rocket A device that expels gas in one direction to move in the
advertisement
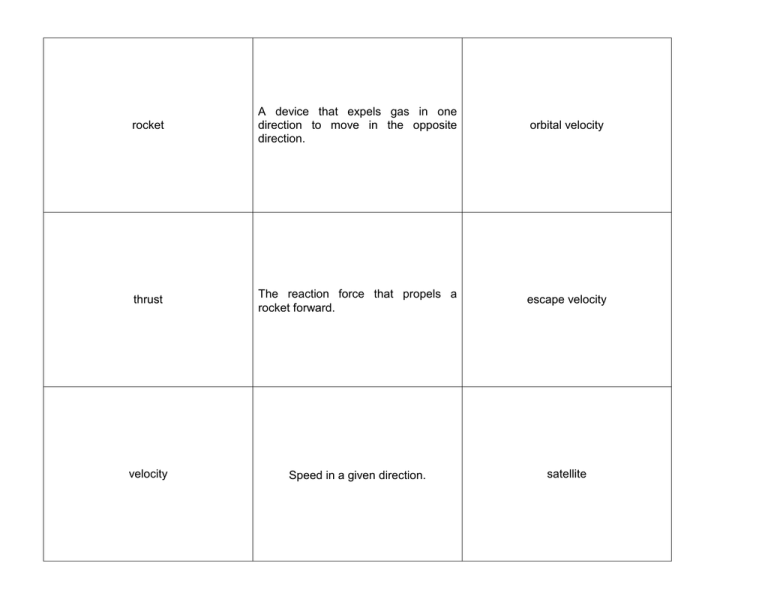
rocket A device that expels gas in one direction to move in the opposite direction. orbital velocity thrust The reaction force that propels a rocket forward. escape velocity velocity Speed in a given direction. satellite The velocity a rocket must achieve to establish an orbit around a body in space. space shuttle A spacecraft that can carry a crew into space, return to Earth, and then be reused for the same purpose. The velocity an object must reach to fly beyond a planet’s or moon’s gravitational pull. space station A large artificial satellite on which people can live and work for long periods. space probe A spacecraft that has various scientific instruments that can collect data, including visual images, but has no human crew. An object that revolves another object in space. around rover A small robotic space probe that can move about the surface of a planet or moon. space spinoff vacuum A place that is empty of all matter. remote sensing microgravity The condition of weightlessness in orbit. experiencing geostationary orbit ASTRONOMY An orbit in which a satellite orbits An item that has uses on Earth, but Earth at the same rate as Earth was originally developed for use in rotates and thus stays over the same space. place all the time. CHAPTER 2 SECTIONS 2.1 – 2.4 FLASHCARDS The collection of information about Earth and other objects in space using satellites or probes.







