standard close process definitions & practices
advertisement

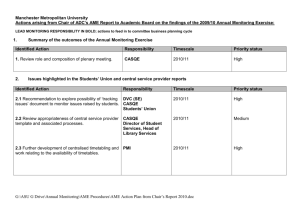
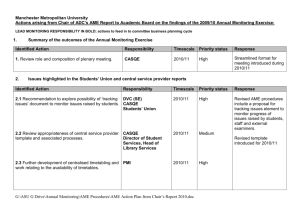
finreporting.com free online financial services STANDARD CLOSE PROCESS DEFINITION & PRACTICES finreporting.com free online financial services 1 Standard Close Process Definition& Practices Process Owner: The owner of the site close process is the site controller. Process Scope: The site close process starts with systems cut-off and ends with system transmission to corporate consolidations and the generation of standard financial reports. Based on our review of various site close processes, we have compiled and are recommending the following high level standard practices: Standard Practices: Every site should develop a calendar for the year with all major close related dates identified. This should be supported with details about feeder cutoff dates and interfaces, and a detailed listing of activities and responsibilities. finreporting.com free online financial services 2 All companies should accelerate their efforts to implement global integrated systems that capture data at source accurately. These systems validate financial data elements related to operational events against a centralized database containing all possible valid values and rules. With these systems in place, error corrections and rework during the close cycle resulting from invalid elements and code combinations will be minimized. Materiality limits need to be established for accruals and error corrections. These limits should be defined within the standard processes for finance. Any accruals or error corrections under $5,000 should be deferred to the following month. As a practice processes and checks should be put in place to ensure that not more than 2 days elapse between the occurrence of an economic event and the capture of the financial information relating to that event. Routine transaction-based feeder systems like accounts payable, accounts receivable, billing, inventory etc should be posted to the G/L daily/weekly. Intercompany invoices and charges should be processed daily. As a practice, all intercompany charges should be sent by the accounting month-end (AME). Most companies need to address & correct the issue of having a majority of intercompany transactions occurring at the end of the month, finreporting.com free online financial services 3 Payroll should be processed monthly or bi-weekly (depending on local customs). If any payroll payment for the month is scheduled to fall outside of the accounting month-end, an accrual should be made for this final payroll entry based on the last payroll journal entry. T&E should be booked daily if processed through A/P or monthly/bi- weekly if processed through payroll. T&E guidelines for punctual submission of expense statements should be communicated to all functional areas of your company and should be strictly adhered to. Maintenance contract billings should be run and posted two days before the accounting month-end. The deferred revenue related to these billings and the recurring entries from prior on-going contracts should be booked one day before the AME. Fixed Asset (F/A) in-process accounting should be tracked and posted daily/weekly in concert with the A/P postings and intercompany transacting. The final week's in-process transactions should be completed two days before AME. As much of the final week's A/P invoices as possible should be reviewed for inclusion in the current month's F/A additions entry. The remainder of the F/A related A/P invoices should be left in the in-process account and actioned the following month. F/A additions, deletions, transfers, etc transactions should be done during the month as these events occur. The posting of F/A transactions and the calculation and posting of depreciation should be done before the AME. finreporting.com free online financial services 4 AII routine reversals, recurring accruals, recurring allocations; allocations, based on standard or plan rates and other recurring entries should be booked six days before the AME. Sites should conduct business units (BU) reviews with functional managers four days before the AME. This meeting should be used to appraise the BU managers of potential revenue misses, and potential cost/expense overages or underspending as compared to the outlook/forecast. AII sub-Iedger to G/L high level reconciliations should be done at the time of postings. This high level reconciliation Should be a cursor check to ensure that the sub-Iedger materially ties to the GL balance. AII detailed reconciliations should be done immediately following the close cycle and completed within three weeks of the AME. AII sites should hold a post-close meeting to discuss risk items for the following month based on reconciliations, meetings with functional departments. The prior month close process should be discussed to identify roadblocks and to identify and resolve the root causes of errors. Errors should be classified (adjustments, reclassifications, rework, etc) and tracked to determine frequency, recurrence and to identify improvement opportunities. finreporting.com free online financial services 5 Standard Close Process Description: The process begins with: Systems cutoff and accounting month-end on the last Friday of the month. Suppliers to the process are: General Accounting Payroll, Accounts Payable, Travel & Entertainment, Fixed Assets, Customer Service Accounting, Intercompany Accounting, and Revenue Accounting. Inputs to the process are: Timely accurate; and error free journals from Payroll, Travel & Entertainment, Fixed Assets, Accounts Payable, Customer Service, Revenue and Intercompany Accounting. The Process ends with: The system files transmitted to corporate consolidations and financial standard management reports generated. Outputs of the process activities are: Timely accurate and error free journals, non-GL items, financial statements, and system file. Customers of the process activities are : General Accounting Controller Planning Manager, Industry/BU Managers and Corporate Consolidations. finreporting.com free online financial services 6 STANDARD CLOSE PROCESS BLOCK DIAGRAM Supplier Input Owner : Site Controller /Finance Payroll Dept. Payroll , A/P Dept Finance Dept. Payroll Exp. & Liabilities T&E Exp. &Liabilities Finance & Deprec. Exp. Maint Revenue Payables Exp. Inventory & order system Revenue & A/R InterCo Chgs Posted prior to AME Only week 4 activity posted on AME Posted prior to AME CS Acctg. A/P Revenue Acctg Revenue Acctg InterCo Acctg Revenue Acctg Accounting Reports Reserves, Provisions & Releases Manual JEs Allocations Adjustments Posted prior to AME Only week 4 activity posted on AME 1 AME Consolidation Data Accounting finreporting.com free online financial services Customer Journal Entries Accounting Journal Entries Allocations Manual JE s Accounting Only week 4 activity posted on AME Only week 4 activity posted on AME Only Friday AME Posted. Remainder accrued to the forced record acct 3 AME + 2 WD 2 AME + 2WD 4 AME + 3WD 5 AME + 3WD Accounting Accounting Output P&L Balance Sheet, non-GL Items 6 AME + 4WD System File 7 AME + 5WD Standard Financial reports Controller Planning Mgr Corporate Consolidati ons Industry / BU Managers Activities : 1. Systems cutoff. 2. Finalize Revenue and order system 3. Finalize other cost of revenue, marketing, selling G&A& R&D 4. GL translation and business review 5. Finalize non-GL reporting elements 6. Load data into system, validate and transmit 7. Print standard financial reports Legend AME – Acctg month end WD – Work days 7 Close Calendar Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 1 4 5 6 7 11 12 13 14 18 19 20 21 Maint Billings, F/A inprocess postings 25 26 InterCo cut-off, 27 Force record InterCo post system chgs received Friday, entries, print correcting entries, reports, high reserves, provisions, level recon, releases, allocations, adjusting translation entries Finalize Rev, Costs, and Expense 2 3 Reconciliations 28 Cursory Business Review, adjusting entries, reallocate, DOH, DRO rec, aging, inventory aging etc., extract system file 1 Business review Assumptions : Payroll is processed monthly T& E statements are processed through A/P finreporting.com free online financial services 4 Friday Saturday 2 Week 1 A/P , Inventory, 3 Billings, A/R , T&E and FIN in-process Posting 8 9 Week 2 A/P , Inventory, 10 Billings, A/R , T&E and FIN in-process Posting 15 17 Routine reversals, 16 Week 3 A/P , Inventory, recurring accruals, Billings, A/R , T&E and recurring alloc, FIN in-process Posting alloc based on std or plan rates etc, 22 Deferred Rev. , 23 AME and Systems cut-off 24 F/A journal entries Week 4 A/P , Inventory, Billings, A/R , T&E and FIN in-process Posting, Final InterCo charges processed 29 Load System File, Enter Non G/L information, Check Validations, Check for 5 30 Print BU reports, Management reports, & other Std Financial Rpts. 31 6 Post Close meeting 7 Depicts the close cycle 8 Conclusion Companies need to rigorously follow up the close cycle with formal reconciliations and with a post close meeting. During this meeting, companies should review risks and issues raised as a result of the reconciliations and should identify actions required to alleviate these risks. This forum should also be used to discuss the error log. Reviews of prior error logs should be done to track successes and to ensure that the same errors are not recurring. Root causes need to be identified by process owners, and actions and timeframes determined to resolve all errors. Companies should strive to minimize nonvalue added activities like reviews, inspection, checks, error correction, duplication of tasks, etc. within the close process . finreporting.com free online financial services 1