICIENCY: Ability to achieve desired results with a minimum of wasted effort, expense or waste. Ant: Waste; inefficiency. “Both conservatives and liberals agree on the value of efficiency in government.”Adj: Efficient. Similar: effectiveness, efficacy. Related adjectives: effective, effectual. ETHNICITY: a division of humankind linked together by common culture and language (not necessarily the same as “race.”) Adj: Ethnic. Ethnocentrism: attitude that one’s own culture is superior to all others. EQUALITY: The state of being neither inferior nor superior; having the same rights, respect and privileges. Related: MERITOCRACY, or “EQUAL OPPORTUNITY” (as distinguished from equality of RESULT, where everyone gets the same reward, meritocracy allows greater or lesser awards but, ideally gives each individual equal CHANCES to succeed.) Adjectives: equalitarian or egalitarian (both mean characterized by equality.) “Communists consider themselves the most egalitarian because they do not believe in granting greater rewards to people with greater abilities; noncommunists think unequal talents and efforts should result in unequal rewards, but many believe public education is essential to guarantee equality of opportunity, as distinguished from equality of result.” (see MERITOCRACY) FASCISM: A political ideology with an extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the rule of elites, and the desire to create a “people’s community”, in which individual interests would be subordinated to the good of the nation. It was a movement that dominated many parts of central, southern, and eastern Europe between 1919 and 1945. FEDERALISM: The mode of political organization that unites separate state and local governments within an overarching national political system in such a way as to allow each to maintain its own fundamental political integrity. Federal systems do this by requiring that basic policies be made and implemented through negotiation in some form, so that all the members can share in making and executing decisions. State and local governments typically have somewhat separate responsibilities. FEUDALISM – The system of political organization prevailing in Europe from the 9th to about the 15th centuries having as its basis the relation of lord to vassal with all land held in fee and as chief characteristics homage, the service of tenants under arms and in court, wardship, and forfeiture. GEOGRAPHY: The study of the physical features of the earth and its atmosphere, and of human activity as it affects and is affected by these, including the distribution of populations and resources, land use, and industries. It also encompasses the nature and relative arrangement of places and physical features. HIERARCHY: Pronounced “High’-er-Arky”: a group of persons arranged in order of rank, grade, class, etc. Also known as a “pecking order” or a “caste system” if it is rigid. A hierarchy that is UNEARNED, such as aristocracy or monarchy, has traditionally been frowned on as “un-American” since it is not meritocratic. (see also MOBILITY.) Adjective: hierarchical. Antonym: equality. “Military decision-making is often more hierarchical than political decision-making in a democracy; voters in a democracy are presumed equal but officers near the top of the hierarchy (such as a president, general or admiral) outrank those lower in the chain of command.” Note: Except for communists, most people believe SOME hierarchy may be earned and useful to society, to maintain order and give incentives for productive behavior. HUMANITY: Kindly sympathy for others; MERCY. “The eighth amendment bars cruelty and requires humanity even to convicts.” Ant: CRUELTY. Also a reference to “HUMANKIND” Related adjectives: HUMANE, HUMANITARIAN; related but not quite synonymous is HUMANISM: the philosophy or belief that human beings may solve the world’s problems on their own (even without the aid of a divine power.) HUMILITY: Modesty; absence of pride. “Popularity in a democracy demands at least a little humility.” HYPOCRISY (pronounced “hip-POCK’- rasy”): Pretending (claiming) to be good and moral, but not living up to one’s self-proclaimed high standards. “Don’t claim to have high ideals if you’re not going to ‘walk the talk’: that’s just being hypocritical.” (From “hypo,” UNDER, and “criteria,” STANDARDS.) Ant: Honesty; integrity. Adj: HYPOCRITICAL (pronounced “HIP’po-CRIT’-ical”) IDENTITY: Individual self-definition. “For some people, their family name, nationality, class or ethnic group is an important part of their identity; others determine their identity without reference to those.” Verb: identify. Related noun: identification. Also: Identity crisis; identity politics. IDEOLOGY: Opinions; ways of thinking; idealistic beliefs of a group or individual. “It may not be possible to take ideology out of politics, but decision-makers must separate fact from fiction and opinion.” Examples: communism, liberalism, libertarianism, conservatism, fascism. IDEOLOGIES are generally political, and like “IDEALS” they are beliefs about how the world SHOULD BE as distinguished from mere reality. IMPERIALISM: The state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas. Because it always involves the use of power, whether military force or some subtler form, imperialism has often been considered morally reprehensible, and the term is frequently employed in international propaganda to denounce and discredit an opponent’s foreign policy. INDIVIDUALITY: Nonconformity; leading one’s own life and making up one’s own mind singly, regardless of what others think or do. Adj: Individualistic. Ant: Conformity; obedience; ”groupthink” Related: INDIVIDUALISM: the belief that government should not discourage or punish individuality. INTEGRITY: Soundness of moral habits; uprightness, honesty and sincerity. “Ability is not enough in a leader; he or she must also have INTEGRITY.” Syn: Morality or Ethicality. Ant: Corruption. Integrity is CENTRAL to Bulldog PRIDE because our reputation depends on it more than any other value. INTERNATIONALISM – The principle of cooperating among nations for the promotion of their common good, sometimes as contrasted with nationalism, or devotion to the interests of a particular nation. INTERVENTIONISM – A government policy or practice of doing things to directly influence the country’s economy or the political affairs of another country. The most common applications of the term are for economic interventionism (a state's intervention in its own economy), and foreign interventionism (a state's intervention in the affairs of another nation as part of its foreign policy). ISOLATIONISM: A national policy of avoiding political or economic entanglements with other countries. Isolationism has been a recurrent theme in U.S. history. It was given expression in the Farewell Address of Pres. George Washington and in the early 19th-century Monroe Doctrine. JINGOISM – Extreme patriotism, especially in the form of aggressive or warlike foreign policy. JUDICIARY: The court judges and Supreme Court Justices; the judicial branch as a whole. “The president makes appointments to the judiciary; the Senate confirms or denies these judicial appointments.” Adj: Judicial. LIBERALISM: A political philosophy which stresses equality, experimentation and toleration in order to reduce unjust barriers to opportunity for dissenters and the less-fortunate. Synonym: “Progressivism.” Liberals typically believe that government is necessary to protect individuals from being harmed by others; but they also recognize that government itself can pose a threat to liberty. LIBERTY: Freedom from captivity or slavery. Ant: slavery, tyranny. But differs from “libertine,” one who indulges one’s passion, especially sexual passion, without ethical restraint (also known as “license” or “licentiousness.”) “Liberty is about our rights; morality is about what’s right or wrong.” Verb: liberate (to free); related noun: LIBERATION (the freeing of a person or group, e.g.,”women’s liberation.”) MARXISM: The political, economic, and social principles and policies advocated by Karl Marx, which includes the theory and practice of socialism including the labor theory of value, dialectical materialism, the class struggle, and dictatorship of the proletariat until the establishment of a classless society. Marx believed that the struggle between social classes is a major force in history and that there should eventually be a society in which there are no classes. MERITOCRACY: a system of hierarchy that has equal opportunity and justice, that is, each person gets the ranking and rewards that they earn and deserve—no more and no less—without regard to friends, relations, origins, luck or inheritance. Ant: Aristocracy (unmerited ranking by inheritance); communism (equality without opportunity to rise above anyone else.) Adj: meritocratic. MOBILITY: Ability to move around, and, in social science and history, often refers to the ability of a person to move upward in social and economic status. “A meritocratic society allows for people of every race, religion and gender to move up the social ladder to a higher position.” Ant: Caste system. MONARCHY: Kingship; government by an aristocratic ruler who inherits the job, such as a king or czar. MONOPOLY: Exclusive control of a line of business; lack of competition. Adj: Monopolistic. Syn: Trust MORALITY: Right conduct; ethicality; staying true to principles of right versus wrong. Verb: moralize—to speak about matters of right and wrong. BUT “moralism” is NOT really synonymous with “true morality,” since it implies being judgmental, but not necessarily moral; a moralistic person may be hypocritical. NATIONALISM – The ideology based on the premise that the individual’s loyalty and devotion to the nationstate surpass other individual or group interests. While elements have been present throughout history, it was not until the end of the 18th century that nationalism began to be a generally recognized sentiment molding public and private life. NATIVISM: The political position of demanding a favored status for certain established inhabitants of a nation as compared to claims of newcomers or immigrants. Nativism typically means opposition to immigration and support of efforts to lower the political or legal status of specific ethnic or cultural groups because the groups are considered hostile or alien to the natural culture, and assumptions that they cannot be assimilated OLIGARCHY: Rule or government by the few, not the many. PATRIOTISM – The love for, or devotion to, one’s country. POPULISM – A political program or movement and style that appeals to elements of society that believe their interests are being ignored by powerful and wealthy decision-makers in the establishment. Some populists are reactionary, while others are liberal; and some like William Jennings Bryan were liberal on some issues and reactionary on others. PRIMARY (SOURCE): In social science, a source of information that was there at the time and place of an historical event (as opposed to a SECONDARY source which was not there at the time, but later.) Note: Primary sources do not necessarily have more credibility than secondary ones, as they may be self-interested parties as easily as a secondary one, such as an historian. PRODUCTIVITY: Bringing forth a positive result, product or service through effort. “There can be no prosperity without productivity, but the productive should share in the fruits of their productivity, or we won’t really have a meritocracy.” Adj: Productive. Ant: laziness; waste. PRODUCTIVITY is the first value in Bulldog “PRIDE;” it is also an especially important requirement for a good ECONOMY. RATIONALITY: Power of REASON; thinking (as oppose to merely feeling or having opinions); intellect. Related: INTELLECTUALITY. Antonym: IRRATIONALITY, confused thinking or non-thinking. Also related: RATIONALE (reason, motive for an action or proposed action.) BUT to “rationalize” is neither honest nor ethical; it is to claim a reasonable motive instead of the real, selfish one. RESPONSIBILITY: follow-through; being liable and accountable for duties and promises. Related: Liability. To be liable is to be legally bound to make good any loss or damage that is your fault; “you could get sued if you are liable.” In our Bulldog PRIDE acronym, RESPONSIBILITY means dependability and honor SOCIALISM: A social and economic doctrine that calls for public rather than private ownership or control of property and natural resources. According to the socialist view, individuals do not live or work in isolation but live in cooperation with one another. Furthermore, everything that people produce is in some sense a social product, and everyone who contributes to the production of a good is entitled to a share in it. Society as a whole, therefore, should own or at least control property for the benefit of all its members. COMMUNISM is a more extreme form of socialism which advocates methods of change that are more rapid or more violent than election, to arrive at equality of result and not merely of opportunity.” It’s a political and economic doctrine that aims to replace private property and a profit-based economy with public ownership and communal control of at least the major means of production (e.g., mines, mills, and factories) and the natural resources of a society. SOVEREIGNTY: (has a silent “g”; pronounced “SAHV’-er-en-tee”): Right to exercise authority over an area and its boundaries; right to govern (oneself or one’s country) without interference from outside powers. “The United Nations seeks to guarantee every nation the right to its own sovereignty and security from invasion.” adj: Sovereign (“SAHV-er-en”), ruling (adj.) or the ruler (noun.) Also, in U.S. History in the 1850s,”Popular sovereignty,” Senator Douglas’ doctrine that important questions like slavery should be decided by voters of a community at the STATE and LOCAL level, not by the national Congress. TECHNOLOGY: The branch of knowledge that deals with the creation and use of technical means, including machines and machinery, and their interrelation with life, society, and the environment. Of importance is the purposeful application of information in the design, production, and utilization of goods and services, and in the organization of human activities. THEOCRACY: Government by religious officials of one established state church. “Our Constitution forbids any establishment of religion or religious test for office because the Framers of it did not want us to turn into a theocracy.” Ant: religious freedom. Adj: Theocratic. Noun: (person) Theocrat. TYRANNY: Dictatorship; extreme lack of freedom. “Resistance to tyranny is a personal and patriotic duty.” Syn: despotism. Ant: liberty. Adj: Tyrannical. The pronunciation is tricky, because a dictator is a tyrant (pronounced TIE’-rant), but a government run by a tyrant is a tyranny (pronounced TEER’-a-nee); Adj: tyrannical (TEER’-an-ical,) or tyrannous (TEER’-an-nous). Verb: tyrannize (TEER-an-nize)—to govern as a despot (which is a tyrant.) UNITY: Togetherness as one; agreement; harmony; oneness of sentiment or affection. “It is no easy feat to have so much liberty and diversity, and still have the essential harmony and unity we need to get along; but ‘united we stand, divided we fall!’” Verb: Unify. Adj: United. Ant: Division.