Answer
advertisement

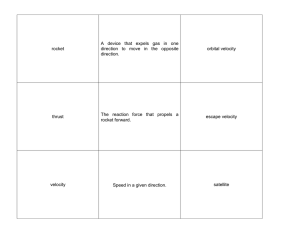
Student Name: __________________________________ Mrs. Lee – 8th Grade Physical Science Period #: ______ Page 1 Chapter 13 Practice Test – Answer Key ______ d 1) If the forces on any object are balanced, a moving object will ______. a) speed up b) slow down c) change direction d) continue on its original path ______ d 2) Which of the following could NOT happen if the forces on a moving object are unbalanced? a) the object will speed up b) the object will slow down c) the object will change direction d) the object will continue on its original path ______ a 3) What force holds the planets in orbit around the sun? a) gravity b) friction c) magnetic force d) atomic force ______ c 4) The force of gravity between two objects depends on the mass of the objects and the ______. a) speed at which they are moving b) amount of friction between them c) distance between them d) volume of the object ______ d 5) The force that propels a rocket forward is called ______. a) velocity b) escape velocity c) microgravity ______ d 6) Humans first landed on the moon in ______. a) 1957 b) 1961 c) 1971 d) 1969 ______ a 7) A ______ can carry satellites into orbit. a) space shuttle b) space station c) space probe d) thrust d) rover ______ c 8) Astronauts orbiting Earth experience microgravity because ______. a) gravity is not pulling on them b) their mass decreases when in space c) they are falling around Earth d) they are in a vacuum ______ b 9) Rockets were first developed in ______. a) the United States b) China c) Great Britain d) the Soviet Union ______ a 10) The goal of the Apollo program was to ______. a) land astronauts on the moon b) establish a permanent colony on the moon c) put the first American in space d) prove that the moon is solid ______ c 11) The main advantage of a multistage rocket is that ______. a) it requires less fuel to overcome gravity at the time of launch b) it can carry humans into space c) the total weight of the rocket is reduced as the rocket rises d) it can be reused after returning to Earth ______ c 12) The main purpose of a space station is to ______. a) show that different countries can work together b) use solar panels to produce electricity for people on Earth c) carry out observations and experiments in space d) take photos and readings of other planets in the solar system Ch 13 Practice Test – Answer Key 1 Student Name: __________________________________ Mrs. Lee – 8th Grade Physical Science Period #: ______ Page 2 Chapter 13 Practice Test – Answer Key ______ b 13) An example of an artificial satellite is ______. a) the Eagle b) Explorer 1 c) a rover d) the moon ______ d 14) Which is a cooperative effort among many different countries? a) the space race b) the Apollo program c) NASA d) the International Space Station ______ b (John Glenn) 15) The first American to orbit Earth was Alan Shepard. a) True b) False ______ a 16) In remote sensing, observation satellites collect data about Earth and other objects without being in direct contact. a) True b) False ______ a 17) A space probe is a spacecraft that has no human crew. a) True b) False ______ b (Escape Velocity) a) True 18) Orbital velocity is the velocity a rocket must reach to fly off into space. b) False ______ b (action) 19) The force of gases shooting out the back of a rocket is an example of a(n) reaction force. a) True b) False ______ a 20) The space race was between ______. a) the United States and the Soviet Union b) the Soviet Union and Great Britain c) the United States and China ______ b 21) Who was the first person in space? a) John Glenn b) Yuri Gagarin c) Alan Shepard ______ b 22) Which kind of spacecraft can carry satellites into orbit? a) space probe b) space shuttle c) space station ______ a 23) A large artificial satellite on which people can live is called a(n) ______. a) space station b) observation satellite c) space probe ______ b 24) An astronaut orbiting Earth experiences microgravity because ______. a) gravity is not pulling on the astronaut b) the astronaut is falling around Earth c) the mass of the astronaut increases in space ______ b (velocity) 25) The speed of a rocket in a given direction is its space spinoffs. a) True b) False Ch 13 Practice Test – Answer Key 2 Student Name: __________________________________ Mrs. Lee – 8th Grade Physical Science Period #: ______ Page 3 Chapter 13 Practice Test – Answer Key ______ b (satellite) 26) An object that revolves around another object in space is a space probe. a) True b) False ______ b (rovers) 27) Some space probes have small robots called satellite that collect samples from another planet. a) True b) False ______ a 28) Space has extreme temperatures because it is nearly a vacuum. a) True b) False ______ b (space spinoffs) a) True 29) Joysticks and memory metals are examples of rovers. b) False ______ a 30) Escape velocity is the velocity a rocket must reach to fly beyond a planet’s gravitational pull. a) True b) False ______ b 31) In a solid-fuel rocket, both the oxygen and the fuel are in liquid form. a) True b) False ______ a 32) Observation satellites collect data using remote sensing. a) True b) False The picture below shows Earth and a spacecraft that is orbiting Earth. The arrows from the spacecraft represent two different factors that keep the spacecraft represent two different factors that keep the spacecraft in orbit. Use the picture to answer the following 3 questions: ______ b 33) Interpreting Diagrams: What does the line labeled “A” represent? a) gravity b) inertia c) friction ______ a 34) Interpreting Diagrams: What force does the line labeled “B” represent? a) gravity b) inertia c) friction ______ a 35) Predicting: If Earth suddenly disappeared, what path would the spacecraft take? a) It would move in the direction of arrow “A”. b) It would move in the direction of arrow “B”. c) It would move in the opposite direction of arrow “A”. Ch 13 Practice Test – Answer Key 3 Student Name: __________________________________ Mrs. Lee – 8th Grade Physical Science Period #: ______ Page 4 Chapter 13 Practice Test – Answer Key Each picture below shows the position of a satellite that is in a geostationary orbit around Earth. Use the pictures to answer the following 2 questions: ______ c 36) Interpreting Diagrams: The “X” in Figure A shows the position of the satellite at 6:00 A.M. Later that same day, the satellite is in the position shown by the “X” in Figure B. What time is it in Figure B? a) 6:00 A.M. b) 9:00 A.M. c) 6:00 P.M. ______ b 37) Applying Concepts: Where will the satellite be the next morning at 6:00 A.M.? a) It will be at the “X” in Figure B b) It will be at the “X” in Figure A c) It will be midway between the “X” in Figure A and the “X” in Figure B Ch 13 Practice Test – Answer Key 4