Unit 5 Test Review
advertisement

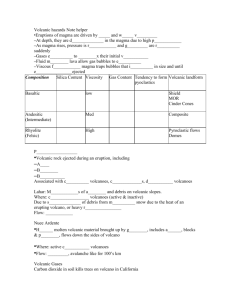
Unit Five Test Review Name ________________________ Hour _____ Date _____________ Use your reading guides, power point lecture notes, flashcards/quizzes and lab handouts to answer the following questions. Study! 1. Draw a cross-section of the earth’s interior. Label: crust, mantle, inner core, outer core, lithosphere and asthenosphere. Indicate (as best you can) where most of the Earth’s volume is located. 2. What does a P-wave travel through? An S-wave? 3. Explain how the behavior of seismic waves gives us an idea of the interior of the Earth. (Be sure to discuss the behavior of both P and S waves in your explanation.) 4. Our “best guess” of the Earth’s interior contains some uncertainties. List and discuss two. 5. Compare and contrast continental and oceanic crust. 6. Where do convection currents occur? Explain how temperature and density differences create these currents. 7. Define slab-pull. 8. Define ridge-push. 9. Convection currents (thermal convection) that drive plate motion is caused by an _____________ distribution of __________ . 10. Define whole-mantle convection AND deep-layer convection. 11. Explain our “best-guess” on how the Earth’s magnetic field is generated. 12. What are two uncertainties with our “best-guess” magnetic field explanations? 13. Lithospheric plates contain both ______________ and ______________ crust. 14. Define divergent boundary. 15. Define convergent boundary. 16. Define transform boundary. 17. Complete the following chart. Check features associated with each boundary. Volcanic NonDeep Mntns. Volcanic E-Q Mntns. Shallow E-Q Rift Subduction Zones Zones Convergent (C-C)_ Convergent (C-O) Convergent (O-O) Divergent Transform 18. Define hot spot. 19. Define seafloor spreading. 20. How do the following support seafloor spreading? Magnetic Polarity: Rock ages (distance from MOR): 20. Name three factors that plate tectonics CANNOT yet explain. Trenches Volcanic Island Arcs Location Example 21. Define Moho. What happens to the speed of seismic waves at this boundary? Why? 22. Define focus. 23. Define epicenter. 24. Define fault. 25. What does the Richter scale measure? Mercalli scale? 26. How is an earthquake’s epicenter determined? 27. Define locked faults. Why is this an important feature for seismologists to observe? 28. Define Elastic Rebound Theory. 29. How would an offset fence support the Elastic Rebound theory? 30. Where do most earthquakes occur? 31. Complete the following chart on earthquake occurrences. How occurs Landslides Fire Tsunamis 32. Define liquifaction. Human implications 33. On average, lithospheric plates move A. a few centimeters per year B. a few inches per year 34. Define viscosity. 35. How does viscosity and gas composition impact the explosiveness of volcanoes? 36. How does the temperature of magma impact viscosity? 37. Complete the following table. Check the appropriate categories. Cinder Composite Shield Fluid Basaltic Magma Violent Quiet 38. Describe the shape of cinder cones. 39. Describe the shape of composite (strato) volcanoes. 40. Describe the shape of shield volcanoes. 41. Describe factors that determine quiet volcanic explosions. 42. Describe factors that determine violent volcanic explosions. Highly Viscous Magma