Volcanic hazards Note helper
advertisement
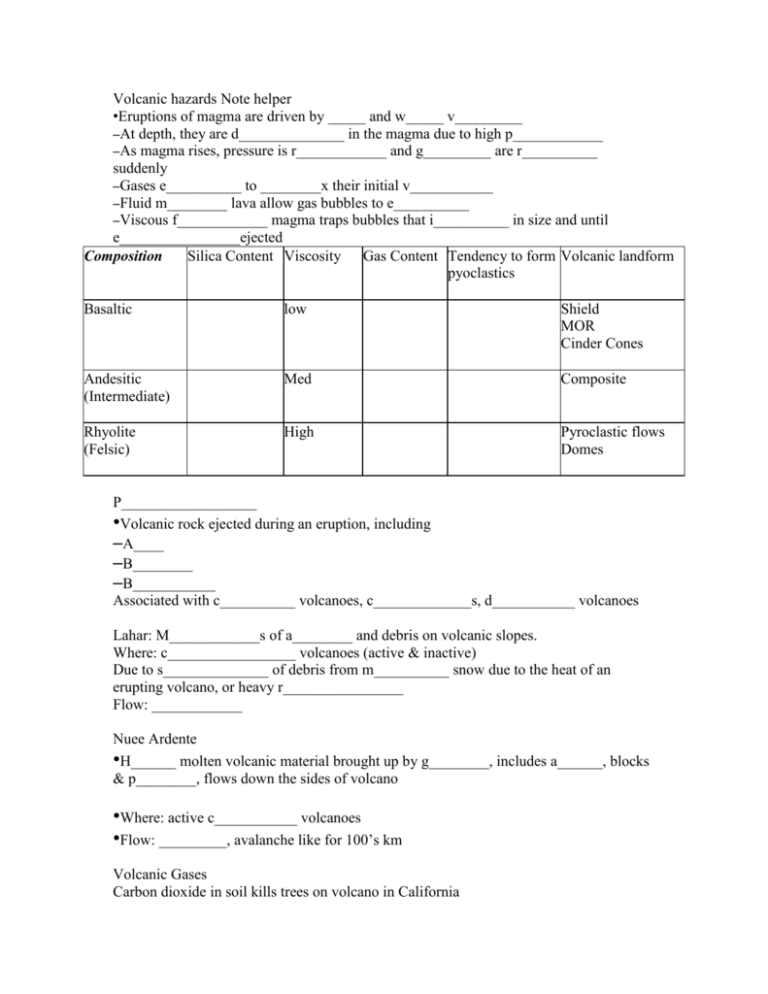
Volcanic hazards Note helper •Eruptions of magma are driven by _____ and w_____ v_________ –At depth, they are d______________ in the magma due to high p____________ –As magma rises, pressure is r____________ and g_________ are r__________ suddenly –Gases e__________ to ________x their initial v___________ –Fluid m________ lava allow gas bubbles to e__________ –Viscous f____________ magma traps bubbles that i__________ in size and until e________________ejected Silica Content Viscosity Gas Content Tendency to form Volcanic landform Composition pyoclastics Basaltic low Shield MOR Cinder Cones Andesitic (Intermediate) Med Composite Rhyolite (Felsic) High Pyroclastic flows Domes P__________________ •Volcanic rock ejected during an eruption, including –A____ –B________ –B___________ Associated with c__________ volcanoes, c_____________s, d___________ volcanoes Lahar: M____________s of a________ and debris on volcanic slopes. Where: c_________________ volcanoes (active & inactive) Due to s______________ of debris from m__________ snow due to the heat of an erupting volcano, or heavy r________________ Flow: ____________ Nuee Ardente •H______ molten volcanic material brought up by g________, includes a______, blocks & p________, flows down the sides of volcano •Where: active c___________ volcanoes •Flow: _________, avalanche like for 100’s km Volcanic Gases Carbon dioxide in soil kills trees on volcano in California Volcanic Ash •Fine grained, travel __________’s km carried by wind •Flows down hill in Nuee Ardentes Phreatic eruptions are s_______-driven explosions that occur when w________ beneath the ground or on the surface is h_________ by magma, lava, hot rocks, or new volcanic deposits causing an e__________ of s_________, water, a______, blocks, and b________. P___________ Eruptions •Increased local s___________ •B__________________ of the mountain •I____________ in g________s being emitted (carbon dioxide, sulfur, water)