Determining the Ka of Acetic Acid - SCH4U1-02-2010
advertisement
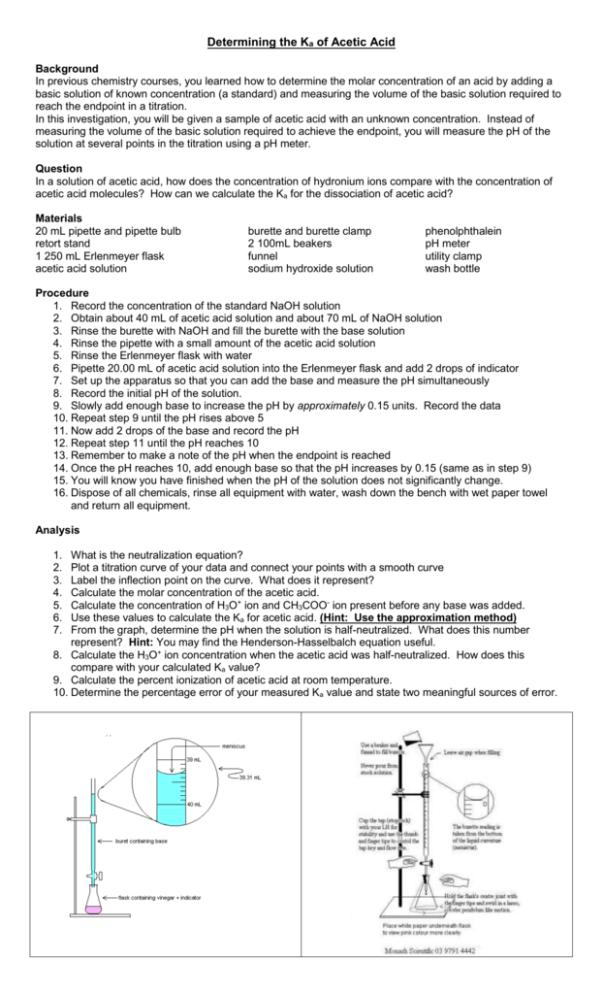
Determining the Ka of Acetic Acid Background In previous chemistry courses, you learned how to determine the molar concentration of an acid by adding a basic solution of known concentration (a standard) and measuring the volume of the basic solution required to reach the endpoint in a titration. In this investigation, you will be given a sample of acetic acid with an unknown concentration. Instead of measuring the volume of the basic solution required to achieve the endpoint, you will measure the pH of the solution at several points in the titration using a pH meter. Question In a solution of acetic acid, how does the concentration of hydronium ions compare with the concentration of acetic acid molecules? How can we calculate the Ka for the dissociation of acetic acid? Materials 20 mL pipette and pipette bulb retort stand 1 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask acetic acid solution burette and burette clamp 2 100mL beakers funnel sodium hydroxide solution phenolphthalein pH meter utility clamp wash bottle Procedure 1. Record the concentration of the standard NaOH solution 2. Obtain about 40 mL of acetic acid solution and about 70 mL of NaOH solution 3. Rinse the burette with NaOH and fill the burette with the base solution 4. Rinse the pipette with a small amount of the acetic acid solution 5. Rinse the Erlenmeyer flask with water 6. Pipette 20.00 mL of acetic acid solution into the Erlenmeyer flask and add 2 drops of indicator 7. Set up the apparatus so that you can add the base and measure the pH simultaneously 8. Record the initial pH of the solution. 9. Slowly add enough base to increase the pH by approximately 0.15 units. Record the data 10. Repeat step 9 until the pH rises above 5 11. Now add 2 drops of the base and record the pH 12. Repeat step 11 until the pH reaches 10 13. Remember to make a note of the pH when the endpoint is reached 14. Once the pH reaches 10, add enough base so that the pH increases by 0.15 (same as in step 9) 15. You will know you have finished when the pH of the solution does not significantly change. 16. Dispose of all chemicals, rinse all equipment with water, wash down the bench with wet paper towel and return all equipment. Analysis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What is the neutralization equation? Plot a titration curve of your data and connect your points with a smooth curve Label the inflection point on the curve. What does it represent? Calculate the molar concentration of the acetic acid. Calculate the concentration of H3O+ ion and CH3COO- ion present before any base was added. Use these values to calculate the Ka for acetic acid. (Hint: Use the approximation method) From the graph, determine the pH when the solution is half-neutralized. What does this number represent? Hint: You may find the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation useful. 8. Calculate the H3O+ ion concentration when the acetic acid was half-neutralized. How does this compare with your calculated Ka value? 9. Calculate the percent ionization of acetic acid at room temperature. 10. Determine the percentage error of your measured Ka value and state two meaningful sources of error.