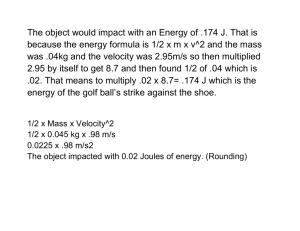Work Problems V A F & W
advertisement

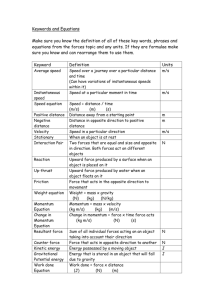
Work is a force that moves through a distance. W=FD How much work is done when a 50kg (500N) person climbs a ladder to a height of 2.5m? W=F·D W= (mg)D W= ( 50kg 9.80m/s2) · 2.5m W= 1225Nm or 1200Joules 1Nm = 1Joule How much work is done when a force of 1000N is used to slide a 20kg crate a distance of 4.0m across a floor? W= F·D W= 1000N 4.0m W= 4000J How much power is required when a force of 1000N is used to slide a 20kg crate a distance of 4.0m across a floor in 20s? Power is the rate at which work is done. P=Work /time or P=W/t P=W/t P= (FD) / t P= (1000N 4.0m) / 20s P= 200J/s or 200Watts 1J/s = 1 Watt How much Gravitational potential energy does a 1.0kg book have when it sits on a shelf 1.0m above the floor? Energy is the capacity to do work. Gravitational Potential Energy is the energy an object has with respect to some reference point within a gravitational field. GPE= mass times gravity times height or GPE = mgh GPE= 1.0kg · 9.8m/s2 ·1.0m GPE= 9.8J 1kgm2/s2 = 1Joule What is the Kinetic energy of a 2.0kg toy car that has a velocity of 2.0m/s? Kinetic Energy is energy of motion. KE = ½ mv2 KE= ½ 2.0kg · (2.0m/s)2 KE= 4J What is the momentum of a 2.0kg toy car that has a velocity of 2.0m/s? Momentum is strength of motion Momentum = mass times velocity ρ= mv ρ= 2.0kg 2.0m/s ρ= 4kgm/s Define “force” Explain how force is calculated and show an example problem. What is net force? Suppose a 200N block is sitting on a shelf. ( See Diagram A) What is the weight of the block? In what direction is the weight acting? Assuming the shelf CAN hold the block, how much force is the shelf applying to the block? d) In what direction is the shelf applying a force to the block? e) What is the net force on the block? 1. 2. 3. 4. a) b) c) Diagram A 5. 1N equals 1kgm/s2. What is a Dyne equal to? 6 How much force is required to accelerate a 1800kg car at 3.00m/s/s? 7. What is the weight of the 1800kg car in question G? 8. What is the difference between mass and weight? 9. What unit is weight measured in? 10. What is inertia? 11. What do automobile seatbelts have to do with inertia? 12. A 1813.939kg crash test car with a velocity of 20.000m/s strikes a concrete wall and comes to a complete stop in 1.300s. a) What is the weight of the car? b) What is the acceleration of the car? ( remember: a=vf-vi/t) c) What is the force of impact? d) Given that 1kg=9.8N and 1kg = 2.20lb. Convert the impact force to pounds. 13. A skydiver jumps from an airplane and freefalls until he reaches terminal velocity. a.) Explain what terminal velocity is. b.) What is the net force acting on once the skydiver once he reaches terminal velocity? c.) What is his downward acceleration before and after he reaches terminal velocity?