Poetic Structure
advertisement
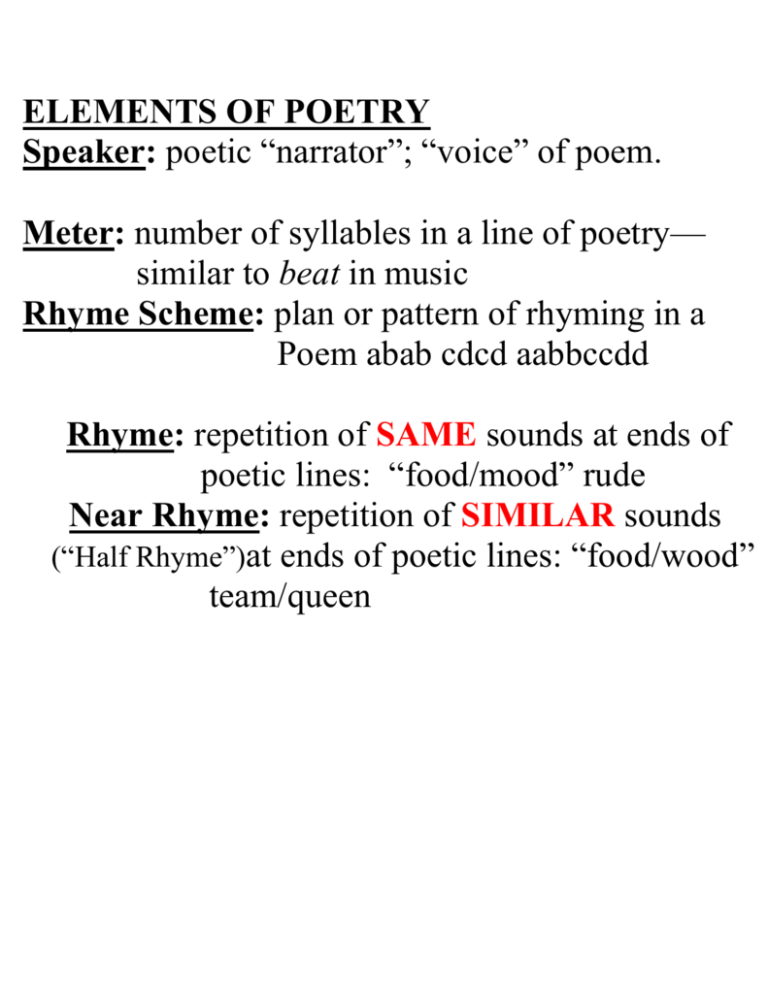
ELEMENTS OF POETRY Speaker: poetic “narrator”; “voice” of poem. Meter: number of syllables in a line of poetry— similar to beat in music Rhyme Scheme: plan or pattern of rhyming in a Poem abab cdcd aabbccdd Rhyme: repetition of SAME sounds at ends of poetic lines: “food/mood” rude Near Rhyme: repetition of SIMILAR sounds (“Half Rhyme”)at ends of poetic lines: “food/wood” team/queen Stanza: a group of lines in a poem—similar to a paragraph in prose. Prose: writing in sentences & paragraphs FOUR BASIC STANZAS Couplet: two-line stanza Heroic Couplet: ten syll./rhymed Quatrain: four-line stanza; most popular stanza in English poetry Sestet: six-line stanza Octet: eight-line stanza TYPES OF POEMS Haiku: Japanese-inspired; 5-7-5 meter Narrative Poem: poem that tells a story Lyric Poem: short poem that expresses feelings & thoughts of speaker; in ancient times, played to music of a lyre. Free Verse: 1)usually unrhymed 2) no consistent meter 3) relies heavily on cadences and cataloguing. Verrrry non-traditional. “Writing free verse is like playing tennis without a net.” --Robert Frost Ballad Stanza: a type of LYRIC POEM that usually includes the following: -Quatrain -Rhyme Scheme: abab cdcd efef -Meter: 8-6-8-6 Amazing grace, how sweet the sound,a That saved a wretch like me;b I once was lost, but now am found,a Was blind but now I see!b End-stopped Lines: pause/stop reading at end of line, usually for punctuation Enjambed Lines: do not stop reading, b/c the thought continues onto the next line. --“Enjambment” THE SONNET Italian Sonnet: invented by Petrarch (Renaissance poet & scholar) *14 lines *1 Octet, 1 Sestet *Rhyme Scheme: abbaabba cdcdcd *Ten syllables per line English Sonnet: a.k.a. “Shakespearean” *14 lines *3 Quatrains, 1 Couplet *Rhyme Scheme: abab cdcd efef gg *Ten syllables per line











