Sylvia S

Sylvia S. Mader; Biology
Reading Guide Chapter 5: Membrane Structure and Function
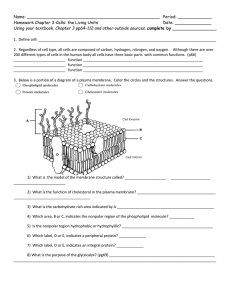
1) Draw a picture of a plasma membrane and label (use page 85 as a guide).
2) What is the function of cholesterol?
3) List three functions of the “glycocalyx” or sugar chains on the surface of the plasma membrane.
4) Why is it necessary for the plasma membrane to have a carbon chain (i.e.; glycoprotein) that acts as a “fingerprint”?
5) Add an integral protein to your plasma membrane (from question #1), and label this protein type using the list of integral proteins below, for the following:
* a protein that allows Cl
-
to pass through
* a protein that allows the cell to identify itself from foreign invaders such as a bacteria
* that builds or breaks down a macromolecule
* that runs the sodium/potassium pumps in a neuron
* that binds a growth hormone
Channel Proteins Carrier Proteins Cell Recognition Proteins Receptor Proteins Enzymatic Proteins
6) Define differentially permeable and give one example.
7) List three ways that passive and active transport differ.
8) Draw a picture of a blood cell in a 0.9% salt solution, a 5.0% salt solution and a 0.01% salt solution and label the solutions in each picture as hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic to the blood cell. Which picture represents “crenation”?
9) Draw a picture of a plant cell in a solution that will cause the plant cell to increase in turgor pressure.
10) Draw a simple picture of a plasma membrane with a proton pump and describe how a H
+
pump (also called a proton pump) would work in a cell.
11) How do large macromolecules (polypeptides, polysaccharides and polynucleotides) enter and/or exit a cell?
12) Define the following and give one example of each:
* adhesion junction
tight junction
gap junction
13) What are plasmodesmata?