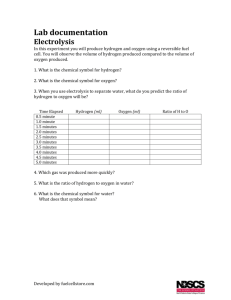
Hydrogen USPS Affirmative Table of Contents
advertisement

Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Hydrogen USPS Affirmative Table of Contents HYDROGEN USPS AFFIRMATIVE TABLE OF CONTENTS ..........................................................................................1 1AC 1/12 ..................................................................................................................................................................................3 1AC 2/12 ..................................................................................................................................................................................4 1AC 3/12 ..................................................................................................................................................................................5 1AC 4/12 ..................................................................................................................................................................................6 1AC 5/12 ..................................................................................................................................................................................7 1AC 6/12 ..................................................................................................................................................................................8 1AC 7/12 ..................................................................................................................................................................................9 1AC 8/12 ................................................................................................................................................................................ 10 1AC 9/12 ................................................................................................................................................................................ 11 1AC 10/12 .............................................................................................................................................................................. 12 1AC 11/12 .............................................................................................................................................................................. 13 1AC 12/12 .............................................................................................................................................................................. 14 INHERENCY ........................................................................................................................................................................... 15 HYDROGEN CARS NOT AVAILABLE ......................................................................................................................................... 15 NOT ENOUGH R & D............................................................................................................................................................... 16 PREVIOUS FAILED ................................................................................................................................................................... 17 OIL ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 18 SOLVES OIL ............................................................................................................................................................................ 18 SOLVES OIL ............................................................................................................................................................................ 19 SOLVES OIL ............................................................................................................................................................................ 20 SOLVES OIL ............................................................................................................................................................................ 21 TRANSITION POSSIBLE ............................................................................................................................................................ 22 ENVIRONMENT..................................................................................................................................................................... 23 SOLVES EMISSIONS ................................................................................................................................................................. 23 SOLVES EMISSIONS ................................................................................................................................................................. 24 HYDROGEN ECONOMY SOLVES CLIMATE CHANGE .................................................................................................................. 25 ADD-ON ADVANTAGES....................................................................................................................................................... 26 USPS ADVANTAGE................................................................................................................................................................. 26 HYDROGEN SOLVES NAT SECURITY - GRID ............................................................................................................................. 27 HYDROGEN LEADS TO PEER TO PEER ..................................................................................................................................... 28 PEER TO PEER SOLVES HACKERS ........................................................................................................................................... 29 HACKERS = ECON COLLAPSE.................................................................................................................................................. 30 HYDROGEN SOLVES POVERTY ................................................................................................................................................ 31 POVERTY IMPACT ................................................................................................................................................................... 32 POVERTY IMPACT ................................................................................................................................................................... 33 SOLVENCY ............................................................................................................................................................................. 34 FLEET VEHICLE SOLVENCY .................................................................................................................................................... 34 POSTAL SERVICE SOLVENCY .................................................................................................................................................. 35 POSTAL SERVICE SOLVENCY .................................................................................................................................................. 36 POSTAL SERVICE SOLVENCY .................................................................................................................................................. 37 POSTAL SERVICE SOLVENCY .................................................................................................................................................. 38 POSTAL SERVICE SOLVENCY .................................................................................................................................................. 39 POSTAL SERVICE SOLVENCY .................................................................................................................................................. 40 NICHE SOLVENCY ................................................................................................................................................................... 41 NICHE SOLVENCY ................................................................................................................................................................... 42 SUBSIDIES SOLVE ................................................................................................................................................................... 43 SUBSIDIES SOLVE ................................................................................................................................................................... 44 1 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie REFUELING INFRASTRUCTURE KEY ........................................................................................................................................ 45 REFUELING INFRASTRUCTURE KEY ........................................................................................................................................ 46 REFUELING INFRASTRUCTURE KEY ........................................................................................................................................ 47 REFUELING INFRASTRUCTURE KEY ........................................................................................................................................ 48 SUGAR SOLVENCY .................................................................................................................................................................. 49 HOW IT’S MADE ..................................................................................................................................................................... 50 HOW IT’S MADE ..................................................................................................................................................................... 51 HOW IT’S MADE ..................................................................................................................................................................... 52 HOW IT’S MADE ..................................................................................................................................................................... 53 TIMEFRAME ............................................................................................................................................................................ 54 TECH EXISTS .......................................................................................................................................................................... 55 TECH EXISTS .......................................................................................................................................................................... 56 COST OF HYDROGEN ECONOMY ............................................................................................................................................. 57 TRANSPORT SHIT .................................................................................................................................................................... 58 ON-SITE SOLVENCY ................................................................................................................................................................ 59 STORAGE SHIT ........................................................................................................................................................................ 60 GOV KEY ................................................................................................................................................................................ 61 POSSIBLE PLAN MECHANISM .................................................................................................................................................. 62 PLAN POPULAR ....................................................................................................................................................................... 63 AT K ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 64 AT STATES ............................................................................................................................................................................. 65 AT STATES ............................................................................................................................................................................. 66 AT STATES ............................................................................................................................................................................. 67 AT OTHER ALT ENERGY CP ................................................................................................................................................... 68 AT NOT SAFE ......................................................................................................................................................................... 69 AT HINDENBURG.................................................................................................................................................................... 70 AT DIRTY HYDROGEN CP ....................................................................................................................................................... 71 AT OTHER SECTOR CP ........................................................................................................................................................... 73 AT BIOFUEL FOOD DA ........................................................................................................................................................... 74 AT T ALTERNATIVE ENERGY ................................................................................................................................................. 76 AT ON-SITE CP ...................................................................................................................................................................... 77 AT HYDROGEN HIGHWAY CP ................................................................................................................................................ 78 AT HYBRID C/P ...................................................................................................................................................................... 79 URLS ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 80 2 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 1/12 Observation one: Inherency. The Postal Service has infastructure problems that prevent alternatives Government Accountability Office, February 2007, “U.S. POSTAL SERVICE Vulnerability to Fluctuating Fuel Prices Requires Improved Tracking and Monitoring of Consumption Information”, http://www.gao.gov/new.items/d07244.pdf, Accessed July 15, 2008 CM The limited nationwide alternative fuel infrastructure has hindered some of its previous alternative fuel efforts. For example, the Service converted some of its vehicles to operate on CNG in the early 1990s. While this was successful in the short term, manufacturers that the Service worked with to produce the CNG vehicles went out of business or simply stopped producing the vehicles, and many fueling stations that had provided CNG stopped selling it, leading to a shortage in the fuel. Furthermore, even where alternative fuel pumps are available, their distance from a Postal Service facility may be too great to justify the costs to refuel at that pump. Service officials stated that only 0.6 percent of service stations across the country offer alternative fuels. The Service’s continued utilization of public-private partnerships through Shared Energy Savings contracts appear consistent with some elements of leading practices and with federal policies in this area. These contracts are an alternative source of funding for energy-efficient investments. Under these contracts, a private entity (typically an energy company) would fund the initial installation of an energy savings project at a Postal facility. Energy officials at the Service stated that it has advocated the use of these contracts since 1992 as an effective alternative financing method and energy conservation program, and that these projects are an investment aimed at reducing consumption. The savings achieved as a result of these projects would initially be used to pay back the private entity for the installation costs—typically over a 10-year period. According to the Service, savings could accrue (1) at the end of this pay back period, (2) when the outstanding balance is paid prior to the contract’s expiration by the Service using funding from other areas, or (3) during the payback period as consumption is being reduced, actual energy prices exceed the forecasted prices. Table 17 summarizes the Service’s SES contract program, while table 18 shows that many 2006 SES projects are occurring at sites in the Pacific and Southeast areas. Our past work, as well as officials from DOE and GSA have raised similar financial and operational limitations. We recently issued a report on the challenges associated with using alternative fuels, including that the nationwide alternative fuel infrastructure is poor to nonexistent throughout most of the country.23 For example, we reported that there are a limited number of E85 fueling stations nationwide (mostly concentrated in the upper Midwest), and that E85 cannot use the same infrastructure as gasoline because it is more corrosive. As of January 2007, the DOE Website indicates that only 1,003 E85 stations are located throughout the country. Recent studies conducted by DOE have found similar decreased fuel efficiency and increased cost results for ethanol.24 DOE is currently in the process of finalizing guidance on a waiver to EPAct for federal fleets based on factors that may include alternative fuel price and travel distance. 3 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 2/12 Because of the high cost of hydrogen, the post office cannot afford to operate a large scale hydrogen project Dan Davidson, Staff Writer Federal Times, January 11, 2006, “High fuel costs spur conservation” http://www.federaltimes.com/index2.php?S=1452397, Accessed July 16, 2008 CM “The number of operating AFVs is actually less than 30,000,” said Han Dinh, Postal Service engineering program manager for vehicles. “A limited infrastructure limits their employment.” In other words, there are few refueling stations available for AFVs, and there will not likely be many more until demand makes them commercially viable. The Postal Service entered into an agreement with GM in 2004 to test and evaluate a fuel cell vehicle that is powered in part with hydrogen, Dinh said. But so far only one such vehicle is in operation. It runs in the District of Columbia three days each week and between workdays is brought to Fort Belvoir, Va., for refueling and security. “The real challenge is refueling them,’’ Dinh said. “In addition, the cost of a hydrogen-powered vehicle is high, about $1 million now because it is a prototype. But there is also the cost of making hydrogen fuel and the cost of storage.” The hydrogen has to be stored at cold temperatures to keep it in a liquid state, thereby improving the driving range. Even so, GM has predicted that it will be able to produce a fuel cell at a reasonable cost by 2015, Dinh said. How many dollars might be saved with alternative fuels is still an academic question. In the meantime, the Postal Service is making progress where it can, including making bulk purchases of gasoline and diesel, said Dwight Young, Postal Service manager of the portfolio for contract transportation. That has already cut costs by about 9 cents per gallon, Young said. In addition, the agency is proceeding with its fleet card program in rural areas, whereby it enters into agreements to purchase fuel at designated gas stations in exchange for a discount. And it is looking to enter into bulk contracts for aviation fuel. Overall, the Postal Service is optimistic it can build on energy conservation measures it has taken over the past two decades. For facilities, it has reduced its energy use per square foot by about 25 percent from 1985 to 2005, Fanning said. The agency’s fuel use, meanwhile, is up only 2.5 percent since 1999, despite delivering mail to millions of new addresses each year. 4 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 3/12 Observation Two is oil dependency. Hydrogen would significantly reduce the worlds dependence on fossil fuels. David Booth, canwest news service, May 14 2008, The Gazette, pg E8, Thirst for hydrogen but not a drop to drink. At the recent National Hydrogen Association Conference in Sacramento, Calif., General Motors' vice-president for research and development challenged government and the oil industry to build 40 hydrogen refuelling stations in southern California to promote the further development of the "hydrogen infrastructure of automobiles." "While automakers continue to commit resources to the development of full-performance, affordable and durable fuel-cell-electric vehicles, there appears to be comparatively little parallel investment and resource allocation for development and deployment of commercially ready retail hydrogen infrastructure," Larry Burns said. He noted there was only one public hydrogen refuelling station in California, "yet our Equinox Fuel Cell vehicles are already in the hands of customers who are looking for a retail-like refuelling experience." While Burns calls this initial development a "tipping point" that could ultimately service as many as 10,000 hydrogen-fuelled fuel-cell powered vehicles, it is only the beginning of an America-wide infrastructure that will be required before the alternative fuel is widely adopted. As daunting as that may seem, Burns remains convinced a "hydrogen" highway" is attainable within the near future. According to Burns, a network of only 12,000 hydrogen stations would put hydrogen within 3.2 kilometres of 70 per cent of the U.S. population, a far more attainable goal than replacing all of the estimated 170,000 gasoline stations currently operating in the United States. Even "if these stations cost $2 million each," Burns said, "the total cost of $24 billion is not overwhelming," considering the cumulative profits of the oil industry were $123 billion U.S. in 2007 alone. Burns also said the production of hydrogen should not be a problem for the future, since global production is slated to rise to 81 billion kilograms by 2011, half of which is used by oil refineries to remove sulphur from "dirty" crude. Not without irony, Burns notes the hydrogen being used to refine oil into gasoline would be enough to fuel 135 million fuel-cell powered vehicles, which would significantly reduce the world's dependency on fossil fuels. Hydrogen cars would cause a transition to a hydrogen economy Amory B. Lovins, is Chairman and Chief Scientist of the Rocky Mountain Institute, a MacArthur Fellowship recipient (1993), and author and co-author of many books on renewable energy and energy efficiency, 19 98, Winning the Oil Endgame, p. 229, https://nc.rmi.org/NETCOMMUNITY/Page.aspx?pid=192&srcid=271 The hydrogen transition depends on superefficient vehicles and distributed generation taking hold in the U.S., more than either of these breakthroughs depend on the hydrogen economy. There has been much misplaced angst about whether the U.S. should invest now in efficient vehicles or in hydrogen technologies. This debate makes as much sense as arguing about whether star athletes should play football or baseball, which occur during different seasons. The answer is, of course, “both”: first today’s gasoline hybrids, then ultralight hybrids, then ultimately fuel-cell ultralight hybrids. (Some experts believe an intermediate step—efficient hybrids with small hydrogen-fueled internal-combustion engines, like hybrid successors to Ford’s Model U concept car—may also make sense;920 these could be considered a partial backstop technology in case cheap, durable fuel cells take longer to commercialize than expected.) In the case of hydrogen, efficiency and distributed generation should clearly come first because these set the stage for the hydrogen economy, which will have trouble competing without them. That is, hydrogen needs State of the Art-class vehicles far more than they need hydrogen. However, once we have such vehicles and once fuel cells become cheaper, there will be a robust business case for producing the hydrogen that those vehicles would then use. 5 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 4/12 This hydrogen economy would allow a complete transition from fossil fuel usage. Don Sherman, staff at NY times, April 29 2007, The New York Times, section 12 page , Hydrogen’s second coming. The Hindenburg anniversary is not the only reason hydrogen is in the news. Four years ago, in his State of the Union address, President Bush announced a $1.2 billion hydrogen initiative to foster clean air and lessen dependence on imported oil. The Department of Energy has conducted marriages of sorts, joining each domestic automaker with an energy company -- General Motors and Shell; Ford and DaimlerChrysler with BP -- to encourage research and set standards for refueling hardware and safety provisions. As hydrogen gains favor, hydrocarbons seem to be taking over the role of villain. Peak oil theorists, especially Matthew Simmons, chairman of the Simmons & Company investment bank and the author of ''Twilight in the Desert: The Coming Saudi Oil Shock and the World Economy'' contend that increased demand will outpace the ability to increase production. And the Supreme Court's April 2 ruling that the E.P.A. has authority to regulate carbon dioxide as a pollutant, as it does tailpipe emissions, was a powerful vote against fossil fuels. So the three hydrogen-fueled vehicles that gathered at the Hindenburg crash site are harbingers of the future, proof that all of hydrogen's potential in transportation did not go up in flames 70 years ago. The spot where the Hindenburg met its end is now a historic landmark. A heavy yellow anchor chain surrounds a concrete pad replicating the size, shape, and final resting place of the Hindenburg's control car. Rick Zitarosa, historian of the Navy Lakehurst Historical Society, said the Navy intended to preserve the site in its current form. The vehicles here, and three other experimental cars driven elsewhere, cover a broad spectrum of hydrogen possibilities. Here are highlights: FORD E-450 SHUTTLE Ford regards hydrogen-fueled internal-combustion engines as ''a bridge to fuel cells, the powertrain of the future.'' Teamed with BP, Ford built a fleet of 30 E-450 shuttle buses. ''We believe this is an affordable and sensible way to transition from today's fossil fuels to a hydrogen-based economy,'' John Lapetz Jr., the Ford program manager, said. His company also has several active fuel-cell vehicle projects [INSERT IMPACTS FROM OIL FILE] 6 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 5/12 And our reliance on fossil fuels will decrease united states competitiveness and hegemony in a world where other nations transition to hydrogen. Seth Dunn, worldwatch institute in Washington D.C., March 20 02, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 27, Issue 3, Pg 235-264, Hydrogen Futures: Towards a sustainable energy system Yet Iceland and other nations represent just the bare beginning in terms of the changes that lie ahead in the energy world. The commercial implications of a transition to hydrogen as the world's major energy currency will be staggering, putting the $2 trillion energy industry through its greatest tumult since the early days of Standard Oil and Rockefeller. Over 100 companies are aiming to commercialize fuel cells for a broad range of applications, from cell phones, laptop computers, and soda machines, to homes, offices, and factories, to vehicles of all kinds. Hydrogen is also being researched for direct use in cars and planes. Fuel and auto companies are spending between $500 million and $1 billion annually on hydrogen. Leading energy suppliers are creating hydrogen divisions, while major carmakers are pouring billions of dollars into a race to put the first fuel cell vehicles on the market between 2003 and 2005. In California, 23 auto, fuel, and fuel cell companies and seven government agencies are partnering to fuel and test drive 70 cars and buses over the next few years. Hydrogen and fuel cell companies have captured the attention of venture capital firms and investment banks anxious to get into the hot new space known as “ET”, or energy technology [6]. The geopolitical implications of hydrogen are enormous as well. Coal fueled the 18th- and 19th-century rise of Great Britain and modern Germany; in the 20th century, oil laid the foundation for the United States’ unprecedented economic and military power. Today's US superpower status, in turn, may eventually be eclipsed by countries that harness hydrogen as aggressively as the United States tapped oil a century ago. Countries that focus their efforts on producing oil until the resource is gone will be left behind in the rush for tomorrow's prize. As Don Huberts, CEO of Shell Hydrogen, has noted: “The Stone Age did not end because we ran out of stones, and the oil age will not end because we run out of oil.” Access to geographically concentrated petroleum has also influenced world wars, the 1991 Gulf War, and relations between and among western economies, the Middle East, and the developing world. Shifting to the plentiful, more dispersed hydrogen could alter the power balances among energy-producing and energy-consuming nations, possibly turning today's importers into tomorrow's exporters [7]. The most important consequence of a hydrogen economy may be the replacement of the 20th-century “hydrocarbon society” with something far better. Twentieth-century humans used 10 times as much energy their ancestors had in the 1000 years preceding 1900. This increase was enabled primarily by fossil fuels, which account for 90 percent of energy worldwide. Global energy consumption is projected to rise by close to 60 percent over the next 20 years. Use of coal and oil are projected to increase by approximately 30 and 40 percent, respectively [8]. [insert some fucking impacts] 7 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 6/12 Observation Three: The environment. A hydrogen economy would stop greenhouse gasses and other pollutants. United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen The combustion of fossil fuels accounts for the majority of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions released into the atmosphere. Although international efforts to address global climate change have not yet resulted in policies that all nations have accepted, there is growing recognition that steps to reduce greenhouse gases are needed, and many countries are adopting policies to accomplish that end. Energy and transportation companies, many of which have multi-national operations, are actively evaluating alternative sources of energy. Hydrogen can play an important role in a lowcarbon global economy, as its only byproduct is water. With the capture and sequestration of carbon from fossil fuels, hydrogen is one path for coal, oil, and natural gas to remain viable energy resources, should strong constraints on carbon emissions be required. Hydrogen produced from renewable resources or nuclear energy results in no net carbon emissions Hydrogen should be treated as a first priority with warming issues because short-term goals are key to solve Alexander E. Farrell et al, Energy and Resources Group at UC Berkeley, David W. Keith, Department of Engineering and Public Policy at Carnegie Mellon, James J. Corbett, Marine Policy Program at the University of Delaware. October 20 03, Energy Policy, Volume 31, Issue 13, pages 1357-1367, A strategy for introducing hydrogen into transportation. Most of the recent interest in hydrogen is due to concerns about carbon dioxide (CO2, the principal greenhouse gas) and petroleum imports (or scarcity). Since light duty vehicles (LDVs) dominate fuel consumption and CO2 emissions in the transportation sector, effectively dealing with these problems will likely require changes in LDV design and use. The best strategy for attaining these long-term goals may not, however, involve the early introduction of hydrogen-powered LDVs. Focusing on the ultimate goal—low CO2 emissions and/or petroleum independent transportation—without paying sufficient attention to the role of near-term decisions in shaping long-term technological innovation and change is a serious gap since these processes are central to the ultimate costs of meeting policy goals (Grübler et al., 1999; Peters et al., 1999). The strategy outlined here will not achieve immediate deep reductions in CO2 emissions or petroleum use, but should subsequently allow an efficient introduction of hydrogen as transportation fuel on a widespread basis to help achieve those long-term goals. [insert some impacts about GHG] 8 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 7/12 Plan: The United States federal government should subsidize the United States Postal Service for the transition of 37,000 of its vehicles to be powered by hydrogen and subsidize the creation of sugar based hydrogen fueling plants required by the Postal Service. 9 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 8/12 Observation 4: Solvency The USPS could introduce the public to hydrogen on a national level Margo Melendez, senior project Leader at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory & Anelia Milbrandt, member of the International and Environmental Studies Group in the Strategic Energy Analysis and Applications Center., January 2006, “Hydrogen Infrastructure Transition Analysis”, http://www.nrel.gov/hydrogen/pdfs/38351.pdf Because the U.S. Postal Service (USPS) operates roughly 170,000 vehicles—nearly 37,000 of them capable of being powered by alternative fuel—across the country, it could be a valuable partner in infrastructure and vehicle deployment. In particular, remote post offices may have potential for co- generation options. A rural facility can meet its energy demands using a stationary fuel cell for power, while allowing local postal or public vehicles to refuel. This could stimulate demand for hydrogen (by building energy demand), while introducing the vehicles into the community. Figure 4 shows that postal facilities are widespread across the country. Many stations from the FY 2005 analysis are within the proximity of post offices and could be designed to coordinate with a post office co-generation project. Figure 4. USPS Facilities Nationwide Non-postal federal facilities are also prevalent nationwide. Coordination with non-postal federal entities is important because federal agencies are subject to Executive Order 13149, which requires certain federal fleets to utilize alternative fuels. They are also covered under Executive Order 13123, which requires renewable energy use in federal facilities. The combination of these requirements makes federal entities an important factor in the transition to hydrogen. For example, Figure 5 shows the federal facilities in the Denver metropolitan area. Federal facilities are located widely across the country and could be key to transition from a geographic, as well as logistic, standpoint. 10 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 9/12 The auto industry is waiting on governments to provide infrastructure for their vehicles Larry Burns, General Motors vice president, research & development and strategic planning., April 2, 2008, “GM Urges More Hydrogen Stations Vehicles Needs to Be Matched With Rapid Progress on Hydrogen Fueling” , http://www.hydrogenassociation.org/media/pressReleases/02apr08_GM.pdf, Accessed July 16, 2008 SACRAMENTO, CA – General Motors today called on the energy industry and governments to step up and help automakers make volume production of fuel cell-electric vehicles a reality by opening more hydrogen fueling stations. That message was delivered by Larry Burns, General Motors vice president, research & development and strategic planning. Burns delivered a keynote address at the National Hydrogen Association’s annual conference in Sacramento, CA. “The automobile industry has reached a critical juncture in our journey to realize the full potential of hydrogen fuel cellelectric vehicles,” said Burns. “While we have made impressive progress, we have now reached a point where the energy industry and governments must pick up their pace so we can continue to advance in a timely manner.” Burns noted that other automakers are also spending significant amounts on developing fuel cell technology and want to bring large numbers of fuel cell vehicles to market, but he points out that parallel investment by the energy industry and governments is urgently required. Burns’s comments coincided with the release of a new study by General Motors and Shell Hydrogen, which concluded that a hydrogen infrastructure is economically viable and doable. “It’s no longer a question of “can it be done?” or “should it be done?” said Burns. “We not only should do it. We must do it. It’s now a question of collective will. Do we have the collective resolve to work together to solve the challenges we face rather than handing them off to future generations?” Burns said addressing the infrastructure challenge is essential because the potential benefits of hydrogen fuel cell technology are clear and compelling. “This technology promises to deliver family-sized vehicles that are fun to drive, safe, look great, refuel fast, go far between fill-ups, and are emissions-free and petroleum-free. It also holds promise to do all of this while keeping automobiles affordable to own and operate. And just like electricity, it can be made from a broad range of renewable and sustainable energy pathways. No other technology offers this exciting potential,” he said. “We have not discovered anything yet to suggest mass volume cannot ultimately be attained. “ He also complimented hydrogen fueling initiatives by FreedomCAR, Shell Hydrogen AND Chevron Hydrogen, the California Fuel Cell Partnership, and the California Hydrogen Highway, but called for efforts like these to accelerate. “What is urgently needed is sufficient investment by energy providers to assure auto companies that the required hydrogen infrastructure will be in place when we deploy our next generation of fuel cell-electric vehicles,” he said. “Clearly, the automobile industry has stepped forward with fuel cell-electric vehicles, and we are doing everything possible to aggressively develop this critically important technology,” Burns said. “However, we have reached a stage where we cannot continue to make significant progress on our own. Our customers must have safe and convenient access to affordable hydrogen. This means the energy industry and governments must join the auto industry in our journey to produce and sell fuel cell-electric vehicles in volume numbers.” 11 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 10/12 Sugar based hydrogen solves the three biggest problems with hydrogen – price, safety and ecofriendliness Susan Trulove, Term director named for critical technology and applied science institute, May 23, 2007, “Novel sugar-tohydrogen technology promises transportation fuel independence”, http://www.vtnews.vt.edu/story.php?relyear=2007&itemno=300, Accessed July 15, 2008 CM It is a new process that aims to release hydrogen from water and carbohydrate by using multiple enzymes as a catalyst, Zhang said. “In nature, most hydrogen is produced from anaerobic fermentation. But hydrogen, along with acetic acid, is a coproduct and the hydrogen yield is pretty low--only four molecules per molecule of glucose. In our process, hydrogen is the main product and hydrogen yields are three-times higher, and the likely production costs are low--about $1 per pound of hydrogen. Over the years, many substances have been proposed as “hydrogen carriers,” such as methanol, ethanol, hydrocarbons, or ammonia--all of which require special storage and distribution. Also, the thermochemical reforming systems require high temperatures and are complicated and bulky. Starch, on the other hand, can be distributed by grocery stores, Zhang points out. “So it is environmentally friendly, energy efficient, requires no special infrastructure, and is extremely safe. We have killed three birds with one stone,” he said. “We have hydrogen production with a mild reaction and low cost. We have hydrogen storage and transport in the form of starch or syrups. And no special infrastructure is needed.” “The next R&D step will be to increase reaction rates and reduce enzyme costs,” Zhang said. “We envision that in the future we will drive vehicles powered by carbohydrate, or energy stored in solid carbohydrate form, with hydrogen production from carbohydrate and water, and electricity production via hydrogen-fuel cells. “What is more important, the energy conversion efficiency from the sugar-hydrogen-fuel cell system is extremely high-greater than three times higher than a sugar-ethanol-internal combustion engine,” Zhang said. “It means that if about 30 percent of transportation fuel can be replaced by ethanol from biomass as the DOE proposed, the same amount of biomass will be sufficient to provide 100 percent of vehicle transportation fuel through this technology.” In addition, the use of carbohydrates from biomass as transportation fuels will produce zero net carbon dioxide emissions and bring benefits to national energy security and the economy, Zhang said. 12 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 11/12 Hydrogen will be key in determining our future and now is the time to act Neil Thomas and Martin Mbugua, UDaily, April 9, 2007, “UD unveils hydrogen-powered bus that produces no pollutants”, http://www.udel.edu/PR/UDaily/2007/apr/bus040907.html, Accessed July 18, 2008 CM 5:21 p.m., April 9, 2007--The University of Delaware will soon be operating a shuttle bus powered by hydrogen fuel cells, a clean energy source that does not require fossil fuels to operate and that produces a benign emission--water. The bus was unveiled during a ceremony on Monday, April 9, on UD's Newark campus. The hydrogen fuel cell bus project is supported by a $1.7 million grant from the U.S. Department of Transportation's Federal Transit Administration, matched by private financing from companies working in partnership with the University. Researchers from the College of Engineering, who are driving the project, said they envision a multidisciplinary demonstration project. Over the course of the project, the team has researched and demonstrated ways to make hydrogen fuel cells more efficient and less expensive to produce and operate, installed fuel cells in a public bus, and will now test the bus as it operates on a regular passenger route around the University's Newark campus. The project also includes development of a safe and efficient hydrogen refueling station to be used by the bus and, eventually, by other hydrogen-powered vehicles. Another goal of the project is to educate the public and transit officials about the developing technology of hydrogen fuel cells. U.S. Sen. Thomas R. Carper (D-Del.) said the University of Delaware has made significant contributions to the development of solar energy during the last three decades. “Our country and our world are at the crossroad,” Carper said during the ceremony. “The decisions that we make in the next 10 years in public policy, in research and development, in lifestyle changes, could determine the fate of our way of life in 50 years, 100 years from now. Today there is still time to make a difference. The University and leaders throughout our state will help to make that difference." “I am very pleased that our faculty and students have been able to take the lead in bringing fuel cell vehicles to Delaware, and I look forward to future successes as they continue to move ahead,” Eric W. Kaler, Elizabeth Inez Kelley Professor of Chemical Engineering and dean of the College of Engineering, said. “A fuel cell vehicle has zero harmful emissions--wisps of steam or a trickle of water, that's all it produces,” Ajay Prasad, professor of mechanical engineering, said. Prasad is the principal investigator for the project, which is being coordinated by the Delaware Center for Transportation in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. Co-investigators on the project are Ardeshir Faghri, professor of civil and environmental engineering and director of the transportation center, and Suresh Advani, George W. Laird Professor of Mechanical Engineering. “Most of the major automotive companies are aggressively pursuing fuel cell technology right now,” Prasad said. “When we sought this funding, we were not interested in just buying a fuel cell powered bus and operating it, which already is being done in some places. We wanted to introduce some innovations and inject some cutting-edge research on fuel cells into this project.” outside of the University. During this period, the researchers said they will be tracking performance, efficiency, control algorithms, emissions levels, operation costs, the frequency of maintenance needed and the ease of repairs. 13 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 1AC 12/12 Hydrogen would single handedly reduce GHG, pollution, and oil dependence. Warren Brown, staff at Washington Post, June 3 2007, Fuel Cells: Out of the News but still in the future, The Washington Post Ballard, born in 1979 as Ballard Research and now headquartered in Burnaby near here, had developed a technology destined to change the world. It was a hydrogen fuel cell with a proton-exchange membrane. In practical application, it would trigger a reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to create electricity. In cars and trucks, hydrogen fuel cells would mean an end to tailpipe pollution as we've come to know and hate it. It would mean less dependence on foreign oil. It would remove the automobile as a negative component in the environmental equation. And there was so much more. The hydrogen fuel cell technology that powered cars and trucks could also be used to power homes and buildings, conceivably removing them from traditional electrical power grids. It was all very wonderful. The media were agog. Politicians were enthralled. Wall Street types were aroused. Institutional environmentalists -- people who take the "right" environmental stance as much for the acquisition of political power as they do for altruism -- were at least interested. Finally, Hydrogen is a key renewable since it would uniquely stimulate other industries and renewables. Seth Dunn, worldwatch institute in Washington D.C., March 20 02, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 27, Issue 3, Pg 235-264, Hydrogen Futures: Towards a sustainable energy system Hydrogen would, in addition, facilitate the transition from limited non-renewable stocks of fossil fuels to unlimited flows of renewable sources, playing an essential role in the “decarbonization” of the global energy system needed to avoid the most severe effects of climate change. According to the World Energy Assessment, released in 2000 by several UN agencies and the World Energy Council, which emphasizes “the strategic importance of hydrogen as an energy carrier”, the accelerated replacement of oil and other fossil fuels with hydrogen could help achieve “deep reductions” in carbon emissions and avoid a doubling of pre-industrial carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations in the atmosphere — a level at which scientists expect major, and potentially irreversible, ecological and economic disruptions. Hydrogen fuel cells could also help address global energy inequities — providing fuel and power and spurring employment and exports in the rural regions of the developing world, where nearly 2 billion people lack access to modern energy services 14 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Inherency Hydrogen Cars not available While hydrogen car prototypes have been created, they aren’t yet commercially available CNet News, 6/16/08, Honda produces first commercial hydrogen cars, http://news.cnet.com/8301-11128_3-996926354.html Honda has begun the first commercial production ever of a hydrogen fuel cell-powered car. The Japanese auto manufacturer ceremoniously launched production of its first hydrogen-powered vehicles on Sunday in Tochigi, Japan, and announced its first customers. The four-door sedan, called the FCX Clarity, runs on electricity from a fuel cell battery that is powered by hydrogen fuel. Steam is the car's only byproduct. The car can get a combined (city and highway driving) fuel efficiency of about 72 miles per kg of H2 which, according to Honda's own estimates, is the equivalent of getting about 74 mpg on a gas-powered car. The car can be driven for about 280 miles before needing to be refueled. While many automakers and researchers have prototypes and pilot projects using hydrogen fuel to power fuel cells on electric hybrids, or as a direct fuel source for vehicles with converted engines, there are no hydrogen-powered cars yet available for lease or purchase to the average consumer. 15 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Not Enough R & D The US is funding hydrogen research now, but more research is needed Peter Schwartz, partner in the Monitor Group and chair of Global Business Network, a scenario-planning firm, and Doug Randall, senior practitioner at GBN, Wired, How Hydrogen Can Save America, April 2003, Issue 11.4, http://www.wired.com/wired/archive/11.04/hydrogen.html The country now faces a similarly dire threat: reliance on foreign oil. Just as President Kennedy responded to Soviet space superiority with a bold commitment, President Bush must respond to the clout of foreign oil by making energy independence a national priority. The president acknowledged as much by touting hydrogen fuel cells in January's State of the Union address. But the $1.2 billion he proposed is a pittance compared to what's needed. Only an Apollo-style effort to replace hydrocarbons with hydrogen can liberate the US to act as a world leader rather than a slave to its appetite for petroleum. 16 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Previous failed Despite large amounts of funding, all of our previous efforts towards a hydrogen economy have failed, now is the time to rethink our strategy Cory Welch, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, February 2006, “Lessons Learned from Alternative Transportation Fuels: Modeling Transition Dynamics Technical Report”, http://www.nrel.gov/hydrogen/pdfs/39446.pdf, Accessed July 18, 2008 CM In recent years, much attention has been given to the use of hydrogen as an alternative transportation fuel. Industry and government have already invested hundreds of millions of dollars to develop the technologies necessary to transition to a “hydrogen economy.” However, hydrogen was certainly not the first fuel considered as an alternative to gasoline for transportation applications. Options ranging from all-electric vehicles to those running on natural gas, propane, ethanol, and biodiesel have also received both industry and government attention as potential substitutes for the conventional gasoline-powered internal combustion engine (ICE). Unfortunately, previous government efforts to encourage widespread adoption of alternative fuel vehicles have been largely unsuccessful. Examples include the failed attempt to mandate a significant percentage of zero emission vehicles in California as well as the recognition that petroleum displacement has fallen far short of the Energy Policy Act (1992) [1] goal of 10% by the year 2000 and will also miss the goal of 30% displacement by the year 2010. A strong tendency in such failed attempts is to attribute failure to individual causes, such as higher vehicle purchase or operating costs, poor vehicle performance, low refueling (or recharging) station coverage, or inadequate government incentives. However, such simplistic attributions fail to consider the entire system and do not appreciate the complexity of overcoming a highly entrenched technology such as the gasoline ICE. Additionally, solutions that encourage alternative-fueled-vehicle adoption often only consider the end states, such as target vehicle or fuel production cost at high volume or large-scale “optimized” solutions to fuel distribution, with little consideration given to the transitional dynamics that would lead to realizing these end states. Recognizing the importance of transitional issues, the National Academy of Engineering [2] suggested that “the DOE might have its greatest impact by leading the private economy toward transition strategies rather than to ultimate visions of an energy infrastructure markedly different from the one now in place” and that “the policy analysis capability of the Department of Energy with respect to the hydrogen economy should be strengthened, and the role of government in supporting and facilitating industry investments to help bring about a transition to a hydrogen economy needs to be better understood.” To better understand the challenges of attempting to displace petroleum-derived fuels, a systems approach is required. 17 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Oil Solves Oil Hydrogen is more than 3 times more efficient than gasoline Woodrow W. Clark et al, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy In terms of the transportation sector, the cost of 1 kg of hydrogen production can be compared to that of 1 gallon of gasoline, the energy content of which is roughly equivalent to 1 kg of hydrogen. Typically, a gasoline internal combustion engine (ICE) with a mechanical drive train is 15–20% efficient, while a hydrogen ICE is about 25% efficient. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles with electric hybrid drive trains can be up to 55% efficient—about 3 times better than today's gasoline fueled engines. Because the production of hydrogen, by steam reformation of natural gas or electrolysis of water, is expected to be about 75–85% efficient, the net energy efficiency of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles will still be better than twice that of gasoline ICE vehicles. Hydrogen, today, at a delivered price of $3.00 per kg (or gallon gasoline equivalent) would be on a par with $1.50/gallon gasoline in a fuel cell automobile. The bottom line is that the costs of hydrogen for the transportation sector provide an economic model for hydrogen energy stations. Hydrogen is oil free Mark Huffman, Staff at Consumeraffairs.com, 6/25/2008, Hydrogen Fuel cell cars bring hope, if not relief. Talk about timing. Honda's rollout of its first hydrogen fuel cell car couldn't have come at a better time. Introducing a vehicle that basically runs on water instead of gasoline quite predictably caught the world's attention. But these cars, called Fuel Cell Vehicles, or FCVs, are highly complex, and to say they run on water greatly oversimplifies the subject and, understandably, has already led to some consumer confusion. FCVs are actually electric cars, running on a set of super-strong batteries. But unlike normal batteries that have to be plugged in to be recharged, FCVs use a hydrogen-based fuel that constantly recharges them. So, far from running on water, these engines require a hydrogen-mix fuel, which combined with oxygen from the air, create a chemical process that powers the batteries. The first FCVs are very, very expensive – in the price range of an Italian sports car. And since you can't just fill the tank with water, fueling stations have to begin providing the hydrogen fuel mix, so that motorists can confidently drive from one point to another, knowing they will be able to fill up when they need to. But even with those problems, petroleum-dependent motorists have reason for excitement. Here is a vehicle that doesn't require oil to operate. While it doesn't run on water, its hydrogen fuel is made from water. There are no carbon emissions, only water vapor. 18 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Solves Oil Hydrogen Economy solves for fucking oil and especially in the transport sector. It would also solve for air quality. Mark Schrope, freelance writer in Melbourne Florida, 12/13/01, Which Way to Energy Utopia, Nature, Vol. 414 pgs 682684 Imagine a world in which everyone uses all the energy they want, yet dependence on oil, with its attendant smog and greenhouse-gas emissions, is a thing of the past. This utopia is plausible — many would say probable. It is one in which hydrogen, rather than fossil fuels, is central to our energy economy. In the most ambitious vision, all the hydrogen we need would be liberated from water using renewable energy sources. Burning it, or using it in battery-like fuel cells that produce electricity, would allow the gas to power everything from buildings to cars. Fossil fuels would be almost totally removed from the energy equation. Although this is seen by most as the best outcome, the way forward is far from clear. The basic technology needed already exists. But renewable energy sources are not mature enough to provide all the hydrogen we would need, so alternative methods are under consideration (see 'Box 1 Cranking up the hydrogen flow'). And it remains unclear how best to lure people away from conventional cars and into hydrogen-powered alternatives. The transport sector is seen by experts as central to the hydrogen economy. It is the main driver of oil dependence — something the developed world wants to reduce, given the vulnerability of supplies to conflict and political disturbance in oil-exporting nations. Exhaust gases from vehicles also damage air quality, and transport as a whole is responsible for around a third of all greenhouse-gas emissions. Hydrogen economy would solve for fossil fuels by supplying more than 35% of all energy needs Philidelphia Inquirer, November 26 2006, Being ready for future key to business success pg E03 Cars fueled solely by hydrogen can be made today. Futurist James Canton rode in one in spring 2005 after fulfilling a speaking engagement at Albany NanoTech on the campus of the State University of New York at Albany. "It handled beautifully, accelerated smartly, and rode smoothly. Other than not making noise and belching black, environmentally unfriendly exhaust, it was indistinguishable from the countless utilitarian compacts zipping alongside me," Canton wrote. There was only one problem with that car. It cost $1.2 million. But Canton, chairman and chief executive officer of the San Francisco-based Institute of Global Futures, predicts that the price will soon come down to a level where nearly everyone can afford one. Automakers, governments, utilities, and oil and gas companies are pouring billions into hydrogen research, he points out, because of accelerating global demand for oil and dwindling oil reserves. "I forecast that more than $10 billion will be needed and spent on hydrogen research over the next 10 to 15 years worldwide. This will lead to a mass-market set of innovations, similar to the innovations that first launched the modern auto, train, and shipping industries. By 2035, or even sooner, hydrogen will be a viable alternative to oil and gas, meeting as much as 35 percent of our energy needs," Canton says. It could happen sooner if hydrogen research were given the priority it merits, Canton writes. "If the Iraq war costs the U.S. between $599 billion and $1 trillion, and we were to invest half of that in hydrogen, we would see dramatic breakthroughs in energy - fast," Canton writes. Canton unequivocally asserts that the oil era is approaching its end and that the information age has evolved into the innovation age. Only those individuals, businesses and governments that achieve "future readiness" soon enough to take advantage of tremendous opportunities presented by the scientific and technological breakthroughs will become commercially viable in the short term. 19 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Solves Oil Hydrogen economy is a transition from fossil fuels Don Sherman, staff at NY times, April 29 2007, The New York Times, section 12 page , Hydrogen’s second coming. The Hindenburg anniversary is not the only reason hydrogen is in the news. Four years ago, in his State of the Union address, President Bush announced a $1.2 billion hydrogen initiative to foster clean air and lessen dependence on imported oil. The Department of Energy has conducted marriages of sorts, joining each domestic automaker with an energy company -- General Motors and Shell; Ford and DaimlerChrysler with BP -- to encourage research and set standards for refueling hardware and safety provisions. As hydrogen gains favor, hydrocarbons seem to be taking over the role of villain. Peak oil theorists, especially Matthew Simmons, chairman of the Simmons & Company investment bank and the author of ''Twilight in the Desert: The Coming Saudi Oil Shock and the World Economy'' contend that increased demand will outpace the ability to increase production. And the Supreme Court's April 2 ruling that the E.P.A. has authority to regulate carbon dioxide as a pollutant, as it does tailpipe emissions, was a powerful vote against fossil fuels. So the three hydrogen-fueled vehicles that gathered at the Hindenburg crash site are harbingers of the future, proof that all of hydrogen's potential in transportation did not go up in flames 70 years ago. The spot where the Hindenburg met its end is now a historic landmark. A heavy yellow anchor chain surrounds a concrete pad replicating the size, shape, and final resting place of the Hindenburg's control car. Rick Zitarosa, historian of the Navy Lakehurst Historical Society, said the Navy intended to preserve the site in its current form. The vehicles here, and three other experimental cars driven elsewhere, cover a broad spectrum of hydrogen possibilities. Here are highlights: FORD E-450 SHUTTLE Ford regards hydrogen-fueled internal-combustion engines as ''a bridge to fuel cells, the powertrain of the future.'' Teamed with BP, Ford built a fleet of 30 E-450 shuttle buses. ''We believe this is an affordable and sensible way to transition from today's fossil fuels to a hydrogen-based economy,'' John Lapetz Jr., the Ford program manager, said. His company also has several active fuel-cell vehicle projects. 20 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Solves Oil Hydrogen solves emissions and other oil problems Alastair Dalton, Transport correspondent for The Scotsman, 6/17/20 08, The Scotsman, pg 11, Revolution as hydrogen-fuel cars roll off production line in japan. The first three of Honda's hydrogen fuel-cell cars - whose exhausts produce only water - have rolled off the production line in Japan. Some 70 trial versions of the FCX Clarity will follow this year - the world's largest production run of such a vehicle. Several will be shipped to California to be tested by customers, including the actress Jamie Lee Curtis and her filmmaker husband, Christopher Guest. The Clarity has a 280-mile range, but there are so far only five hydrogen refuelling stations in southern California. Some 200 of the cars will be made over the next three years for use in the United States and Japan. Drivers will lease them for about GBP 290 a month, including insurance and maintenance. Honda hopes the trials will lead to mass production in future but has not said how much the Clarity would cost or when it would be available in the UK. Environmental groups welcomed the new model but said hydrogen was only as clean as the energy used to produce it. The car's engine comprises a "stack" of several hundred fuel cells, which creates an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to convert chemical energy into electrical energy that powers the car. It generates both electricity and water, but no carbon dioxide or other pollutants. It is twice as energy efficient as petrol-electric hybrids, such as the Prius, the current darling of green-minded celebrities. Unlike many hybrids, the Clarity, which has taken 19 years to develop, was designed from scratch as a dedicated fuelcell vehicle. The launch gives Honda a chance to take the lead in green motoring after its Accord hybrid was trounced by the Prius and discontinued due to poor sales. Toyota announced last month it had sold more than a million Prius models. The firm admitted yesterday it was struggling to meet demand because batteries and other key parts were not being made quickly enough. John Kingston, the environment manager for Honda (UK), said: "The arrival of the first hydrogen fuel-cell car is particularly significant during this time of rapidly increasing oil prices. Honda is proud to offer an alternative energy solution that could reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and the effect of motoring on climate change." The Environmental Transport Association said such vehicles would cut harmful vehicle pollution, and costs were coming down. Yannick Read, its spokesman, said: "The success of new technology can be hampered by high cost, but the viability of such vehicles is set to improve as fossil fuels become increasingly expensive." 21 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Transition Possible A transition to hydrogen could occur immediately with significant investment Amory B. Lovins, is Chairman and Chief Scientist of the Rocky Mountain Institute, a MacArthur Fellowship recipient (1993), and author and co-author of many books on renewable energy and energy efficiency, 1998, Winning the Oil Endgame, p. 229, https://nc.rmi.org/NETCOMMUNITY/Page.aspx?pid=192&srcid=271 The oft-described technical obstacles to a hydrogen economy—storage, safety, cost of the hydrogen, and its distribution infrastructure—have already been sufficiently resolved to support rapid deployment starting now in distributed power production, and could be launched in vehicles upon widespread adoption of superefficient vehicles. (The stationary fuelcell markets will meanwhile have cranked up production to achieve serious cost reductions, even if they capture only a small market share: twothirds of all U.S. electricity is used in buildings, and many of them present favorable conditions for early adoption.) Automotive use of fuel cells can flourish many years sooner if automakers adopt recent advances in crashworthy, cost-competitive, ultralight autobodies. We certainly believe that the transition could be well underway by 2025, and if aggressively pursued, it could happen substantially sooner. Two keys will unlock hydrogen’s potential: early deployment of superefficient vehicles, which shrink the fuel cells so they’re affordable and the fuel tanks so they package, and integration of deployment in vehicular and in stationary uses, so each accelerates the other by building volume and cutting cost.923 In sum, the hydrogen option is not essential to displacing most or all of the oil that the United States uses. But it’s the most obvious and probably the most profitable way to do this while simultaneously achieving other strategic advantages—complete primary energy flexibility, climate protection, electricity decentralization, vehicles-as-power-plants versatility, faster adoption of renewables, and of course deeper transformation of automaking and related industries so they can compete in a global marketplace that’s headed rapidly in this direction. 22 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Environment Solves Emissions A lot of these cards will be in the oil cards, you can say oil = polluting and hydrogen replaces that. Hydrogen just emits h20 United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen Hydrogen can be combusted in the same manner as gasoline or natural gas. The benefit of using hydrogen combustion over fossil fuel combustion is that it releases fewer emissions—water is the only major byproduct. No carbon dioxide is emitted, and nitrogen oxides, produced by a reaction with the nitrogen in the air, can be significantly lower than with the combustion of fossil fuels. This technology is fairly well developed— both the National Aeronotics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Department of Defense use it for applications such as the space shuttle's main engines and unmanned rocket engines. Other combustion applications are being researched, such as new designs of combustion equipment specifically for hydrogen in turbines and engines. Hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicles are being demonstrated—Ford and BMW made significant progress in advanced Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine (H2-ICE) vehicles in 2001. Also, the combustion of hydrogen blends is being practiced, as blends have been shown to emit fewer pollutants than pure fossil fuels once the engine is leaned out, and would promote a transition to the combustion of 100 percent hydrogen fuel Fuel Cells rock and are free of c02 emissions. United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen Fuel cells have operating advantages for both stationary and mobile applications in that they are quiet and typically have high efficiencies at partial loads. They also have environmental advantages. For example, when pure hydrogen is used as the fuel, there are no emissions of sulphur or nitrogen oxides, or particulates. And if the hydrogen comes from a net-carbon-free renewable or nuclear energy source, the system will also be free of carbon dioxide emissions. The direct conversion of the energy stored in the fuel to electricity in a fuel cell can be achieved at high efficiencies, avoiding limitations of standard heat-to-power cycles used in combustion engines and turbines. Fuel cells are also deployable in combined heat and power applications 23 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Solves Emissions Even if hydrogen is only created by 45% renewables it still solves emissions Robert Perkins, staff at Platts oilgram news, February 26 2008, Hydrogen could cut EU oil consumption 40% by 2050, Oilgram news, pg 7 vol 86 no 40 The EU also sees hydrogen and fuel cells use as key to achieving its objective of replacing 20% of vehicle fuels with alternative fuels by 2020. "Hydrogen is one of the most realistic options for environmental and economic sustainability in the transport sector, in particular passenger transport, light duty vehicles and city buses," the European Commission said in a statement presenting the latest study. "However, its introduction requires gradual changes throughout the entire energy system and thus careful planning at this early stage." The study concludes that though hydrogen becomes cost competitive with oil prices over $50-60/barrel, a "substantial increase" in research spending is needed to ensure that the economic breakeven point for the fuel is reached as soon as possible. It also flags a current lack of government supported schemes for hydrogen end-use technologies and infrastructure buildup. The report comes as member states are due to give their approval of a new Eur940 million public/private research partnership for the development of hydrogen and fuel cells. In October, the EU presented two proposals to promote the development and marketing of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles as part of plans to boost clean, renewable energy use and reduce the region's dependence on imported oil. The study assumes that about 45% of the hydrogen produced by 2050 would be by means of electrolysis from renewable, sustainable and nuclear energy, including wind and biomass sources. If hydrogen is introduced into the European energy system, the study concludes, the cost to reduce one unit of CO2 decreases by 4% in 2030 and 15% in 2050, with total "well-to-wheel" reduction of CO2 emissions amounting to 190 million-410 million mt/year in 2050. 24 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Hydrogen economy solves climate change Hydrogen economy emits very little and makes carbon capture easy. D.W. Keith, Department of Engineering and Public Policy, Carnegie Mellon University., A. E. Farrell, Energy and Resources Group, University of California, Berkeley., 7/18/03, Science, Vol. 301. no. 5631, pp. 315 - 316 A near-zero-emission source of hydrogen is required if hydrogen cars are to reduce CO 2 emissions [HN7] substantially. The cost of CO2-neutral hydrogen turns on the viability of CO 2 capture and storage [HN8] (CCS) because it is currently much cheaper to make hydrogen from fossil feedstocks such as coal or gas than from other sources (10, 11). It is substantially easier to capture CO2 from hydrogen production than from electric power plants because the CO2 is at high partial pressure--indeed many existing facilities already vent nearly pure CO 2. If CO2 storage in geological reservoirs (or perhaps elsewhere) is socially acceptable and can be widely implemented, then the cost premium for CO2-neutral hydrogen will likely be less than 30%. Even with these assumptions, hydrogen cars will be an expensive CO2 mitigation option because of the high cost of vehicles and refueling infrastructure. Costs may exceed $1000 per tonne of carbon if hydrogen cars are to match the performance of evolved conventional vehicles (12). With consistent assumptions about CCS, reducing electric sector emissions by 50%--equivalent to eliminating CO2 emissions from all cars--is likely to cost between $75 and $150/tC (13, 14). http://www.cbn.com/cbnnews/usnews/050620a.aspx 25 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Add-On Advantages USPS Advantage The Postal Service is an economic bind because prices are locked from going beyond inflation Randolph E. Schmid, associated press writer, June 15, 2008, “Petrol prices pinching post office”, http://209.85.215.104/search?q=cache:DLkqvr_skx8J:news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20080615/ap_on_go_ot/postal_petrol+usps+fleet +hydrogen&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=60&gl=us&client=safari, Accessed July 16, 2008 CM WASHINGTON - Soccer moms and commuters aren't the only ones feeling the bite of rising fuel costs — every time the price of gasoline goes up a penny it costs the Postal Service $8 million. "We are definitely feeling the pressure," Deputy Postmaster General Patrick R. Donahoe told The Associated Press. Transportation cost the post office $6.5 billion in 2007, $500 million more than the year before. The post office operates the largest civilian fleet of vehicles in the country — 215,000 motor vehicles — and also faces rising costs for fuel from its contract carriers including truckers and airlines. It's both a matter or costs and usage, Donahoe explained — looking for ways to reduce costs and change use patterns to reduce the need for fuel. It's easier for the post office to raise rates than it used to be — the price of sending a letter went up a penny to 42 cents in May. Another price rise is expected next May, but postage increases are legally limited to the rate of inflation. That limit doesn't seem to apply to fuel costs which now top $4-a-gallon nationwide. 26 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Hydrogen Solves nat security - grid Solves oil depdendence and diversifies energy infrastructure United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen The need to enhance the supply of domestically produced transportation fuels is great. The tragic events of September 11, 2001, remind every American of the danger of reliance on oil imports from politically unstable countries, some of which have opposing interests to those of the United States. America’s transportation sector relies almost exclusively on refined petroleum products; more than one-half of the petroleum consumed in the United States is imported, and that percentage is expected to rise steadily for the foreseeable future, unless we change our energy use. Hydrogen (along with biofuels) is a versatile energy carrier that could be produced entirely from domestic sources of fossil fuel (e.g., natural gas and coal with capture and sequestration of carbon dioxide), renewable (e.g., solar, wind, and biomass), and nuclear energy, in large quantities. Its use as a major energy carrier would provide the United States with a more diversified energy infrastructure 27 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Hydrogen Leads to Peer To Peer A hydrogen economy creates peer to peer networking Jeremy Rifkin, Author of "Hydrogen Economy", President of the Foundation on Economic Trends, 20 04, http://www.ari.vt.edu/hydrogen/Resources/ConfDoc/FullText/RifkinTalk.html Good afternoon everybody. It's a pleasure to be here with you. The great economic revolutions in history, the really great ones, occur when two things happen. The first is a basic change in the way we organize the energy of the earth. Second, a basic change in the way we communicate with each other to organize the new energy régime. The coming together, the convergence, of a new energy régime and a new communications régime, these really are the pivotal points in history. Although infrequent, when they happen, they truly are paradigmic. They are a Gestalt change. Let me give you an example. Let's go back to ancient Sumeria, the first great agricultural civilization. Sumerians found a way to capture the Sun’s energy in cereal plants. Those plants became the prime energy mover for human history for 10,000 years - the agricultural era. When the Sumerians went to agriculture it was complicated, involving irrigation, hydraulics and mechanics. They had to know about the changing seasons. They had to deal with cultivation, harvest and storage and distribution. The great changes in energy history are actually great changes in spatial-temporal orientation. Changes in spatial-temporal orientation quickened the pace, the speed, the flow the connectivity and the density of human exchange. When we change energy régimes, we change the density of human exchange. Technologies are an extension of our being. We inflate ourselves with technologies so that we can expropriate our surroundings, compress time and space, and exchange more densely. The locomotives extends our running legs, the computer amplifies memory, the bow and arrow extends our throwing arm. They are all keys to new communications and energy régimes. The coming together of writing and agriculture was a turning point in our species’ history. Gutenberg invents the printing press with movable type; for three centuries that invention had a social value, but not an economic value. The economic mission of the printing press did not really become clear until James Watt invented the steam engine and patented it, signaling the dawn of the Industrial Revolution. We went down to the burial grounds of the Jurassic age and we dug up those remains and we burned them as stored energy and we greatly increased the speed and pace, the connectivity and the density of exchange. It used to be if one wanted to go from London to Manchester it took days; by the time the rails were laid down it was a matter of hours. When we moved to the steam engine and coal, we had to have a new command-and-control mechanism to organize it because it was so complicated. In hindsight, try to imagine organizing the first Industrial Revolution with codex or with oral culture. It would have been slow and parochial, and not expansive enough in time and space to organize that new energy régime. We could not have done it without print. The telegraph and telephone preceded the internal combustion engine by a few years: it became the command-and-control mechanism for a régime ultimately based on the flow of oil. I just want to make this point. We had a dramatic communications revolution in this past decade. Personal computers, the World Wide Web - we've actually connected the central nervous system of a billion people at the speed of light worldwide in less than 12 years. We now have wireless communication, and we are going to move to grid technology. After that, we are going to be moving into parallel computing, quantum mechanics and nanotechnology. But the point of this revolution is this: we did increase productivity with this new communication, because we thought that was its main mission, we did connect the central nervous system of a lot of human beings, but we never did really step back and ask what is the anthropological mission of this communications revolution. It can't be just about increasing traditional productivity or connecting people. I think we are about to be on the cusp of a new convergence, and this decentralized communication revolution of the 1990s will become the command and control mechanism for the new energy régime. That new energy régime is distributed generation and hydrogen. Hydrogen - a basic element of the universe, stuff of the stars, ubiquitous, and when we harness that energy we get just pure water and heat. How does the decentralized communication régime connect to distributed generation of energy in the first few decades of the 21st century? We have to begin to imagine the fuel cell as analogous to the personal computer; there's a direct analogy here. When we use a personal computer we are using our own information; the end-user becomes the author. We have a lot of end-users who are desirous of sharing information, and we took that science-based Internet and turn it into the global Internet, so that you and I can generate information on the personal computer and share it with a billion people. Imagine a fuel cell powered by hydrogen, and now imagine millions and millions of fuel cells by mid-century. Every home, every factory, every office, portables with every human being, 800 million automobiles and trucks, Those will be our power plants. We - the end-users - begin to generate our own power. But then how do we share it? We're just getting to how we share the computers; it's called grid technology. We now realize that we can get the software together to connect all the personal computers, thousands of them, to do work that individual supercomputers could never do. What is the analogy to grid technology? You and I generate our hydrogen from electricity-to-hydrogen powered fuel cells. We send it back to the grid; all the energy we don't need. The problem, though, is that the grid can't handle it now, because the grid is centralized like the old communications grid. What we are going to do in the next 30 years, if we are smart enough, is reconfigure every power grid in America and every power grid in the world, using the architecture and the hardware and the software that was developed in Silicon Valley, so that when you and I generate the electricity, we will be able to send it decentralized, peer-to-peer, with all the appropriate architecture, so that we can say where it is going to go for the grid in real time. 28 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Peer To Peer Solves Hackers Decentralized networks are key to protecting the internet from hackers Richard Downing, Senior Counsel at the Computer Crime and Intellectual Property Section, United States Department of Justice, 2005, Columbia Journal of Transnational Law, Shoring Up the Weakest Link: What Lawmakers Around the World Need to Consider in Developing Comprehensive Laws to Combat Cybercrime, accessed through Lexis Today, the exploding use of information systems and networks has caused countries to become increasingly interconnected. In developed countries, computer networks play a major role in how companies do business, how governments provide services to citizens and enterprises, and how people communicate and exchange information. They support critical infrastructures such as electricity [*708] and gas, transportation, and banking and finance. By providing easy access to information and benefits, "e-government" improves services to citizens and reduces bureaucratic inefficiencies. The number and type of information technologies have multiplied and will continue to grow, and so have the nature, volume, and sensitivity of information that is moving from place to place. As in more developed countries, computer networks hold the potential for economic growth and prosperity in developing countries as well. E-commerce increases productivity and allows access to markets in other countries like never before. Small-and medium-sized enterprises in particular benefit from development of this type. Secure computer networks can improve infrastructure reliability, such as by enhancing transportation services and improving the consistent delivery of electricity and natural gas. Moreover, secure networks and favorable laws attract foreign investment in such industries as information processing and software development. Further, the Internet also holds out the promise of benefits that particularly may assist developing economies. "Telemedicine" may allow doctors to treat patients in remote or rural areas that do not already have access to modern medical care. Similarly, providing educational services over the Internet may allow many to receive training and college degrees who would previously have been unable to obtain them. In sum, providing the right environment for the development of secure computer networks can provide numerous benefits to both developed and developing societies. Yet with this blossoming potential come new dangers. Criminals and terrorists have recognized the potential of the Internet and have exploited it. Hackers have broken into bank computers, transferred funds to their own accounts, and extorted the banks; criminals use computers and computer networks to make child pornography cheaply and easily and to distribute it over the Internet to pedophiles they may never meet in person; and terrorists and drug dealers use encrypted electronic communications to evade government surveillance. Indeed, even improvements of critical infrastructures through computerization have a dark side: insecure information networks make infrastructures vulnerable to the attacks of hackers and "malicious code" such as viruses and worms. For example, in 1997, one hacker recklessly damaged a telecommunications switch that interrupted service at a regional airport in Massachusetts, 1 and malicious code has caused disruptions [*709] in train traffic, automated teller machines, and police emergency phone lines. 2 The threat caused by these crimes is not limited, however, to the direct harms of the crimes themselves: all of the benefits of information networks are at risk if the networks are not safe and secure. If users become unwilling to send their personal and credit card information over the Internet, e-commerce will not flourish. Similarly, citizens will not file their tax returns, bid on government contracts, or use other e-government services if they are afraid to use the networks. Moreover, if a particular country gets a reputation as a haven for Internet crime, consumers and businesses will refrain from interacting with it. For example, the prevalence of fraud by criminals located in Indonesia has caused many online retailers to block Internet Protocol (IP) addresses that originate in Indonesia, affecting online transactions both to and from the country. 29 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Hackers = Econ Collapse A network disruption by hackers crashes the economy Winn Schwartau, Prof. @ Norwich U. Board of Advisors, Information Security Awareness Week, Computer security expert, 1996, Information Warfare, http://www.thesecurityawarenesscompany.com/chez/chez.php?s=3cae5cf34c4a6b3 37d4e1433a22b17d6&menu=3 The foundation of modern society is based on the availability of an access to information that will drive a thriving economy upward on its course or propel a weak one into a position of power. In today's electronically interconnected world, information moves at the speed of light, is intangible, and is of immense value. Today's information is the equivalent of yesterday's factories, yet it is considerably more vulnerable. Right now, the United States is leading the world into a globally networked society, a true Information Age where information and economic value become nearly synonymous. With over 125 million computers inextricably tying us all together through complex land- and satellite-based communications systems, a major portion of our domestic $6 trillion economy depends upon their consistent and reliable operation. Information Warfare is an electronic conflict in which information is a strategic asset worthy of conquest or destruction. Computers and other communications and information systems become attractive first-strike targets. 30 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Hydrogen Solves Poverty A Hydrogen economy allows for electricity in poor communities, which ends poverty Jeremy Rifkin, , Author of "Hydrogen Economy", President of the Foundation on Economic Trends, 2002, The Hydrogen Economy, http://www.emagazine.com/view/?171 Incredibly, 65 percent of the human population has never made a telephone call, and a third of the human race has no access to electricity or any other form of commercial energy. The global average per capita energy use for all countries is only one fifth that of the U.S. The disparity between the connected and the unconnected is deep and threatens to become even more pronounced over the next half century with world population expected to rise from the current 6.2 billion to nine billion people. Most of the population increase is going to take place in the developing world, where the poverty is concentrated. Lack of access to energy, and especially electricity, is a key factor in perpetuating poverty around the world. Conversely, access to energy means more economic opportunity. In South Africa, for example, for every 100 households electrified, 10 to 20 new businesses are created. Electricity frees human labor from day-to-day survival tasks. Simply finding enough firewood or dung to warm a house or cook meals in resource poor countries can take hours out of each day. Electricity provides power to run farm equipment, operate small factories and craft shops, and light homes, schools and businesses. Making the shift to a hydrogen energy regime, using renewable resources and technologies to produce the hydrogen, and creating distributed generation energy webs that can connect communities all over the world, holds great promise for helping to lift billions of people out of poverty. Narrowing the gap between the haves and have-nots requires, among other things, narrowing the gap between the connected and the unconnected. It also presents a significant challenge: developing and harnessing renewable energy sources for hydrogen in countries with no current infrastructure. 31 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Poverty Impact Poverty causes extinction through the inevitable proliferation of insanely destructive devices. The only way to solve is by disseminating tech Dale Carrico, 3/10/06, lecturer in the Department of Rhetoric at the University of California at Berkeley, PhD, Uc Berkeley, Visiting Faculty, Liberal Arts, San Francisco Art Institute, Human Rights Fellow, Institute for Ethics and Emerging Technologies (IEET) amormundi.blogspot.com/2006/03/technology-and-terror.html the power of emerging technologies to redress the sources of legitimate social discontent - to end global poverty, to promote universal health provides the only way to manage the lethal power of emerging weapons of mass destruction, as well as the relative ease with which they could find their way into the hands of those who would express or exploit such discontent. I believe that and education and to develop abiding, genuinely representative and accountable public institutions - Contemplating Insane Destructiveness New technologies will be unprecedented in their creative and their destructive power, as well as in their ubiquity, and this changes everything. Two short essays, one by Lawrence Lessig in the April edition of Wired magazine and the other by Richard Rorty in the April 1 issue of the London Review of Books, address this in interestingly similar terms. These essays look at the problem of the likely near-term development and proliferation of relatively cheap and massively destructive new technologies such as bioengineered pathogens (Lessig) and suitcase nukes (Rorty). "Key technologies of the future - in particular, genetic engineering, nanotech, and robotics (or GNR) because they are self-replicating and increasingly easier to craft - would be radically more dangerous than technologies of the past," writes Lessig in terms that evoke an earlier essay by Bill Joy, but the technophobic conclusions of which Lessig significantly rejects. "It is impossibly hard to build an atomic bomb; when you build one, you've built just one. But the equivalent evil implanted in a malevolent virus will become easier to build, and if built, could become self-replicating. This is P2P (peer-to-peer) meets WMD (weapons of mass destruction), producing IDDs (insanely destructive devices)." Rorty writes in a similar vein that "[w]ithin a year or two, suitcase-sized nuclear weapons (crafted in Pakistan or North Korea) may be commercially available. Eager customers will include not only rich playboys like Osama bin Laden but also the leaders of various irredentist movements that have metamorphosed into well-financed criminal gangs. Once such weapons are used in Europe, whatever measures the interior ministers have previously agreed to propose will seem inadequate." It is probably inevitable that discussions of the threat of weaponized emerging technologies will reflect the distress of the so-called contemporary "War on Terror." But it is important to recognize that present-day terrorism, however devastating, is a timid anticipation of the dangers and dilemmas to come. The March 11, 2004 Madrid attacks made use of conventional explosives, and the September 11, 2001 attacks in the United States involved the crude hijacking and repurposing of fuel-fat jets as missiles. To the extent that these attacks have provoked as a response (or worse, have provided a pretext for) "preemptive" and essentially unilateral military adventures abroad, and assaults on civil liberties at home, it is increasingly difficult to maintain much hope that we are mature enough as a civilization to cope with the forces we have ourselves set in motion. Regulation Between Relinquishment and Resignation Both Lessig and Rorty anticipate that when confronted with the horrifying reality or even simply the prospect of new technological threats the first impulse of the North Atlantic democracies is almost certain to be misguided compensatory expansions of state surveillance and control. Both essays point to the likely futility of such efforts to perfectly police the creation and traffic of unprecedented technologies . In the worst case, with Lessig's designer pathogen or with the goo bestiary that preoccupies the nightmares of nanotech Cassandras (and don't forget the actual story: Cassandra was new massively destructive technologies that might be cooked up in obscure laboratories at comparably modest costs, using easily obtainable materials, employing techniques in the public domain, and distributed via stealthy networks. right!), we are confronted with the prospect of In the Bill Joy essay that inspired Lessig's piece, the epic scale of the threats posed by emerging technologies prompted Joy to recommend banning their development altogether. pre-emptive ban on these unprecedentedly destructive technological unenforceable, and hence would too likely shift the development and use of such technologies to precisely the least scrupulous people and least regulated conditions. And all of this would, of course, exacerbate the very risks any such well-meaning but misguided ban would The typical rejoinder to Joy's own proposal of "relinquishment," of a principled (or panic-stricken) capacities is that it is absolutely have been enacted to reduce in the first place. Definitely I agree with this rejoinder, but it's important not to misapply its insights. The fact that laws prohibiting murder don't perfectly eliminate the crime scarcely recommends we should strike these laws off the books. If Joy's technological relinquishment was the best or only hope for humanity's survival, then we would of course be obliged to pursue it whatever the challenges. But surely the stronger reason to question relinquishment is simply that it would deny us the extraordinary benefits of emerging technologies -— spectacularly safe, strong, cheap materials and manufactured goods; abundant foodstuffs; new renewable energy technologies; and incomparably effective medical interventions. Technophiles often seem altogether too eager to claim that technological regulation is unenforceable, or that developmental outcomes they happen to desire themselves are "inevitable." But of course the shape that development will take —- its pace, distribution, and deployments -— is anything but inevitable in fact. And all technological development is obviously and absolutely susceptible to regulation, for good or ill, by laws, norms, market forces and structural limits. Market libertarian technophiles such as Ronald Bailey sometimes seem to suggest that any effort to regulate technological development at all is tantamount to Joy's desire to ban it altogether. Bailey counters both Joy's relinquishment thesis and Lessig's more modest proposals with a faith that "robust" science on its own is best able to defend against the threats science itself unleashes. This is an argument and even a profession I largely share with him, but only to the extent that we recognize just how much of what makes science "robust" is produced and maintained in the context of well-supported research traditions, stable institutions, steady funding and rigorous oversight, most of which look quite like the "regulation" that negative libertarians otherwise rail against. For me, robust scientific culture looks like the fragile attainment of democratic civilization, not some "spontaneous order." So too "deregulation" is a tactic that is obviously occasionally useful within the context of a broader commitment to reform and good regulation. But treated as an end in itself the interminable market fundamentalist drumbeat of "deregulation" -— so prevalent among especially American technophiles —- amounts to an advocacy of lawlessness. Does this really seem the best time to call for lawlessness? Market libertarian ideologues often promote a policy of "market-naturalist" resignation that seems to me exactly as disastrous in its consequences as Joy's recommendation of relinquishment. In fact, the consequence of both policies seems precisely the same —- to abandon technological development to the least scrupulous, least deliberative, least accountable forces on offer. My point is not to demonize commerce, of course, but simply to recognize that good governance encourages good and discourages antisocial business practices, while a healthy business climate is likewise the best buttress to good democratic governance. While I am quite happy to leave the question of just which toothbrush consumers prefer to market forces, it seems to me a kind of lunacy to suggest that the answer to coping with emerging existential technological threats is, "Let the market decide." What we need is neither resignation nor relinquishment, but critical deliberation 32 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Poverty Impact <card continues, no text removed> and reasonable regulation. What we need is Regulation between Relinquishment and Resignation (RRR). Resources for Hope? Lessig and Rorty make different but complementary recommendations in the face of the dreadful quandaries of cheap and ubiquitous, massively destructive emerging technologies. Taken together, these recommendations provide what looks to me like the basis for a more reasonable and hopeful strategy. Rorty insists, first and foremost, that citizens in the North Atlantic democracies must challenge what he describes as "the culture of government secrecy": "Demands for government openness should start in the areas of nuclear weaponry and of intelligence-gathering," which are, he points out, "the places where the post-World War Two obsession with secrecy began." More specifically, we must demand that our governments "publish the facts about their stockpiles of weapons of mass destruction [and] make public the details of two sets of planned responses: one to the use of such weapons by other governments, and another for their use by criminal gangs such as al-Qaida." He goes on to point out that "[i]f Western governments were made to disclose and discuss what they plan to do in various sorts of emergency, it would at least be slightly harder for demagogic leaders to argue that the most recent attack justifies them in doing whatever they like. Crises are less likely to produce institutional change, and to have unpredictable results, if they have been foreseen and publicly discussed." Never has the need for global collaboration been more conspicuous. Never has the need to unleash the collective, creative, critical intelligence of humanity been more urgent. And yet the contemporary culture of the "War on Terror" has seemed downright hostile to intelligence in all its forms. Efforts to understand the social conditions that promote terror are regularly dismissed as "appeasement." Critical thinking about our response to terror is routinely denigrated as "treason." Authorities strive to insulate their conduct from criticism and scrutiny behind veils of secrecy in the name of "security." (And all of this is depressingly of a piece, of course, with the current Bush Administration's assaults on consensus environmental science, genetic research, effective sex education, and all the rest.) It is no wonder so many of us fear the "War on Terror" quite as much as we fear terrorism itself. But how much more damaging than the self-defeating and authoritarian responses to conventional terrorism can we expect the response to the emerging threats of Lessig's "Insanely Destructive Devices" to be? When devastating technologies become cheap and ubiquitous we must redress the social discontent that makes their misuse seem justifiable to more people than we can ever hope to manage or police. Since we cannot hope to halt the development of all the cheap, disastrously weaponizable technologies on the horizon, nor can we hope to perfectly control their every use, Lessig suggests that "perhaps the rational response is to reduce the incentives to attack... maybe we should focus on ways to eliminate the reasons to annihilate us." Fantasies of an absolute control over these technologies, or of an absolute control through technology (SDI, TIA, and its epigones, anyone?), are sure to exacerbate the very discontent that will make their misuse more widespread. Anticipating the inevitable objection, Lessig is quick to point out that "[c]razies, of course, can't be reasoned with. But we can reduce the incentives to become a crazy. We could reduce the reasonableness - from a certain perspective - for finding ways to destroy us." Criminals, fanatics and madmen are in fact a manageable minority in any culture. (Racist know-nothing slogans to the contrary about a so-called epic and epochal "Clash of Civilizations" deserve our utter contempt.) Although there is no question that Lessig's "Insanely Destructive Devices" could still do irreparable occasional harm in their hands, it is profoundly misleading to focus when it is as often as not the exploitation of legitimate social discontent that makes it possible for lone gunmen to recruit armies to their "causes." Lessig concludes that "[t]here's a logic to p2p threats that we as a society don't yet get. Like the record companies against the Internet, our first response is war. But like the record companies, that response will be either futile or self-destructive. If you can't control the supply of IDDs, then the right response is to reduce the demand for IDDs. [Instead, America's] present course of unilateral cowboyism will continue to produce generations of angry souls seeking revenge on us." For generations, progressives have sought to ameliorate the suffering of the wretched of the Earth. We have struggled to diminish poverty, widen the franchise, and ensure through education and shared prosperity that more and more people (though still obscenely too few people) have a personal stake as citizens in their societies. We have fought for these things because we have been moved by the tragedy of avoidable suffering, and by the unspeakable waste of intelligence, creativity and pleasure that is denied us all when any human being is oppressed into silence by poverty or tyranny. The emerging threat of cheap and ubiquitous, massively destructive technologies provides a new reason to redress social injustice and the discontent it inspires (for those among you who really need another reason): The existence of injustice anywhere might soon threaten you quite literally, and needlessly, with destruction. on the threats posed by crazy and criminal minorities 33 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Solvency Fleet Vehicle Solvency Hydrogen would start with fleet vehicles which would make distribution easy. Christian Azar et al, Department of Physical Resource Theory at Chalmers University of Technology Kristian Lindgren, same qual, Bjorn A. Andersson, same qual, August 2003, Global energy scenarios meeting stringent CO2 constraints--costeffective fuel choices in the transportation sector, Energy PolicyVolume 31, Issue 10, , Pages 961-976. Since hydrogen is a gas at normal temperature and pressure, distribution and refueling is more complicated than what is the case for methanol or any other liquid hydrocarbon. On the other hand, there are several ways hydrogen can be distributed to filling stations, e.g., (1) pipeline distribution from centralized plants, (2) localized steam reforming of natural gas, (3) distribution by truck of liquid hydrogen, and (4) small-scale electrolysis at the filling station.5 In the early stages of a transition towards hydrogen in the transportation sector, fleet vehicles (busses, taxis, government and company vehicles, etc.) would probably dominate. The production technology would be site specific and include steam reforming of methane and electrolysis in hydropower rich countries (having excess capacity night time). If the market starts to expand rapidly beyond that of fleet vehicles, alternatives two, three and four would probably play important roles. The possibility to produce hydrogen via electrolysis or to ship/truck it as liquefied hydrogen to rural areas where pipelines would be expensive, implies that the hydrogen can be made available even before the “final” infrastructure is set up. In the long run, when hydrogen is a very common energy carrier, distribution with pipeline is probably the preferred option. Fleet Vehicles are key – the market has insufficient force to cause a transition. THE EPA has authority. (unpopular warrants too) Alexander E. Farrell et al, Energy and Resources Group at UC Berkeley, David W. Keith, Department of Engineering and Public Policy at Carnegie Mellon, James J. Corbett, Marine Policy Program at the University of Delaware. October 2003, Energy Policy, Volume 31, Issue 13, pages 1357-1367, A strategy for introducing hydrogen into transportation. Because hydrogen has few (if any) private benefits compared to petroleum-based fuels, widespread use will require either radically different market conditions or new policies. The combination of physical challenges to using hydrogen onboard vehicles, the widespread availability of less problematic substitutes for petroleum (e.g. efficiency improvements or bio-ethanol) suggests that market forces are unlikely to induce a switch to hydrogen for the next several decades. Therefore, the introduction of hydrogen is likely to require forceful government action, such as mandates or substantial economic incentives. Unfortunately, this amounts to ‘picking a technological winner’ (hydrogen, in this case), which government often does quite poorly. For instance, owners of vehicle fleets might be required to buy ‘hydrogen fueling’ credits based on their fleet size. These credits would be created by the sale of hydrogen as a transportation fuel, not dissimilar to how a renewable portfolio standard might be implemented (Berry, T. and Jaccard, M., 2001. The renewable portfolio standard: design considerations and an implementation survey. Energy Policy 29, pp. 263–277). Note, however, that DOE was given authority to implement a similar approach under the 1992 Energy Policy Act, but chose not to do so, suggesting significant changes in political conditions might be required before any forceful hydrogen fuel policy might be feasible. Further, because the benefits of switching to hydrogen fuel are largely public and not private, it is not clear that the costs of such a policy should be borne by a single mode (or industry). It is even less clear that forcing one mode to bear such disproportionate costs would be politically feasible. 34 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Postal Service Solvency The Postal service is key to solve – it has developed every mode of transportation. The relationship also uniquely benefits GB General Motors, 9/26/06, http://www.gm.com/experience/technology/news/2006/fc_us_postal_092706.jsp?exist=false, GM Extends Agreement with U.S. Postal Service to Test Fuel Cell Vehicles for Mail Delivery “The U.S. Postal Service has a long history of paving the development of nearly every mode of transportation used in the last 230 years,” said Walter O’Tormey, Vice President, Engineering, U.S. Postal Service. “GM is helping to lead the way to a hydrogen-powered future—with advanced technologies that are more energy efficient, kinder to the environment, and help increase the energy security of our country.” The program extension allows GM to continue to test and validate the hydrogen fuel cell propulsion system in real world driving conditions. This unique demonstration and learning relationship directly benefits GM as it seeks to validate an automotive fuel cell system by 2010—one that would be competitive with current internal combustion systems on durability and performance, and can ultimately be built at scale affordably and brought to market as quickly and efficiently as possible. “GM’s ultimate vision for an environmentally sustainable future is a hydrogen economy with fuel cell based transportation,” said Larry Burns, GM vice president of research and development and strategic planning. “The U.S. Postal Service has been an excellent organization to work with in helping us to test and validate the hydrogen fuel cell propulsion system. Together, we’ve proven what the hydrogen fuel cell vehicle can do on the East Coast, and we’re appreciative of the opportunity for further testing on the West Coast.” Small Niche Markets are key to introduction. Alexander E. Farrell et al, Energy and Resources Group at UC Berkeley, David W. Keith, Department of Engineering and Public Policy at Carnegie Mellon, James J. Corbett, Marine Policy Program at the University of Delaware. October 2003, Energy Policy, Volume 31, Issue 13, pages 1357-1367, A strategy for introducing hydrogen into transportation. Current research and demonstration efforts generally acknowledge that the introduction of hydrogen fuel would be an enormous, expensive change, but they do not attempt to evaluate the relative merits of modes other than LDVs. Because of this, they fail to properly consider the dynamics of a transition to a ‘hydrogen economy’.2 Yet, understanding such a transition is crucial to formulating coherent public policy, and that understanding must build on our growing knowledge of the dynamics of technological change. Using insights from engineering principles and the economics of technological change, we develop the logic needed to identify a lowest-cost, low-risk approach to the introduction of hydrogen fuel into the transportation sector. Current research and demonstration efforts also fail to consider even the possibility of something like ‘strategic niche management’ in which new technologies are introduced (by government action) into a small set of applications where they can be better tested and improved before used in larger applications (Kemp et al., 1998). The basics of technological change are simple; new technologies typically enter tiny niche markets before diffusing into widespread use. Identifying the “lead adopters” who have a high willingness to pay for the new technology and make up those niche markets is the key to successfully introducing new technologies (Griliches, 1956). A related effect is “technological learning” or learning-by-doing, which reduces the cost of producing goods, especially in the early years ( Argote, 2000; Epple et al., 1996). Learning-by-doing promotes the diffusion of new technologies through a virtuous circle in which experience drives down the cost of the new technology, opening up larger markets, which in turn encourages further investment in the new technology and yields greater experience, and so forth. 35 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Postal Service Solvency Postal service rocks, it is at the forefront of development and causes lots of shit in the federal government. Fucking sweet. Han T. Dinh, Program Director, Engineering, of the United States Postal Service, 2005, http://64.233.167.104/search?q=cache:11mBhxkcSDcJ:www.gsa.gov/gsa/cm_attachments/GSA_DOCUMENT/vv34USPSl_ R2E-e1-q_0Z5RDZ-i34KpR.doc+%22United+States+Postal+service%22+or+%22USPS%22+and+hydrogen&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=2&gl=us The USPS has been working with the White House’s Office of Science and Technology to develop a website at http://www.usps.com/environment/fuelcell.htm which is the USPS central source of information on R&D activities related to hydrogen and fuel cells. This web site is part of www.hydrogen.gov which was developed to further the goals of the President's Hydrogen Fuel Initiative and encourage greater collaboration and sharing of information on hydrogen technology development activities among government departments and agencies; commercial entities; state, regional, and international organizations; and the general public. For several decades, the USPS has been a pioneer at the forefront of many alternative fuel initiatives and has set examples for many other Federal agencies. The USPS is one of a handful of federal agencies to comply with the Energy Policy Act of 1992 and 2005 in terms of its alternative fuel vehicle requirements. The USPS currently has the largest AFV fleet in the nation and continues to acquire more EPACT-compliant vehicles. In addition, research is underway to explore other avenues, such as biodiesel, hybrid-electric for the short term and hydrogen fuel cells for the long term. At the present time, fuel cells hold the most promising technology to meet the future needs for transportation. However, several major obstacles such as cost, durability, fuel infrastructure and hydrogen storage need to be overcome before this technology becomes commercially available for the public and the USPS. Postal Service is good – helps efficiency and disseminates tech United States Postal Service, 2007, Strategic Transformation Plan from 2006 to 2010. http://www.usps.com/strategicplanning/stp2007/enhance_003.htm Since 2004, the Postal Service has partnered with General Motors to explore the applicability of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) for mail delivery. The Postal Service FCV program is generating technical and operational information needed to better understand issues related to the infrastructure needed to support hydrogen-fueled vehicles. This demonstration of emerging fuel cell technology, coupled with other advanced and AFV vehicle initiatives, has the potential to provide multiple benefits for the nation, including improved fuel efficiency, increased energy independence, and reduced emissions. The Postal Service will continue to seek opportunities to support fuel cell research and support activities to help transition the technology to the public. 36 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Postal Service Solvency The Postal Service can only consider hydrogen vehicles when the price of hydrogen is lowered Randolph E. Schmid, associated press writer, June 15, 2008, “Petrol prices pinching post office”, http://209.85.215.104/search?q=cache:DLkqvr_skx8J:news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20080615/ap_on_go_ot/postal_petrol+usps+fleet +hydrogen&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=60&gl=us&client=safari, Accessed July 16, 2008 CM Hydrogen fueled vehicles are also under consideration, he said. The agency is working with General Motors on such a vehicle, which could be tested in California where hydrogen filling stations are being established. "We think it's an opportunity if the fuel is available," Donahoe said. The Postal Service is the largest civilian public fleet in the world Government Accountability Office, February 2007, “U.S. POSTAL SERVICE Vulnerability to Fluctuating Fuel Prices Requires Improved Tracking and Monitoring of Consumption Information”, http://www.gao.gov/new.items/d07244.pdf, Accessed July 15, 2008 CM The U.S. Postal Service (the Service) delivered over 213 billion pieces of mail to over 146 million delivery points in 2006.1 Almost $72 billion was spent in providing these and other postal services required as part of meeting its universal service mandate. The Service is one of the major users of fuel in the federal government, spending over $2.3 billion on transportation and facility-related fuel in 2006.2 Its vehicle fleet of over 216,000 vehicles is the largest civilian fleet and consumed over 123 million gallons of gasoline and diesel fuel. The Service also incurs fuel expenses as part of its mail delivery and transportation contracts with highway trucking companies and air carriers.3 Another area where the Service incurs fuel expenses is in heating and operating the over 34,000 facilities it occupies. The Service relies primarily on electricity, natural gas, and heating oil for these operations. The Service is also subject to certain federal energy conservation requirements as part of the Energy Policy Acts of 1992 and 2005. The Energy Policy Act of 1992 (EPAct 1992) required federal agencies to increase their purchase of alternative fuel vehicles (AFV), and the Energy Policy Act of 2005 (EPAct 2005) details requirements for federal fleets to use alternative fuels in these AFVs.4 EPAct 2005 also requires agencies, to the maximum extent practicable, to install meter systems at federal buildings to track energy consumption. 37 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Postal Service Solvency The Postal Service has practiced private-public relationships before Government Accountability Office, February 2007, “U.S. POSTAL SERVICE Vulnerability to Fluctuating Fuel Prices Requires Improved Tracking and Monitoring of Consumption Information”, http://www.gao.gov/new.items/d07244.pdf, Accessed July 15, 2008 CM Use public/private partnerships: We have reported that leading organizations have found that more cooperative business relationships with suppliers have improved their ability to respond to changing business conditions and have led to lower costs. Over 20 years ago, federal government agencies were encouraged to utilize an alternative source of funding investments aimed at promoting energy-efficient projects. Under these projects, a private contractor would identify, design, install, and finance energy conservation measures in federal buildings in exchange for a share of the resultant energy cost savings that would be paid back to the contractor over a set period of time. These alternative funding mechanisms take advantage of public/private partnerships to provide incentives for cost savings and reduce energy consumption. These contracts have been advocated by the President and the Department of Energy as an effective energy conservation measure, and EPAct 2005 recently extended the authority for these financing mechanisms through 2016. When the Postal Service replaces their fleet, the only thing that is preventing hydrogen is price Government Accountability Office, January 8, 2008, “HYDROGEN FUEL INITIATIVE DOE Has Made Important Progress and Involved Stakeholders but Needs to Update What It Expects to Achieve by Its 2015 Target”, http://www.gao.gov/new.items/d08305.pdf, Accessed July 15, 2008 CM The U.S. Postal Service conducted a 3-year hydrogen fuel cell demonstration program with mail delivery vehicles at test sites in Virginia and California. Plans are underway to continue the effort using the next generation of hydrogen vehicles in partnership with General Motors and DOE. In addition, the Postal Service is considering hydrogen technology as an option for its planned replacement of its fleet of about 215,000 vehicles in 2018. Incentives to the Postal Service are key for hydrogen infrastructure Margo Melendez, senior project Leader at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory & Anelia Milbrandt, member of the International and Environmental Studies Group in the Strategic Energy Analysis and Applications Center., March 2005, “Analysis of the Hydrogen Infrastructure Needed to Enable Commercial Introduction of Hydrogen-Fueled Vehicles”, http://www.nrel.gov/hydrogen/pdfs/37903.pdf, Accessed July 18, 2008 CM This shows that, given the right incentives, federal facilities could provide a good starting point for a transitional hydrogen infrastructure because they offer broad geographic coverage. In particular, federal agencies that have been proactive with the introduction of other alternative fuels into their fleets may have an interest in pursuing hydrogen for not only their fleet, but also for co-generation and public fueling. Figure 9 shows U.S. Postal Service (USPS) facilities. The USPS is a good candidate for the co-generation option in the near term because it operates its own fleet, which could use hydrogen, and is dispersed widely across the country. 38 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Postal Service Solvency The plan would cost only a fraction of what the Postal Service loses because of gas rates yearly and it would make it self-sustainable quickly Margo Melendez, senior project Leader at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory & Anelia Milbrandt, member of the International and Environmental Studies Group in the Strategic Energy Analysis and Applications Center., March 2005, “Analysis of the Hydrogen Infrastructure Needed to Enable Commercial Introduction of Hydrogen-Fueled Vehicles”, http://www.nrel.gov/hydrogen/pdfs/37903.pdf, Accessed July 18, 2008 CM 6. Results and Conclusions Overall, 284 stations were identified that could make up a potential transitional national hydrogen fueling infrastructure backbone, with a total construction cost of $837 million if constructed to meet the needs of 2020. This is based on the aggressive assumptions of a 50% fuel cell vehicle stock by 2050, and approximately 1% in 2020 and 20% in 2030. Section 9 shows the complete list of station locations selected. The construction cost of $837 million is an initial cost for the early hydrogen network. Because the infrastructure is based on anticipated station use, many of the stations could be economically self sustaining in the near term (2020–2030). This depends on how evenly the fuel cell vehicles are distributed geographically. Most likely, they would be concentrated in key urban areas, making those stations economically viable, whereas rural stations that do not serve as many vehicles may need additional financial support until sufficient vehicles are operating in their region. One way to help the economic viability of stations is to incorporate co-generation. In particular, using co-generation (hydrogen for fuel cell vehicles and powerproducing stationary fuel cells) at federal facilities could reduce the federal government’s overall fossil fuel consumption and environmental impacts while helping facilitate interstate travel in fuel cell vehicles for the driving public. 39 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Postal Service Solvency Current postal service programs including working with the private sector at local post offices Dan Davidson, Staff Writer Federal Times, January 11, 2006, “High fuel costs spur conservation” http://www.federaltimes.com/index2.php?S=1452397, Accessed July 16, 2008 CM Faced with unexpectedly high fuel costs this year, the U.S. Postal Service has been ramping up savings measures, hoping to cut hundreds of millions of dollars from energy bills over the next decade. In the last fiscal year that ended Sept. 30, the additional cost to the agency resulting from the summer energy crisis and the post-Katrina natural gas shortage totaled about $400 million, according to Michael Fanning, Postal Service program manager for energy management. That is on top of an already huge energy bill. “Energy is the third-largest cost center in the Postal Service, following salaries and benefits, and automation,” Fanning said. “In fiscal year 2005, facility energy costs were almost $600 million and mobile energy costs were nearly $1.5 billion.” High energy costs will likely continue into the new year and beyond and the Postal Service must take steps on many fronts to cut energy use where it can and get the most of its fuel where it can’t, Fanning said. These steps include everything from turning down the thermostat to exploiting recent advances in wind-powered technology. Fanning was hired last fall to develop and implement energy policy and strategy, coordinate organizational efforts and establish metrics to measure progress. One significant energy-saving move could come after a suppliers’ conference Jan. 13 at Postal Service headquarters in Washington, at which the agency will explain to prospective contractors its desire to award Shared Energy Savings contracts. Under these deals, contractors outfit postal facilities to be more energy efficient — such as with renewable energy, geothermal heat pumps, photovoltaic energy sources and micro-turbine wind power — and then they and the Postal Service share in any savings. The SES contracts will be open for work at postal facilities in all each of the 50 states. What type of energy-saving mechanism would be suitable will depend on the type of postal facility, how it is geographically situated and the likely return on investment, Fanning said. “These contracts will require no USPS capital investment but could produce energy cost avoidance of more than $1 billion over the next decade,” Fanning said. The agency plans to award contracts by the end of February. The use of Shared Energy Savings contracts is not new. The agency hired Chevron Energy Solutions to perform energy audits on its facilities in Northern California, and since 2004 Chevron has completed work, or is engaged in work, on 16 postal facilities. The company has upgraded the efficiency of compressed air systems, which are used to move the mail about, and installed more efficient lighting, heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems, said Chevron Energy Solutions president Jim Davis. At the West Sacramento mail-processing and distribution facility, Chevron introduced a massive solar system mounted on a new parking structure to generate power. This and other improvements by Chevron cut the facility’s energy costs by one-third, Davis said. At the San Francisco mail-processing facility, electricity savings resulting from the upgrades should be about $1.2 million annually, Davis said. On average, energy-efficient upgrades will reduce electricity and natural gas costs by 30 to 40 percent, Davis said. 40 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Niche Solvency Putting hydrogen in to a single small market, like the post service, makes it competitive more quickly than anything else. Alexander E. Farrell et al , Energy and Resources Group at UC Berkeley, David W. Keith, Department of Engineering and Public Policy at Carnegie Mellon, James J. Corbett, Marine Policy Program at the University of Delaware. October 2003, Energy Policy, Volume 31, Issue 13, pages 1357-1367, A strategy for introducing hydrogen into transportation. One way to reduce the cost of the introduction of hydrogen fuel is to limit it to a single mode, in line with the notion of strategic niche management discussed above. If an entire mode shifts to hydrogen, competitive pressures will act to reduce costs and improve performance. Before commitments in vehicles and infrastructure are made for a wide range of transportation modes, it would be better to start small, to let innovation and competition weed out lower-performance technologies before risking broader disruptions of the transportation system. In order to achieve real learning by doing and advance the hydrogen technology cluster effectively, however, one cannot start out too small. Isolated demonstration projects often accomplish little in the way of innovation because market forces, among the most powerful influences on technological innovation, are not at work. Instead of focusing on reducing costs and meeting customer needs, government-funded demonstration projects often focus on public relations and overtly political objectives. In addition, demonstration projects tend to be one-off efforts that offer little opportunity to realize the benefits of learning-by-doing. These benefits can be brought about only by a significant level of adoption, which will create competition between different providers and create demand for the associated products and services in the technology cluster. By introducing hydrogen so that it achieves significant market penetration into a single transportation mode, or perhaps in a geographically restricted area, the benefits of learning-by-doing will be maximized while society incurs the minimal overall costs and risks.4 41 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Niche Solvency Niches like the postal service would help weed out weak technology and solve competitiveness. Alexander E. Farrell et al, Energy and Resources Group at UC Berkeley, David W. Keith, Department of Engineering and Public Policy at Carnegie Mellon, James J. Corbett, Marine Policy Program at the University of Delaware. October 2003, Energy Policy, Volume 31, Issue 13, pages 1357-1367, A strategy for introducing hydrogen into transportation. Our review suggests that the overarching goal of introducing hydrogen as a transportation fuel should be to develop the cluster of technologies and practices associated with its use at least public cost and social disruption. This will reduce the cost and other social disruptions of wide-scale use, should that be the outcome of either market or policy choices. In committing public funds and political will to introducing hydrogen fuel vehicles and infrastructure for a wide range of transportation modes, the best strategy would be to start with protected niches, and to let innovation and competition weed out lower-performance technologies before risking broader disruptions of the transportation system. A protected niche would allow for companies to learn by doing in the design and operation of hydrogen-fueled vehicles. Relying on demonstration projects alone to spur the necessary technological innovation is inadequate because insufficient incentive or experience exists to achieve real learning by doing and advance the hydrogen technology cluster effectively. The guidelines developed here suggest that the cost of introducing hydrogen fuel can be minimized by selecting a mode that uses a small number of relatively large vehicles, which are owned by a small number of technologically sophisticated firms and operated by professional crews, and which are used intensively along a limited number of point-to-point routes or operated within a small geographic area. In addition, technological innovation in vehicle design will take place most quickly in modes where individual vehicles are produced to order and each receives significant engineering attention (not those manufactured in vast quantities on assembly lines). The immediate environmental benefits of introducing hydrogen fuel will occur in modes that have little or no pollution regulations applied to them. These results suggest that heavy-duty modes would be a less costly way to introduce hydrogen as a transportation fuel and a more effective way to advance hydrogen-related technologies so that they could be used widely in light-duty vehicles. Using the example of international marine freight, we identify interesting opportunities as well as considerable barriers. Similar complex trade-offs are likely to appear for every mode, and these need to be more systematically evaluated. More generally, freight modes appear to be more consistent than LDV with a strategic approach for early public efforts to introduce hydrogen into transportation. 42 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Subsidies Solve Government subsidizing technology key to hydrogen Julie Foley, institute for public policy research sustainability team, 2003, Tomorrow’s Low Carbon Cars Driving innovation and long term investment in low carbon cars, IPPR, www.ippr.org] If hydrogen-powered cars are to become a future reality, tax incentives for hydrogen will need to be complemented by policies and programmes that support technological innovation over the longer term. Innovation is a common theme in government strategy papers. But the Government has yet to adequately recognize the links between innovation and environmental policy. Innovation can be difficult concept for government to grapple with. Policy makers like to know what a particular policy measure is likely to cost and what its environmental outcomes are likely to be. The hitch with innovation is that the process of research, development and .learning by doing. yields options whose costs and benefits are as yet unknown (Anderson et al, 2001). It might even result in options that prove to be a dead end. Innovation by definition is uncertain and can appear highly risky for government. But in the decades to come, mitigating climate change could depend on developing policies that foster technological innovation in the development of hydrogen powered vehicles. Political leadership will be essential to supporting technological innovation of this kind and the Government appears to be waking up to this fact. Following the Johannesburg World Summit, Tony Blair wrote a joint letter with Goran Persson, Prime Minister of Sweden, to Romano Prodi, President of the European Commission, calling for greater EU commitment to the innovation of environmental technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cells. .Faster development and greater use of new technologies has the potential massively to modernise the way our economy works. It can modernise our production and consumption patterns, our infrastructures and our technologies. Clean and more resource efficient technologies can contribute to a rich and healthy environment, and be a driving force for innovation, development of new businesses, job creation and growth.. (Blair and Persson, 2003). 43 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Subsidies Solve Government subsidy of technology leads to hydrogen development and use. [A.A. Van Benthem et al, Faculty of Economics and Econometrics, University of Amsterdam, G.J., Kramer Shell Global Solutions International, R. Ramer, Faculty of Economics and Econometrics, University of Amsterdam, Energy Policy, Vl. 34 Issue 17 Nov 2006, Pages 2949-2963, An Options approach to investment in a hydrogen infrastructure Instead of subsidizing the actual investment, the government could also consider to focus on subsidizing nationwide research & development, hoping that this will increase the speed of cost reductions. Table 9 compares the effects of increasing the speed of cost reductions versus a tax cut on hydrogen Table 8): Although we will not attempt to estimate the cost of reducing the expected time between cost reductions, Table 9 shows that the expected time until investment decreases dramatically if technology matures faster. Therefore we suspect that R&D subsidies will be a more effective type of government policy. In summary, looking at the effectiveness of government spending in relation to the advancement of hydrogen deployment, we find that ‘state-independent’ tax incentives are relatively ineffective. The reason for this is once again the fact that deployment timing is set by technology maturation rather than by the absolute profits of direct investment. By the same token, government subsidy for technology development could be a more effective means to achieve earlier investment.9 [Continued three paragraphs later] Because of environmental and possible long-term energy security advantages associated with hydrogen, it is widely believed that governments will provide some sort of fiscal support. We have looked at the effectiveness of government spending in relation to the advancement of hydrogen deployment. We find that ‘state-independent’ tax incentives are relatively ineffective. The reason for this is once again the fact that deployment timing is set by technology maturation rather than by the absolute profits of direct investment. Though outside the scope of the present model, we are lead to believe that government subsidy for technology development is more effective in reducing the time until investment, as faster production cost reductions for hydrogen and FCVs lead to accelerated investment. 44 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Refueling Infrastructure Key Refueling infrastrucucture key to stimulate demand for hydrogen vehicles. Alexander E. Farrell et al, Energy and Resources Group at UC Berkeley, David W. Keith, Department of Engineering and Public Policy at Carnegie Mellon, James J. Corbett, Marine Policy Program at the University of Delaware. October 20 03, Energy Policy, Volume 31, Issue 13, pages 1357-1367, A strategy for introducing hydrogen into transportation. In addition to these purely physical factors, there is a significant problem associated with the introduction of a new fuel (sometimes called the “chicken and egg” problem) of coordinating between investments in hydrogen vehicles and refueling infrastructure (Jensen and Ross, 2000; Winebrake and Farrell, 1997). Simply put, consumers and businesses are reluctant to buy vehicles for which no refueling infrastructure exists while investors are reluctant to build refueling infrastructure for which there is no demand. These difficulties have plagued efforts to introduce alternative fuels less exotic than hydrogen, such as natural gas, because both refueling infrastructure and vehicle conversion remained unprofitable ( Flynn, 2002). “The primary barriers for alternativefuel vehicles are cost, market acceptance, and deployment because a variety of proven technologies are already commercially available” ( US Department of Energy, 2000, pp. 4–48). Refueling infrastructure before cars Woodrow W. Clark et al , leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy Today, the number of hydrogen fueled cars is so few in number that refueling stations for these vehicles alone are economically unfeasible. That is why a number of companies and regions, including SCAQMD, are advocating and installing “hydrogen energy stations” first for stationary energy storage and off-peak power which can supply stored hydrogen to homes and business in the local community from renewable resources until the demand for hydrogen fuel for vehicles arrives. And that time frame appears shorter than most researchers predict. One Japanese research and development institution privately predicts instead that there will 50,000 hydrogen fuel cell powered vehicles in and around Tokyo by the end of 2005 with sufficient hydrogen refueling stations readily available. The future, however, may well go beyond public commercial stations and see hydrogen powered fuel cells located in homes for both domestic power and fuel for family cars. Furthermore, leveraging existing solar powered electric vehicle recharging stations at various public parking lots could serve as a key inter-modal transportation component to station feasibility. The hydrogen infrastructure issue need not limit the evolution of fuel cells and hydrogen technology. Rather, many companies are now commercializing “hybrid technologies” (Clark, 2004) envisioning a distributed model for hydrogen production and delivery to integrate the gas, electricity, building, and mobility infrastructures. Instead of building a costly new distribution infrastructure for hydrogen, excess existing gas and electricity distribution capacity can supply local hydrogen production needs. Only after this decentralized approach has built up a large hydrogen market for power to buildings and then vehicles later will central production merit substantial investment. 45 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Refueling Infrastructure Key Public policies are key to facilitate the 30% of fueling stations that are required to cause a hydrogen transportation sector. United States Department of Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen Economy – to 2030 and beyond. While hydrogen may be able to use some of the existing infrastructure, specific upgrades and enhancements will be needed to accommodate the unique features of hydrogen, particularly in storage and distribution. The technologies needed to convert the natural gas infrastructure for the use of hydrogen are available today, but are not yet cost- effective. At present there is no motivation to convert to hydrogen, as there are essentially no markets for distributed use of hydrogen energy. Additional infrastructure costs will have to be incurred in the future, when cost-competitive products are available, to enable the transition to the hydrogen economy. The technical and economic barriers to upgrading the Nation’s fueling stations to provide hydrogen represents one of the major stumbling blocks to the expanded use of hydrogen-fueled vehicles. Some automakers estimate that hydrogen would have to be available in at least thirty percent of the nation’s fueling stations for a viable hydrogen- based transportation sector to emerge. Private investment in such an infrastructure will not be forthcoming in the absence of supporting and sustained, supportive public policies Infrastructure key for some reason I don’t know. United States Department of Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen Economy – to 2030 and beyond. One major foundation for this vision is the development of an energy infrastructure that can support the expanded production, delivery, storage, and use of hydrogen energy. A hydrogen infrastructure is likely to develop on a regional level, since it can be made from a variety of feedstocks, and will resemble the electricity grid more than the current oil delivery system. Construction of this infrastructure will take time and will require significant resources. As a result, the hydrogen economy will evolve over the next several decades. Hydrogen storage weight and volume reductions, mass production of fuel cells, construction of the necessary infrastructure, and expanded use of portable and distributed power generation devices will sustain the momentum towards a hydrogen economy. Infrastructure will begin with pilot projects and expand to local, regional, and ultimately national and international applications. Infrastructure key to investment Mark Schrope, freelance writer in Melbourne Florida, 12/13/01, Which Way to Energy Utopia, Nature, Vol. 414 pgs 682684 Infrastructure issues play a big role in the debate over which approach should be taken. The lack of an existing system for storing and distributing hydrogen presents a dilemma. Car manufacturers do not want to sell vehicles that people cannot fuel, and energy companies do not want to spend money developing a hydrogen distribution infrastructure when there are no hydrogen cars on the road. The equation becomes more complicated with fuels cells because they have yet to be produced in large numbers and their long-term reliability has not been proven. 46 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Refueling Infrastructure Key Yo it’s key to cause competitive car growth Soultek.com October 24 2007, Is Hydrogen Worth the Investment? http://www.soultek.com/clean_energy/hybrid_cars/worth_15_billion_to_kick_start_hydrogen_economy.htm By 2010, if a hydrogen highway existed to fuel around 1,000,000 fuel cell vehicles, GM believes if could produce hydrogen fuel-celled vehicles at a price competitive with conventional technology. Ultimately, the problem with the hydrogen economy isn't fuel cell vehicles, it's the lack of hydrogen fuel pumps. To build enough hydrogen filling stations to make fuel cell vehicles convenient in the top 100 metro areas, plus enough stations interspersed along all major highways to enable transportation between these 100 metro areas, would cost between $10 - 15 billion according to GM. 47 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Refueling Infrastructure Key The auto industry is waiting on governments to provide infrastructure for their vehicles Larry Burns, General Motors vice president, research & development and strategic planning., April 2, 2008, “GM Urges More Hydrogen Stations Vehicles Needs to Be Matched With Rapid Progress on Hydrogen Fueling” , http://www.hydrogenassociation.org/media/pressReleases/02apr08_GM.pdf, Accessed July 16, 2008 SACRAMENTO, CA – General Motors today called on the energy industry and governments to step up and help automakers make volume production of fuel cell-electric vehicles a reality by opening more hydrogen fueling stations. That message was delivered by Larry Burns, General Motors vice president, research & development and strategic planning. Burns delivered a keynote address at the National Hydrogen Association’s annual conference in Sacramento, CA. “The automobile industry has reached a critical juncture in our journey to realize the full potential of hydrogen fuel cellelectric vehicles,” said Burns. “While we have made impressive progress, we have now reached a point where the energy industry and governments must pick up their pace so we can continue to advance in a timely manner.” Burns noted that other automakers are also spending significant amounts on developing fuel cell technology and want to bring large numbers of fuel cell vehicles to market, but he points out that parallel investment by the energy industry and governments is urgently required. Burns’s comments coincided with the release of a new study by General Motors and Shell Hydrogen, which concluded that a hydrogen infrastructure is economically viable and doable. “It’s no longer a question of “can it be done?” or “should it be done?” said Burns. “We not only should do it. We must do it. It’s now a question of collective will. Do we have the collective resolve to work together to solve the challenges we face rather than handing them off to future generations?” Burns said addressing the infrastructure challenge is essential because the potential benefits of hydrogen fuel cell technology are clear and compelling. “This technology promises to deliver family-sized vehicles that are fun to drive, safe, look great, refuel fast, go far between fill-ups, and are emissions-free and petroleum-free. It also holds promise to do all of this while keeping automobiles affordable to own and operate. And just like electricity, it can be made from a broad range of renewable and sustainable energy pathways. No other technology offers this exciting potential,” he said. “We have not discovered anything yet to suggest mass volume cannot ultimately be attained. “ He also complimented hydrogen fueling initiatives by FreedomCAR, Shell Hydrogen AND Chevron Hydrogen, the California Fuel Cell Partnership, and the California Hydrogen Highway, but called for efforts like these to accelerate. “What is urgently needed is sufficient investment by energy providers to assure auto companies that the required hydrogen infrastructure will be in place when we deploy our next generation of fuel cell-electric vehicles,” he said. “Clearly, the automobile industry has stepped forward with fuel cell-electric vehicles, and we are doing everything possible to aggressively develop this critically important technology,” Burns said. “However, we have reached a stage where we cannot continue to make significant progress on our own. Our customers must have safe and convenient access to affordable hydrogen. This means the energy industry and governments must join the auto industry in our journey to produce and sell fuel cell-electric vehicles in volume numbers.” 48 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Sugar Solvency Sugar based hydrogen makes the hydrogen economy not far away Susan Trulove, Term director named for critical technology and applied science institute, May 23, 2007, “Novel sugar-tohydrogen technology promises transportation fuel independence”, http://www.vtnews.vt.edu/story.php?relyear=2007&itemno=300, Accessed July 15, 2008 CM BLACKSBURG, Va., May 23, 2007 -- The hydrogen economy is not a futuristic concept. The U.S. Department of Energy’s 2006 Advance Energy Initiative calls for competitive ethanol from plant sources by 2012 and a good selection of hydrogenpowered fuel cell vehicles by 2020. Researchers at Virginia Tech, Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), and the University of Georgia propose using polysaccharides, or sugary carbohydrates, from biomass to directly produce low-cost hydrogen for the new hydrogen economy. According to the DOE, advances are needed in four areas to make hydrogen fuel an economical reality for transportation: production, storage, distribution, and fuel cells. Most industrial hydrogen currently comes from natural gas, which has become expensive. Storing and moving the gas, whatever its source, is costly and cumbersome, and even dangerous. And there is little infrastructure for refueling a vehicle. “We need a simple way to store and carry hydrogen energy and a simple process to produce hydrogen, said Y.H. Percival Zhang, assistant professor of biological systems engineering at Virginia Tech. Using synthetic biology approaches, Zhang and colleagues Barbara R. Evans and Jonathan R. Mielenz of ORNL, and Robert C. Hopkins and Michael W.W. Adams of the University of Georgia, are using a combination of 13 enzymes never found together in nature to completely convert polysaccharides (C6H10O5) and water into hydrogen when and where that form of energy is needed. This “synthetic enzymatic pathway” research appears in the May 23 issue of PLoS ONE, the online, openaccess journal from the Public Library of Science. Polysaccharides like starch and cellulose are used by plants for energy storage and building blocks and are very stable until exposed to enzymes. Just add enzymes to a mixture of starch and water and “the enzymes use the energy in the starch to break up water into only carbon dioxide and hydrogen,” Zhang said. A membrane bleeds off the carbon dioxide and the hydrogen is used by the fuel cell to create electricity. Water, a product of that fuel cell process, will be recycled for the starch-water reactor. Laboratory tests confirm that it all takes place at low temperature--about 86 degrees F--and atmospheric pressure. The vision is for the ingredients to be mixed in the fuel tank of your car, for instance. A car with an approximately 12-gallon tank could hold 27 kilograms (kg) of starch, which is the equivalent of 4 kg of hydrogen. The range would be more than 300 miles, Zhang estimates. One kg of starch will produce the same energy output as 1.12 kg (0.38 gallons) of gasoline. Since hydrogen is gaseous, hydrogen storage is the largest obstacle to large-scale use of hydrogen fuel. The Department of Energy’s long-term goal for hydrogen storage was 12 mass percent, or 0.12 kg of hydrogen per one kg of container or storage material, but such technology is not available, said Zhang. Using polysaccharides as the hydrogen storage carrier, the research team achieved hydrogen storage capacity as high as 14.8 mass percent, they report in the PLOS article. 49 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie How It’s Made Hydrogen is made by natural gasses but costs less than other shi. D.W. Keith, Department of Engineering and Public Policy, Carnegie Mellon University., A. E. Farrell, Energy and Resources Group, University of California, Berkeley., 7/18/03, Science, Vol. 301. no. 5631, pp. 315 - 316 Like electricity, hydrogen is an energy carrier that must be produced from a primary energy source [HN3]. Today, hydrogen is produced from natural gas on a large scale and at low cost: hydrogen production consumes ~2% of U.S. primary energy, and at the point of production, it costs less than gasoline per-unit of energy. Although hydrogen production is simple, as a low-heating-value, low-boiling-point gas, it is inherently expensive to transport, store [HN4], and distribute--all strong disadvantages for a transportation fuel. Hydrogen can be made by purely renewables. General Motors, 9/26/06, http://www.gm.com/experience/technology/news/2006/fc_us_postal_092706.jsp?exist=false, GM Extends Agreement with U.S. Postal Service to Test Fuel Cell Vehicles for Mail Delivery Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe and can be obtained using renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass as well as using conventional sources like oil, natural gas, and nuclear. A fuel cell is an electrochemical device that combines hydrogen and oxygen into water, producing an electrical current as a byproduct. A fuel cell energized by hydrogen emits just pure water, produces no greenhouse gases and is twice as efficient as an internal combustion engine. Hydrogen can be made by lots of things Robert L. Hirsch et al, SAIC, project leader of the national energy technology laboratory at the Department of Energy, Roger Bezdek, MISI, Robert Wendling, MISI, February 20 05, PEAKING OF WORLD OIL PRODUCTION: IMPACTS, MITIGATION, & RISK MANAGEMENT, http://www.netl.doe.gov/publications/others/pdf/Oil_Peaking_NETL.pdf Hydrogen has potential as a long-term alternative to petroleum-based liquid fuels in some transportation applications. Like electricity, hydrogen is an energy carrier; hydrogen production requires an energy source for its production. Energy sources for hydrogen production include natural gas, coal, nuclear power, and renewables. Hydrogen can be used in internal combustion engines, similar to those in current use, or via chemical reactions in fuel cells. New ways to make hydrogen that re clean are being developed. Woodrow W. Clark et al, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy A significant paradigm shift is now under way as a major change in the way government policy makers and industry leaders are looking for clean fuels and renewable energy for their own nation-states (Clark and Bradshaw, 2004). Current and future markets in fossil fuels subject to volatile prices changes (e.g. gasoline and natural gas) as well as national and international energy/environmental crises, conflicts and now war in the Middle East are combining to motivate this dramatic paradigm shift from the fossil fuel age to a worldwide hydrogen future (Bernstein et al., 2002 and CAISO, 2002). Moreover, the international limitations on fossil fuel supplies cause more concern not only on the economic, but also on domestic and international political levels. The motivation, furthermore, is to find new clean sources of fuels to convert to hydrogen in both economical and efficient ways so that the industrial and developing worlds do not become dependent upon “foreign” fossil fuel sources (Grandy et al., 2002). 50 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie How It’s Made Made by renewables, and dirt cheap/cost declining Woodrow W. Clark et al, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy An energy independent future means regional renewable hydrogen production, implementation and use. Hydrogen can be produced from renewable resources, such as biomass—however, the process emits some carbon dioxide. Hydrogen can also be derived by using wind, hydroelectric, or solar power, to electrolyze water. Today electrolysis is still expensive, but companies like Stuart Energy (2003b) in Toronto and Norsk Hydro (Hexerberg, 2004) in Norway see the costs rapidly declining. Others like Proton (now listed as Distributed Energy Systems Corporation, DESC on Nasdaq) integrate hydrogen systems for stationary power supply to reduce costs even more. The key for renewable hydrogen energy stations is to provide base load or constant energy supply for consumers. Renewables by themselves are intermittent and hence need to be integrated with other technologies in order to be economic. Power purchase agreements for stationary energy generation can do just that with long term contracts for energy on a 24-h and seven day a week basis. The energy required to produce hydrogen via electrolysis is about 48 kWh/kg. At 5 cents/kWh, electrolytic hydrogen contains about $2.50 worth of electricity in one-gallon gasoline equivalent. Wind electricity at utility scales is now 4.5–6.5 cents/kWh and in some locations even less. These costs have been reduced by a factor of two in the last five years alone, and further reductions in production costs through lower cost electrolyzers, and the use of low-cost, off-peak renewable electricity could dramatically reduce the future cost of electrolytic hydrogen Natural Gas Key to the Short term, but renewable would later develop. Woodrow W. Clark et al, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy Since hydrogen is a paradigm change of enormous magnitude, the need for a robust and well thought out transition is critical. In order to accelerate both the timely development and installation of the hydrogen economy, the use of natural gas needs to be seen as merely a transition fuel within three to five (3 to 5) years for producing and making hydrogen commercially available. The key will be to ensure that the expenditures for reforming natural gas are coupled with the electrolyzing of renewable electricity sources into hydrogen. As The Economist (May, 2004) indicated in “The Energy Internet” it would be a financial and environmental disaster to delay this paradigmatic revolution 30–50 years, if large investments were made solely in the central electric grid and natural gas or liquefied natural gas infrastructure rather than devoting the necessary funds to lowering the costs spent on renewable production of hydrogen. Such investments, and at lower numbers, in the billions of dollars could be better spent on renewable energy hydrogen generation. In the short-term, most hydrogen will come from distributed production using natural gas (steam reformation) and/or electricity (electrolysis). The ability of the central utility grid to provide affordable, reliable, and stable power will be enhanced through a greater reliance on more distributed and regional power generation, including “on-site” generation from renewable energy technologies and from the cogeneration of combined heat and power. Some major manufacturing companies, such as auto-makers, Honda and Toyota in California at their North American Headquarters, have started to lead this effort. Those in public policy and industrial planning should take advantage and leverage such short to mid-term transition phases (again within 3 to 5 years), and plan capital investment strategies accordingly. 51 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie How It’s Made Hydrogen has external economic benefits and saves up natural gas so that it turns out to be equal. Woodrow W. Clark et al, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy The economic advantages of distributed energy resources are diverse and compelling, although realizing these benefits requires further regulatory market reform. Moreover, the application of distributed fuel cell cogeneration can save enough natural gas in displaced power plants, furnaces, and boilers to compensate for much of the gas needed to fuel hydrogen vehicles. In addition, because the generation of energy will be far more dispersed and clean, end users will be less dependent on centralized grid operated fossil-fueled power plants and the transmission of electrons over long distances. The analogy by The Economist (May 2004) to the “internet” is very significant and a good working model to consider. Clark and Bradshaw (2004) argue in their book, “Agile Energy Systems” for a very similar idea whereby the analogy with the internet means rather than one central grid or computer center, there are dispersed sources of energy generation. Hence like the internet, energy needs to be a mix of local on-site and central grid generation. Herein is both the real economic and market competition as well as the secure and diverse sources of power. Steam Reforming United States Department of Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen Economy – to 2030 and beyond. In the United States, approximately 95 percent of hydrogen is currently produced via steam reforming. Steam reforming is a thermal process, typically carried out over a nickel-based catalyst, that involves reacting natural gas or other light hydrocarbons with steam. This is a three-step process that results in a mixture of hydrogen and carbon dioxide, which is then separated by pressure swing adsorption, to produce pure hydrogen. Steam reforming is the most energy efficient commercialized technology currently available, and is most cost-effective when applied to large, constant loads. Research is being conducted on improving catalyst life and as heavy oils and hydrocarbon solids. However, it has a higher capital cost because it requires pure oxygen to minimize the amount of gas that must later be treated. In order to make partial oxidation cost effective for the specialty chemicals market, lower cost fossil fuels must be used. Current research is aimed at improving membranes for better separation and conversion processes in order to increase efficiency, and thus decrease the consumption of fossil fuels. Hydrogen can also be produced by using renewable and nuclear resources to extract hydrogen from water, but these methods are currently not as efficient or cost effective as using fossil fuels. Biomass can be thermally processed through gasification or pyrolysis to produce hydrogen. Research on nuclear-based hydrogen production is mostly conducted on thermo-chemical processes, which makes use of high reactor exit temperatures. Both are continuing to be developed. Creation of more efficient, less expensive electrolyzers using renewables and nuclear power is also ongoing. heat integration, which would lower the temperatures needed for the reformer and make the process even more efficient and economical. 52 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie How It’s Made Hydrogen could easily be made by 90% renewables Margo Melendez, senior project Leader at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory & Anelia Milbrandt, member of the International and Environmental Studies Group in the Strategic Energy Analysis and Applications Center., January 2006, “Hydrogen Infrastructure Transition Analysis”, http://www.nrel.gov/hydrogen/pdfs/38351.pdf Renewable Infrastructure Scenario One of the advantages of using hydrogen as a transportation energy source is the ability to generate it in many ways from many resources. This diversity allows each region to utilize its best resources to produce hydrogen. If transition infrastructure is installed at each station using a forecourt technology, such as electrolysis, renewable energy could be incorporated at each station. Because of the relatively low volumes at more rural stations, forecourt technologies could present an opportunity to utilize renewables. Using NREL analysis5 as a basis, the availability of renewables was evaluated at each station to determine whether there were sufficient resources to meet the hydrogen demand at each site (at a 1.1% vehicle penetration). Each of the stations had sufficient renewable capacity. All 284 stations had enough usable solar resources to satisfy the hydrogen demand for vehicle refueling. Wind and biomass resources were sufficient at 163 and 281 stations, respectively. Solar has the ability to meet the demands at nearly every station during the transition phase where demand is relative low. The most abundant and accessible in more rural areas, wind can meet demands at a little more than half of the stations with lower volume, and biomass can meet demands at more than 90% of the stations. 53 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Timeframe 2010 driving today news, oct 20 2006, http://www.drivingtoday.com/news_this_week/2006-10-20-3464-driving/index.html "The HydroGen3 has been making routine deliveries three days a week and has delivered 600,000 pieces of mail in the DC area," Walter O'Tormey, vice president of engineering for the U.S. Postal Service, said. "We know it works on the East Coast; now we will see it in operation on the West Coast." With luck it can stand up to those grueling conditions in Southern California, where it rains once in a while and temperatures can vary by as much as 30 or even 40 degrees during the course of a year. GM says the tests are in the process of validating an automotive fuel cell system by 2010. 54 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Tech Exists Tech has already been demonstrated for fueling stations Associated Press 6/27/2008, LA Gas station gets hydrogen fuel pump. LOS ANGELES (AP) - City Councilman Bill Rosendahl drove into a corner gas station with a big grin on his face. He stepped out of a sports utility vehicle, pumped fuel into the tank and declared it "the most joyous moment I've had since being elected to office." That's because Rosendahl was marking the opening of California's first retail hydrogen station on Thursday, and the Chevrolet Equinox he was riding in emits nothing but water vapor. "This is the car of the future," he said. "Let's get rid of gasoline." While there are few hydrogen powered fuel-cell vehicles on the road now, supporters hope the station will show the public that hydrogen can become a mainstream, eco-friendly alternative to petroleum. State officials see it as part of the "Hydrogen Highway," a developing network of fueling stations to promote commercialization of hydrogenpowered cars. "It was only a few years ago that this was just a concept, now you can see it, touch it and feel it," Fred Joseck, technology analyst of the U.S. Department of Energy's hydrogen program, said at the opening ceremony. 55 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Tech Exists Yo tech is ready and there is people wanting to invest. United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen Today’s emerging hydrogen energy industry is eager to develop hydrogen fuel infrastructure technology that can be used to generate power for stationary, transportation, and portable power applications. Much work needs to be done to reach this goal, but a foundation for future efforts has been established by these various technology sectors. 56 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Cost of Hydrogen Economy Hydrogen Infrastructure will only cost $100 billion a year Greg Blencoe, Chief Executive Officer Hydrogen Discoveries, Inc., August 3, 2007, “Hydrogen: Fuel of the Future”, http://www.hydrogendiscoveries.com/FueloftheFuture.pdf Reliance on foreign oil Price shocks that can wreck the economy Wars Air pollution Global warming These are the problems we have with energy. And every time you and I fill up our cars with gasoline, we are contributing to them. Up until this point, we haven’t had a choice, because there was no viable alternative. But within a couple of years we will have a choice, because of the technologies our company and other companies have developed. This paper describes a vision for a future with clean energy. This is the solution to the problems listed above. A key point to mention upfront is that this isn't going to happen overnight and it will not be easy (though much less painful than if we maintain our current path). But if we begin the transition in the next few years, our goal of powering the world with clean energy by the end of 2020 is achievable. A fair estimate is that it is going to cost about $1 trillion to pay for the infrastructure to power cars with hydrogen in the U.S. This is obviously a lot of money and critics use this as an excuse not to take action. However, it is not as much as you think when you realize that it would be spent over many years. For example, if it took ten years, the cost would still be $100 billion a year, but that is a small price to pay for all of the problems that would be solved. In addition, when you pay for gasoline, the price that is paid at the pump is only the beginning. There are many more costs that are not included in this price. For example, how much has the Iraq war cost us? What does it cost to protect the global oil infrastructure each year? How much are the health-related costs of air pollution? What is the cost of global warming? In the future, these hidden costs to what is paid at the pump will far exceed one trillion dollars if we don't do something soon about the serious energy problems that we have. Some people might ask: Is this possible? The answer is absolutely yes. The timeline on the following page shows our plan for making it happen. 57 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Transport Shit It’s transported through pipeline now but renewables allow to be built on site. Woodrow W. Clark et al, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy Currently, hydrogen is transported by pipeline (more than 400 miles in the U.S. today) or by road via cylinders, tube trailers, and cryogenic tankers, with a small amount shipped by rail or barge. Pipelines, which are owned by merchant hydrogen producers, are limited to a few areas in the U.S. where large hydrogen refineries and chemical plants are concentrated, such as Indiana, California, Texas, and Louisiana. Hydrogen distribution via highpressure cylinders and tube trailers has a range of 100–200 miles from the production facility. For longer distances of up to 1000 miles, hydrogen is usually transported as a liquid in super-insulated, cryogenic, over-the-road tankers, railcars, or barges, and then vaporized for use at the customer site. Hydrogen would be better controlled, stored and less costly if produced locally from renewable energy sources and used for hydrogen power generation as well as refueling vehicles. Hydrogen can be stored as a compressed gas or liquid, or in a chemical compound. The key issue today is not to have stranded or sunk costs made in the conventional infrastructures for natural gas or other methods converting fossil fuels into hydrogen. The same, and even cheaper, costs can be invested in renewable energy production that is converted into hydrogen. Blah Blah some bull shi about transport United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen A hydrogen energy infrastructure would include production and storage facilities, structures and methods for transporting hydrogen, fueling stations for hydrogen-powered applications, and technologies that convert the fuel into energy through end-use systems that power buildings, vehicles, and portable applications. This section focuses on existing infrastructure that moves the hydrogen from its point of production to an end-use device. Today hydrogen is produced primarily in decentralized locations and is used on-site for making chemicals or upgrading fuels. Approximately 17 percent of hydrogen is centrally produced for sale and distribution, and is transported through pipelines or via cylinders and tube trailers. Air Products and Chemicals Inc., Air Liquide Group, Praxair Inc., and the BOC Group are major producers of merchant hydrogen. Together these companies operate about 80 plants in the United States that are dedicated to the production of merchant hydrogen. 58 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie On-site Solvency Whatever Woodrow W. Clark et al, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy Based on the success of that initiative, several states and nations now have similar programs. The micro fuel cell industry stands ready to be the leading edge of large-scale profitability for the rest of the industry. It is leveraging public funds in small and large companies. In northern Italy, for example, ASM (the Piedmont Region energy supplier) in partnership with Pianeta , 2004 Pianeta srl, Settimo, Italy (Piedmonte Region), 2004.Pianeta (private company) have designed and created such hydrogen energy stations for on-site local power and transportation refueling. The capital generated could exceed the expectations of the most ambitious public programs, similar to the leading growth edge of the microcomputer industry. Once profitable, the fuel cell and allied hydrogen and renewable industries will evolve in a self-sustaining way, more effectively solving the technical challenges that lead us to the large-scale sustainable energy economy. As fuel cell system costs decline, the economics of fuel cells—supported by the public sector through buy-downs and tax breaks—will gradually be able to be transformed into more demand-driven business and consumer markets (CPUC, 2003 and Swisher, 2002). This process should be aided by the multiple economic benefits of distributed stationary on-site generation and fuel cell vehicles. Importantly, there presently are hindrances to these benefits being included in project planning assessments that need to be addressed, such as valuing the full fuel cycle emissions of various vehicle types and the valuation of stationary fuel cell systems and other DG/CHP in distributed generation networks, particularly where they are supplying important services to the grid as well as power to the local loads. 59 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Storage Shit Blah Blah, many mechanisms to store United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen Hydrogen can be stored as a gas or liquid or in a chemical compound using a variety of technologies. Compact storage of hydrogen gas in tanks is the most mature storage technology, but is difficult because hydrogen is the lightest element and has very low density under normal conditions. This is addressed through compression to higher pressures or interaction with other compounds. In addition, storage tank materials are advancing—they are getting lighter and better able to provide containment. Some have a protective outside layer to improve impact resistance and safety. Liquid hydrogen is stored in cryogenic containers, which requires less volume than gas storage. However, the liquefaction of hydrogen consumes large quantities of electric power, equivalent to about one-third the energy value of the hydrogen. hydrides. In reversible storage, metals are generally alloyed to optimize both the system weight and the temperature at which the hydrogen can be recovered. When the hydrogen needs to be used, it is released from the hydride under certain temperature and pressure conditions, and the alloy is restored to its previous state. In irreversible storage, the material undergoes a chemical reaction with another substance, such as water, that releases the hydrogen from the hydride. The byproduct is not reconverted to a hydride. Laboratory research continues in the development of carbon-based storage systems. Hydrogen storage in carbon structures is achieved chemically in fullerenes or by physical sorption in carbon nanotubes. These processes are controlled through temperature and pressure and are still a long way from development 60 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Gov Key Government is key and plan is unpopular with thtem mofos Seth Dunn, worldwatch institute in Washington D.C., March 20 02, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 27, Issue 3, Pg 235-264, Hydrogen Futures: Towards a sustainable energy system There are no major technical obstacles to the alternative path to hydrogen. As one researcher has put it, “If we really decided that we wanted a clean hydrogen economy, we could have it by 2010”. But the political and institutional barriers are formidable. Both government and industry have devoted far more resources to the gasoline- and methanol-based route than to the direct hydrogen path. Hydrogen receives a fraction of the research funding that is allocated to coal, oil, nuclear, and other mature, commercial energy sources. Within energy companies, the hydrocarbon side of the business argues that oil will be dominant for decades to come, even as other divisions prepare for its successor. And very little has been done to educate people about the properties and safety of hydrogen, even though public acceptance, or lack thereof, will in the end make or break the hydrogen future [16]. The societal and environmental advantages of the cleaner, more secure path to hydrogen point to an essential — and little recognized — role for government. Indeed, without aggressive energy and environmental policies, the hydrogen economy is likely to emerge along the more incremental path, and at a pace that is inadequate for dealing with the range of challenges posed by the incumbent energy system. Neither market forces nor government fiat will, in isolation, move us down the more direct, more difficult route. The challenge is for government to guide the transition, setting the rules of the game and working with industry and society toward the preferable hydrogen future Us Gov Key to leadership in the sector Seth Dunn, worldwatch institute in Washington D.C., March 20 02, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 27, Issue 3, Pg 235-264, Hydrogen Futures: Towards a sustainable energy system This catalytic leadership role would be analogous to that played by government in launching another infrastructure in the early years of the Cold War. Recognizing the strategic importance of having its networks of information more decentralized and less vulnerable to attack, the US government engaged in critical research, incentives, and public/private collaboration toward development of what we now call the Internet. An equally, and arguably even more, compelling case can be made for strategically laying the groundwork for a hydrogen energy infrastructure that best limits vulnerability to air pollution, energy insecurity, and climate change. Investments made today will heavily influence how, and how fast, the hydrogen economy emerges in coming decades. As with creating the Internet, putting a man on the moon, and other great human endeavors, it is the cost of inaction that should most occupy the minds of our leaders now, at the dawn of the hydrogen age [18] 61 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Possible Plan Mechanism Dope shit – best way to hydrogen econ is starting with fleet vehicles and supporting infrastructure and mandating the selling of hydrogen vehicles in the future Mark Schrope, freelance writer in Melbourne Florida, 12/13/01, Which Way to Energy Utopia, Nature, Vol. 414 pgs 682-684 Given these problems, some experts argue that the most sensible route to a hydrogen economy is to tackle the infrastructure issue head on. With proper planning, says Williams, a hydrogen infrastructure could be created gradually and economically. Fleet vehicles, such as city buses, government vehicles and delivery trucks, would be the starting point. Because all the vehicles return to the same place every night, only one refuelling station would be needed for each fleet. Prototype projects of this type are currently under way in several European countries and the United States. Williams suggests that governments could then encourage further dissemination of the technology by requiring vehicle manufacturers to sell a certain number of fuel-cell cars every year. A related scheme is being used by the California state government to encourage sales of conventional electric vehicles. Governments could also help by offering drivers the chance to earn income-tax credits if they buy hydrogen vehicles. As use grows, the energy companies would have more incentive to expand the hydrogen distribution system. Such a plan could get hydrogen-powered vehicles powered by fuel cells on the road, but others argue that the process would be quicker if hydrogen were burned instead. All conventional engines powered by petrol, from turbines to cars, could be made to burn hydrogen with fairly minor alterations. Both Ford and BMW have developed vehicles that use hydrogen to power modified internal combustion engines (ICEs). Hydrogen ICEs still have to face the problem of developing an infrastructure for hydrogen distribution, but because only minor re-engineering of vehicles is needed, large-scale production would be cheaper and quicker than producing fuel-cell cars. Bob Natkin, leader of Ford's hydrogen ICE programme at the company's laboratories in Dearborn, Michigan, says he could have a hydrogen ICE available in three to five years. BMW is running on a similar timetable. Some more dope shit Lisa Zyga, staff writer at physorg.com, 4/24/2007, http://www.physorg.com/news96631073.html In a recent study, scientists have demonstrated that a hybrid system of hydrogen and carbon can produce a sufficient amount of liquid hydrocarbon fuels to power the entire U.S. transportation sector. Using biomass to produce the carbon, and solar energy to produce hydrogen, the process requires only a fraction of the land area needed by other proposed methods. According to Purdue University scientists Rakesh Agrawal, Navneet Singh, Fabio Ribeiro, and Nicholas Delgass, this appealing scenario is well within reach of current or near-future technology. “Enough technology exists to build the main concept of this process today,” Agrawal told PhysOrg.com. “H2CAR could also endure sustainably for thousands of years. [We hope that] this process will lead to the birth of a new economy, a ‘hybrid hydrogen-carbon economy.’” The hybrid hydrogen-carbon (H2CAR) process takes advantage of the energy density of liquid hydrocarbons (currently provided from oil), but it uses a sustainable and environmentally-friendly method. Because the fuel is essentially the same, though, the H2CAR process could conveniently merge into the existing infrastructure and bypass delivery problems associated with other alternative energy carriers. 62 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Plan Popular Plan is popular due to concerns about the status quo Seth Dunn, worldwatch institute in Washington D.C., March 20 02, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 27, Issue 3, Pg 235-264, Hydrogen Futures: Towards a sustainable energy system Fueled by concerns about urban air pollution, energy security, and climate change, the notion of a “hydrogen economy” is moving beyond the realm of scientists and engineers and into the lexicon of political and business leaders. Interest in hydrogen, the simplest and most abundant element in the universe, is also rising due to technical advances in fuel cells — the potential successors to batteries in portable electronics, power plants, and the internal combustion engine. But where will the hydrogen come from? Government and industry, keeping one foot in the hydrocarbon economy, are pursuing an incremental route, using gasoline or methanol as the source of the hydrogen, with the fuel reformed on board vehicles. A cleaner path, deriving hydrogen from natural gas and renewable energy and using the fuel directly on board vehicles, has received significantly less support, in part because the cost of building a hydrogen infrastructure is widely viewed as prohibitively high. Yet a number of recent studies suggest that moving to the direct use of hydrogen may be much cleaner and far less expensive. Just as government played a catalytic role in the creation of the Internet, government will have an essential part in building a hydrogen economy. Research and development, incentives and regulations, and partnerships with industry have sparked isolated initiatives. But stronger public policies and educational efforts are needed to accelerate the process. Choices made today will likely determine which countries and companies seize the enormous political power and economic prizes associated with the hydrogen age now dawning. Otra vez Michael Gardner, staff at Copley news service, November 22 20 04, http://www.signonsandiego.com/news/science/20041122-9999-1n22hydrogen.html "There is tremendous political momentum," said Jon Slangerup, president of Stuart Energy, an international hydrogen concern. Hydrogen fueling stations are springing up in Los Angeles, Las Vegas and Washington, D.C. – and even Chula Vista. Public agencies are testing small fleets of hydrogen buses and delivery vehicles. Automakers are experimenting with Hummers and BMWs, not content to sacrifice power or popularity. And the oil industry is investing in the hydrogen market. Schwarzenegger has pledged to lay out a network of up to 200 fueling stations by 2010, effectively creating a $90 million "hydrogen highway" by the time novelty models are expected to trickle into showrooms. 63 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT K Plan is part of a paradigm shift and social revolution -> knowledge. Woodrow W. Clark et al, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy A significant paradigm shift is now under way as a major change in the way government policy makers and industry leaders are looking for clean fuels and renewable energy for their own nation-states (Clark and Bradshaw, 2004). Current and future markets in fossil fuels subject to volatile prices changes (e.g. gasoline and natural gas) as well as national and international energy/environmental crises, conflicts and now war in the Middle East are combining to motivate this dramatic paradigm shift from the fossil fuel age to a worldwide hydrogen future (Bernstein et al., 2002 and CAISO, 2002). Moreover, the international limitations on fossil fuel supplies cause more concern not only on the economic, but also on domestic and international political levels. The motivation, furthermore, is to find new clean sources of fuels to convert to hydrogen in both economical and efficient ways so that the industrial and developing worlds do not become dependent upon “foreign” fossil fuel sources (Grandy et al., 2002). The paradigm change can be construed furthermore as a new “mindset” or as “social constructionism” which is a European social science term that applies to a social-cultural revolution or change in public opinion (Pool, 1997). In spite of ideological or political agendas, the hydrogen economy is such a change since it is basically a non-political movement supported by science and technology that the public wants without any universal vote or election. In California, there is very real awareness of the effects of pollution in the environment (air and water) with our dependency on fossil fuels. The general public has become increasingly aware of these issues and now polls show consistently over 80% of all citizens want governmental oversight, protection and dramatic change. 64 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT States Either a perm card or a fed key card, depends on highlithgint. Woodrow W. Clark, leader of Clark Communications at Beverly Hills and The Green Hydrogen Scientific Advisory Committee formed by the Foundation on Economic Trends, Jeremy Rifkin, Todd O'Connor, Joel Swisher, Tim Lipman, Glen Rambach and Clean Hydrogen Science and Technology Team, March 2005, Utilities Policy, Volume 13 Issue 1, Pages 4150, Hydrogen energy stations: along the roadside to the hydrogen economy Innovations and advanced technologies emerge historically when national government helps clear the way for the establishment of mass markets. Historically, Edison, for example, was only able to establish a commercial electricity company when the costs could first be “supported” (i.e., paid for) by local governments and then be made available at regulated reasonable prices to the consumers in the mass market. Since the end of the World War II, the industrialized nations have all used government research and development monies to support the commercialization of everything from diesel fuels to the internet. In fact, American government officials traditionally justify the funding of national labs, NASA and even the U.S. Department of Defense, based on the “dual use” or “transfer of technologies” from its basic research projects. National and local government incentives, tax breaks, and procurement are critical to the commercialization of more advanced technologies, such as hydrogen. Government assists in the introduction of new technologies in still another way: regulations and standards. Today, the advancements of technology to speed communications and to slow global warming are often linked to government regulations and oversight. California has often helped lead the way in this regard with its emission controls, environmental laws, and atmospheric regulations. The hydrogen economy is no different. Appropriate and targeted government regulations can ease the way for public/private partnerships. Together, government and the commercial sector can work collaboratively to create new industries and jobs, as evidenced by the zero emission vehicle (ZEV) regulations in California which began in the early 1990s with a focus on electric batterypowered vehicles (Clark, 1997 and Clark and Paulocci, 2001). This California standard set the standard and goals for ZEV for the entire USA and impacted other nations. More importantly, the size of the California market forced automanufacturers to produce vehicles to meet these standards (see CFCP, 2003, CFCP, 2001 and CFCP, 2000). California's progressive regulatory regime has stimulated the market for clean running automobiles as well as new advanced technologies for the vehicles themselves and the infrastructure that serves them. With regard to regulation or privatization, the international carmakers have been the driving force for change while the Detroit carmakers have either stalled or sued the state of California to stop the regulations from being implemented. The last of these was only settled in August 2003 despite the fact that the American based car company (GM) had been heavily invested in research and developed vehicles that exceeded the California standards (Shnayerson, 1996). Over the years in California, both the California Public Utility Commission (CPUC, 2003) and the California Energy Commission (California Energy Commission, 2000 and California Energy Commission, 2001) have funded the development and deployment of renewable and distributed technologies. The consumers of power literally funded natural gas and electric vehicle infrastructure through rate paying, which exemplifies the need for state regulators to become more involved in the initial investment in hydrogen fueling infrastructure. By utilizing a dedicated account similar to the approach adopted by the CPUC to fund the low emission vehicle refueling infrastructure, participating states and nations also will be able to jumpstart the necessary public investment without constraining their general revenue budgets, while simultaneously attracting private investment. For some examples of how larger regions and diverse nation-states specifically focused on hydrogen, see various European Union reports throughout 2003 (EU, 2003a, EU, 2003b, EC, 2003c and EC, 2003d). 65 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT States State restrictions have hindered progress done by the federal programs Paul Rodgers, San Jose Mercury News, March 31, 2008, “ Hydrogen highway hits roadblock”, http://drivingamericasfuture.org/cgi-data/news/files/38.shtml, Accessed July 16, 2008 CM There are just 175 vehicles in California running on hydrogen, nearly all of them experimental and in government fleets. Retail sales are about 10 years away by most expectations. The lack of stations is due to restrictions on the state funding, said Steve Ellis, Honda's national manager of alternative fuel vehicles. "It was well-intentioned but misguided," Ellis said. "At this early stage, saddling hydrogen with an expectation of perfection is like asking a newborn infant to walk out of the hospital and be able to change its own diaper." Since 2005, the Legislature has provided $19 million to the state Air Resources Board. About half of the money, $9 million, has been spent on staffing eight positions and issuing grants to cities to buy 22 hydrogen buses and other vehicles. The rest remains unspent. Roughly a year ago, the air board signed agreements to build three stations. But all the deals fell apart, including one in San Carlos, when Pacific Gas & Electric pulled out and opted instead to spend money on electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids. Some blame the program's rocky start. In 2005, Democrats in Sacramento refused Schwarzenegger's first year request of $12 million to get the $53 million plan started. A few lawmakers didn't like the idea of the state giving money to oil companies. Others didn't want Schwarzenegger to get political credit for an environmental issue. And many were wary of hydrogen because President Bush had announced a $1.2 billion federal hydrogen program in his 2003 State of the Union speech. Environmentalists in Sacramento and their Democratic allies worried that if coal or other high-polluting fuels were used to make electricity to create hydrogen, then smog and greenhouse gases would increase, defeating the whole point. Democrats eventually agreed to release just $6.5 million - and as a condition, they mandated that no money could be given out unless the stations used 33 percent renewable energy, reduced greenhouse gases 30 percent compared with gasoline and remained open to the public. The federal program doesn't require the high environmental hurdles. Since 2004, there have been 12 hydrogen fueling stations built in California - many built with funding from the Bush program in partnership with companies like BP, Chevron and Shell. Terry Tamminen, Schwarzenegger's first EPA chief, said the legislature should relax the state rules for the first 100 stations. 66 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT States States destroy federal efforts for alternative fuels Eric, Kelderman, Staff Writer, Stateline.org, April 7, 2005, "States start building hydrogen highway", http://www.stateline.org/live/ViewPage.action?siteNodeId=136&languageId=1&contentId=23741, Accessed July 15, 2008 CM In the meantime, record-high gas prices may lead states to promote more electric-gasoline hybrid cars or vehicles that use ethanol or bio-diesel -- fuels produced from organic materials and usually blended with gasoline, he said. Joe O'Neill, executive director of the National Conference of State Fleet Administrators, said states have a poor track record promoting alternative auto fuels such as natural gas, liquid petroleum, ethanol and methanol. For example, state governments largely have sidestepped a federal requirement that 75 percent of new fleet vehicles run on something besides gasoline, he said. Instead states mostly have bought cars and trucks that are capable of running on ethanol, but have fueled them with ordinary gasoline, he said. Switching the focus to hydrogen makes it even less likely that states will support other fuel types in the short term, he said. "Everybody's waiting for hydrogen fuel cells," he said. "There has to be a long-term commitment to one technology before anybody is going to invest." 67 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT Other Alt Energy CP Yo hydrogen key to set the government straight United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen The United States is missing a sustained national commitment to environmental and energy security goals, and the policies to support them. Hydrogen could provide the basis for such a policy. Since 1990 Congress has authorized funds in support of hydrogen energy research, development, and demonstration. Market-based environmental policies that provide industries with financial reasons to invest in low- emission or carbon-free energy systems could accelerate hydrogen energy development substantially. The public needs to understand the value of a hydrogen economy in order for businesses to invest in new energy technologies. Public policies need to be developed by government and private entities and put into place to facilitate public acceptance. This in turn would lead to greater market incentives for significant private investment in hydrogen 68 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT Not Safe Not only is it safe – but plan demonstration solves public perception. United States Department of Economy – to 2030 and beyond. Energy, February 2002, A National Vision of America’s Transition to a Hydrogen Perceptions about the safety of hydrogen remain a deterrent to many consumers. The public needs to be aware that safety issues related to hydrogen are being addressed, and perceptions based on misinformation need to be corrected. A public information campaign can help eliminate many of the concerns about hydrogen safety. Effective codes and standards are needed to ensure that these concerns are addressed in equipment designs, manufacturing practices, and operation and maintenance procedures. Appropriate field tests and demonstrations will be needed to increase public confidence and acceptance of hydrogen technologies 69 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT Hindenburg Yo hell no Michael Gardner, staff at Copley news service, November 22 20 04, http://www.signonsandiego.com/news/science/20041122-9999-1n22hydrogen.html To many motorists, the very term hydrogen conjures up images of the zeppelin Hindenburg's fiery crash in 1937. But industry officials point out that NASA scientists later found that the Hindenburg's shell was coated with a compound similar to what's in solid rocket fuel. When the ship docked, an electrical charge ignited the coating. Gasoline is just as risky, promoters add. 70 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT Dirty hydrogen CP Dirty hydronge fucking takes out solvency Seth Dunn, worldwatch institute in Washington D.C., March 20 02, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 27, Issue 3, Pg 235-264, Hydrogen Futures: Towards a sustainable energy system One of the most significant obstacles to realizing the full promise of hydrogen is the prevailing perception that a fullfledged hydrogen infrastructure — the system for producing, storing, and delivering the gas — would immediately cost hundreds of billions of dollars to build, far more than a system based on liquid fuels such as gasoline or methanol. As a result, auto and energy companies are investing millions of dollars in the development of reformer and vehicle technologies that would derive and use hydrogen from these liquids, keeping the current petroleum-based infrastructure intact [13]. This incremental path — continuing to rely on the dirtier, less secure fossil fuels as a bridge to the new energy system — represents a costly wrong turn, both financially and environmentally. Should manufacturers “lock in” to massproducing inferior fuel cell vehicles just as a hydrogen infrastructure approaches viability, trillions of dollars worth of assets could be wasted. Furthermore, by perpetuating petroleum consumption and import dependence and the excess emission of air pollutants and greenhouse gases, this route would deprive society of numerous benefits. Some 99 percent of the hydrogen produced today comes from fossil fuels. Over the long run, this proportion needs to be shifted toward renewable sources, not maintained, for hydrogen production to be sustainable [14]. Dirty Hydrogen is basically working backwards Michael Gardner, staff at Copley news service, November 22 2004, http://www.signonsandiego.com/news/science/20041122-9999-1n22hydrogen.html So why are some leading environmentalists still alarmed? The primary reason: The Bush administration favors hydrogen produced by fossil fuels – mostly coal – or nuclear power. Most hydrogen produced today is generated by natural gas, which is not renewable. "It's really another subsidy to the coal and nuclear industry," said Robert F. Kennedy Jr., one of the nation's preeminent environmental lawyers. Environmental groups are pushing for renewable sources, such as solar, hydro, wind and biomass. "If you make hydrogen from coal, you're just going backward," said Carl Pope, executive director of the Sierra Club. "The promise of hydrogen is making it from the sun. The risk of hydrogen is making it from coal." The Bush administration's preference to tap fossil fuels puts it at odds with a more environmentally friendly camp in California. 71 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 72 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT Other Sector CP Transportation key sector for comp and global warming Seth Dunn, worldwatch institute in Washington D.C., March 20 02, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 27, Issue 3, Pg 235-264, Hydrogen Futures: Towards a sustainable energy system Most of the future growth in energy is expected to take place in transportation, where motorization continues to rise and where petroleum is the dominant fuel, accounting for 95 percent of the total. Failure to develop alternatives to oil would heighten growing reliance on oil imports, raising the risk of political and military conflict and economic disruption. In industrial nations, the share of imports in overall oil demand would rise from roughly 56 percent today to 72 percent by 2010. Coal, meanwhile, is projected to maintain its grip on more than half the world's power supply. Continued rises in coal and oil use would exacerbate urban air problems in industrialized cities that still exceed air pollution health standards and in megacities such as Delhi, Beijing, and Mexico City — which experience thousands of pollution-related deaths each year. And prolonging petroleum and coal reliance in transportation and electricity would increase annual global carbon emissions from 6.1 to 9.8 billion tons by 2020, accelerating climate change and the associated impacts of sea level rise, coastal flooding, and loss of small islands; extreme weather events; reduced agricultural productivity and water availability; and the loss of biodiversity [9]. 73 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT Biofuel food DA Don’t fear. Love biofuels. Lisa Zyga, staff writer at physorg.com, 4/24/2007, http://www.physorg.com/news96631073.html One concern about the use of biomass to produce fuel is the estimated amount of land area: in conventional methods, biomass would require 25-58% of the total U.S. land area to provide fuel for the country. Based on the current scenario of growth rates and gasifier efficiencies, the scientists estimate the H2CAR process to require about 15% of the land—and with reasonable future projections, just 6%. Significantly, this scenario would avoid the land competition with food growth. This study comes nearly on the heels of the 2005 “Billion Ton Biomass Study,” which estimated that the current amount of recoverable biomass could meet just 30% of the U.S. transportation needs. But because the H 2CAR process supplements biomass with hydrogen, the same amount of biomass could provide liquid fuels for nearly 100% of U.S. transportation needs, according to Agrawal et al.’s estimates. “The reason for significant decrease in land area requirement for the H2CAR process as compared to conventional processes is that hydrogen production from solar energy is an order of magnitude more efficient than biomass growth, which typically grows with an average energy efficiency of less than 1%,” Agrawal explained. “This decreases the land area required to produce same quantity of liquid fuel by a factor of nearly one-third.” 74 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie 75 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT T Alternative Energy Alternative Fuels include hydogen U.S. Department of Energy, March 11, 2008, “Federal Incentives & Laws”, http://www.eere.energy.gov/afdc/progs/view_ind_fed.php/afdc/391/0 The following fuels are defined as alternative fuels by the Energy Policy Act (EPAct) of 1992: pure methanol, ethanol, and other alcohols; blends of 85% or more of alcohol with gasoline; natural gas and liquid fuels domestically produced from natural gas; liquefied petroleum gas (propane); coal-derived liquid fuels; hydrogen; electricity; pure biodiesel (B100); fuels, other than alcohol, derived from biological materials; and P-Series fuels. In addition, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is authorized to designate other fuels as alternative fuels, provided that the fuel is substantially nonpetroleum, yields substantial energy security benefits, and offers substantial environmental benefits. For more information about the alternative fuels defined by EPAct 1992 as well as DOE's alternative fuel designation authority, visit the EPAct Web site. (Reference 42 U.S. Code 13211) 76 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT On-Site CP Hydrogen fueling stations cannot meet the demand of normal gasoline Greg Blencoe, Chief Executive Officer Hydrogen Discoveries, Inc., July 12, 2008, “Hydrogen fueling stations where the hydrogen is produced on-site with solar power are not viable; Hydrogen pipelines will be needed to distribute the hydrogen from large solar facilties”, http://hydrogendiscoveries.wordpress.com/2008/07/12/hydrogen-fueling-stations-where-thehydrogen-is-produced-on-site-with-solar-power-are-not-viable-hydrogen-pipelines-will-be-needed-to-distribute-thehydrogen-from-large-solar-facilties/ One of the key issues with hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is where the hydrogen comes from. The two most preferable options are to make the hydrogen from solar or wind power. There are a few prototype hydrogen fueling stations where the hydrogen is produced on-site from solar power. This has caused some people to believe that locations with high-quality solar resources such as California could simply replicate this model. Is it viable to have lots of hydrogen fueling stations where the hydrogen is produced on-site from solar power without any more infrastructure requirements? The answer is no. The main reason is that the amount of solar panels that could cover a typical fueling station will not produce very much hydrogen. In early April as part of the National Hydrogen Association (NHA) annual conference in Sacramento, I went on a tour of the Sacramento Municipal Utility District (SMUD) hydrogen fueling station. It produces hydrogen on-site from solar panels and electrolyzers. The facility was definitely impressive. But as shown on page 7 of the Fuel Cell Today NHA 2008 annual conference report, the SMUD hydrogen fueling station only produces 12 kilograms of hydrogen per day. Furthermore, in order to get an idea of the size of the solar panels at the SMUD hydrogen fueling station, here is a picture of the facility: As you can see, the solar panels are pretty big. The bottom line is that not enough hydrogen can be produced from solar panels that would fit on a piece of land the size of a typical fueling station. And it is not even close. In Hydrogen Fact #7 where I analyzed the cost of hydrogen from wind power, I mentioned that 388.6 million gallons of gasoline are currently sold in the U.S. each day at 170,000 fueling stations which equals an average of 2286 gallons sold per fueling station each day. Since a kilogram of hydrogen in a fuel cell will get twice the mileage of a gallon of gasoline in an internal combustion engine, I assumed that each hydrogen fueling station would sell an average of 1500 kilograms per day. There is obviously a big difference between 12 kilograms and 1500 kilograms per day. Therefore, hydrogen from solar power will have to be produced at large facilities in places like the Mojave Desert. Hydrogen pipelines will then distribute the hydrogen close to fueling stations and then tanker trucks will deliver the hydrogen to individual fueling stations. 77 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT Hydrogen Highway CP The hydrogen highway has failed – lack of demand and state mishaps have led it nowhere Paul Rodgers, San Jose Mercury News, March 31, 2008, “ Hydrogen highway hits roadblock”, http://drivingamericasfuture.org/cgi-data/news/files/38.shtml, Accessed July 16, 2008 CM Four years ago this month, Gov. Arnold Schwarzenegger signed an executive order to create a "hydrogen highway" - a network of hydrogen fueling stations where California motorists could fill up fuel cell cars that release no smog, only water vapor. "Hundreds of hydrogen fueling stations will be built," Schwarzenegger vowed, as TV cameras rolled. "And these stations will be used by thousands of hydrogen-powered cars and trucks and buses. This starts a new era for clean California transportation." The issue became an environmental hallmark of his governorship. But today, not a single hydrogen fueling station has been built under the program. In February, the state Legislative Analyst's Office, a non-partisan agency, recommended the Legislature not fund the program this year because "the administration has little visible progress to show." The reasons vary, depending on who is offering explanations. Large corporations that traditionally sell energy, like oil companies and utilities, have not stepped forward to take the state matching money to build stations. Some experts familiar with the program say that there are not enough hydrogen cars yet to justify the expense. Others say Democratic lawmakers in Sacramento attached so many restrictions on the money - requiring renewable energy to make the hydrogen, for example - that they hamstrung the program and scared away partners. A federal program to subsidize hydrogen stations with fewer restrictions has helped some in the state get built, including one that's opening today in Sacramento. Currently, there are 24 hydrogen stations in California - three in the Bay Area. Some believe Schwarzenegger overpromised and didn't do his homework. Mary Nichols, chair of the state Air Resources Board, said the "hydrogen highway" program is behind schedule but still on track. "Hydrogen vehicles are definitely going to be part of our future. They are just not as big a part today as was hoped in 2004," she said. Fuel cells produce electricity by taking in oxygen and hydrogen, then separating protons and electrons in a membrane, and routing the electrons to create an electrical current that powers a vehicle's motor. Nichols, who was not part of the Schwarzenegger team that drew up the original plan in 2004 and 2005, said her agency will meet its goal of having between 50 and 100 stations built with a partnership of state funds and private money. But it will be by 2015, she predicted, not by 2010 as originally envisioned. There are two reasons for the lack of progress, Nichols said. First, state contracts are cumbersome and complex and take time work out with private partners. Second, automakers have not made hydrogen fuel cell cars fast enough. "Fuel cell vehicles have rolled out more slowly than had been hoped for in the beginning," Nichols said. 78 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie AT Hybrid C/P Hybrids fail because they have short lives Associated Press June 17 2008, printed in the New Zealand Herald, Fuel Prices are in the Post. In some warm-weather areas such as Florida, Texas and California, consideration is being given to starting bicycle routes. Hydrogen-fuelled vehicles are also under consideration, Donahoe said. Hybrid vehicles can save fuel, but they may not be best for the Postal Service, because the agency tends to keep its vehicles for a long time. While hybrids save on fuel, batteries have to be replaced, and that can be expensive, he said. Yeah Hybrids suck dick Soultek.com October 24 2007, Is Hydrogen Worth the Investment? http://www.soultek.com/clean_energy/hybrid_cars/worth_15_billion_to_kick_start_hydrogen_economy.htm Countries such as China are completely dependent upon coal for their electricity consumption, so electric cars are a scary proposition in such a country. Additionally, in terms of larger vehicles and long distance commuting, hydrogen seems a much better solution than electric vehicles. Moreover, there are still problems with lithium batteries, such as weight and cost - even safety. Furthermore, the world's cleanest and greenest automakers - Honda and Toyota - believe in the future of both hydrogen and fuel cell vehicles. So, can American afford not to be at the forefront of this technology? Finally, GM's current fuel cell vehicle, the Chevy Equinox Fuel Cell Vehicle utilizes a NiMH battery that provides supplementary power to the fuel cell vehicle for extra acceleration or going up a hill, but that electricity does not extend range. With lithium batteries, combined with next generation fuel cell technology, it would seem to make far more sense to enable the regenerative-braking Equinox fuel cell vehicle to use a lithium pack to extend the range of the vehicle, much the way as does a plug-in hybrid - reducing the the amount of hydrogen needed. Inevitably, it appears unclear as to whether hydrogen is worth the investment, at least in terms of hydrogen vehicles. If, however, a better way to isolate hydrogen - a better method of electrolysis, for example - were developed, $15 billion would seem like chump change. 79 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie URLS Solvency for storage and transportation, hydrogen solves emissions http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6V1T-3YDG9GMK&_user=4257664&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000022698&_version=1&_urlVersion=0& _userid=4257664&md5=28f079cf3ec6070c1b5cea99d207194f#sec3 Has good footnotes too from the international journal of hydrogen energy. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/03603199 http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&q=%22hydrogen+highway%22&btnG=Google+Search Hydrogen Highway shit http://www.hcn.org/servlets/hcn.Article?article_id=17108 http://gov.ca.gov/press-release/3105/z http://www.nytimes.com/2007/04/29/automobiles/29INFRA.html http://64.233.167.104/search?q=cache:QUvOZmjO2gcJ:www.calcars.org/H2BridgeV3.pdf+%22hydrogen+highway%22&hl =en&ct=clnk&cd=38&gl=us http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qn4176/is_20080401/ai_n24978383 http://ezinearticles.com/?Hydrogen-Highway&id=1206094 case neg http://www.mcclatchydc.com/staff/robert_boyd/story/16179.html http://www.wired.com/cars/energy/news/2008/05/hydrogen http://www.technologyreview.com/blog/guest/22087/ http://online.wsj.com/article/SB120468405514712501.html research journal http://www.google.com/search?num=100&hl=en&q=%22united+states+postal+service%22+and+%22modeling%22+or+%2 2investment%22+or+%22spillover%22+and+%22fuel&btnG=Search http://www.google.com/search?num=100&hl=en&q=%22United+States+Postal+service%22+or+%22USPS%22+and+hydro gen&btnG=Search google “hydrogen highway” and “federal government” and “incentives” or combination/permutation lexis that shit too. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6V3F-44TSXJS1&_user=4257664&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000022698&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_ userid=4257664&md5=e33d3be563250e4dc0b45150daa5a054 80 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie Hydrogen will be key in determining our future and now is the time to act Neil Thomas and Martin Mbugua, UDaily, April 9, 2007, “UD unveils hydrogen-powered bus that produces no pollutants”, http://www.udel.edu/PR/UDaily/2007/apr/bus040907.html, Accessed July 18, 2008 CM 5:21 p.m., April 9, 2007--The University of Delaware will soon be operating a shuttle bus powered by hydrogen fuel cells, a clean energy source that does not require fossil fuels to operate and that produces a benign emission--water. The bus was unveiled during a ceremony on Monday, April 9, on UD's Newark campus. The hydrogen fuel cell bus project is supported by a $1.7 million grant from the U.S. Department of Transportation's Federal Transit Administration, matched by private financing from companies working in partnership with the University. Researchers from the College of Engineering, who are driving the project, said they envision a multidisciplinary demonstration project. Over the course of the project, the team has researched and demonstrated ways to make hydrogen fuel cells more efficient and less expensive to produce and operate, installed fuel cells in a public bus, and will now test the bus as it operates on a regular passenger route around the University's Newark campus. The project also includes development of a safe and efficient hydrogen refueling station to be used by the bus and, eventually, by other hydrogen-powered vehicles. Another goal of the project is to educate the public and transit officials about the developing technology of hydrogen fuel cells. U.S. Sen. Thomas R. Carper (D-Del.) said the University of Delaware has made significant contributions to the development of solar energy during the last three decades. “Our country and our world are at the crossroad,” Carper said during the ceremony. “The decisions that we make in the next 10 years in public policy, in research and development, in lifestyle changes, could determine the fate of our way of life in 50 years, 100 years from now. Today there is still time to make a difference. The University and leaders throughout our state will help to make that difference." 81 Hydrogen Transport Aff DDI 2008 SS Taylor/Charlie “I am very pleased that our faculty and students have been able to take the lead in bringing fuel cell vehicles to Delaware, and I look forward to future successes as they continue to move ahead,” Eric W. Kaler, Elizabeth Inez Kelley Professor of Chemical Engineering and dean of the College of Engineering, said. “A fuel cell vehicle has zero harmful emissions--wisps of steam or a trickle of water, that's all it produces,” Ajay Prasad, professor of mechanical engineering, said. Prasad is the principal investigator for the project, which is being coordinated by the Delaware Center for Transportation in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. Co-investigators on the project are Ardeshir Faghri, professor of civil and environmental engineering and director of the transportation center, and Suresh Advani, George W. Laird Professor of Mechanical Engineering. “Most of the major automotive companies are aggressively pursuing fuel cell technology right now,” Prasad said. “When we sought this funding, we were not interested in just buying a fuel cell powered bus and operating it, which already is being done in some places. We wanted to introduce some innovations and inject some cutting-edge research on fuel cells into this project.” outside of the University. During this period, the researchers said they will be tracking performance, efficiency, control algorithms, emissions levels, operation costs, the frequency of maintenance needed and the ease of repairs. think different. peace[darfur 82